Visualizing DNA
... moving through the gel than smaller fragments. Thus, larger fragments will move slower than smaller fragments. This allows separation of all different sizes of DNA fragments. ...
... moving through the gel than smaller fragments. Thus, larger fragments will move slower than smaller fragments. This allows separation of all different sizes of DNA fragments. ...
File
... Use pages 125-132 of the BC Science 9 text to help you answer questions 1-16. There will be one mark awarded for each blank except where noted. ...
... Use pages 125-132 of the BC Science 9 text to help you answer questions 1-16. There will be one mark awarded for each blank except where noted. ...
Slide 1
... fact that no two people, except identical twins, have exactly the same DNA; the use of STRs that do differ from person to person ...
... fact that no two people, except identical twins, have exactly the same DNA; the use of STRs that do differ from person to person ...
Next Generation Sequencing
... •. It is DNA sequencing technology which has revolutionized genomic research • Increasing the speed due to parallel analysis technology, and increase accuracy which decreased manpower and cost. • An entire human genome can be sequenced within a single day. In contrast, the previous Sanger sequencing ...
... •. It is DNA sequencing technology which has revolutionized genomic research • Increasing the speed due to parallel analysis technology, and increase accuracy which decreased manpower and cost. • An entire human genome can be sequenced within a single day. In contrast, the previous Sanger sequencing ...
Genetic Engineering Powerpoint
... DNA molecules too large to work with Can be cut up using Restriction Enzymes They cut DNA at specific nucleotide ...
... DNA molecules too large to work with Can be cut up using Restriction Enzymes They cut DNA at specific nucleotide ...
Systematic Implications of DNA variation in subfamily
... Should be present in all taxa to be compared Must have some knowledge of the gene or other genomic region to develop primers, etc. Evolutionary rate of sequence changes must be appropriate to the taxonomic level(s) being investigated; “slow” genes versus “fast” genes It is desirable that sequences c ...
... Should be present in all taxa to be compared Must have some knowledge of the gene or other genomic region to develop primers, etc. Evolutionary rate of sequence changes must be appropriate to the taxonomic level(s) being investigated; “slow” genes versus “fast” genes It is desirable that sequences c ...
File
... Understanding that most DNA is non-coding can be very counter-intuitive for students. When covering microsatellites, present the topic using a series of diagrams to help students understand this concept. When covering how PCR works, present the topic using a series of diagrams to help students under ...
... Understanding that most DNA is non-coding can be very counter-intuitive for students. When covering microsatellites, present the topic using a series of diagrams to help students understand this concept. When covering how PCR works, present the topic using a series of diagrams to help students under ...
1 Genetics (BIL-250) Review Questions #1 (2
... (3-1) Draw a DNA replication fork and identify and label the locations of the following major components: (1) 5’ and 3’ ends of each strand, (2) leading strand, (3) lagging strand, (4) single-stranded binding proteins, (5) DNA polymerase, (6)Okazaki fragments, (7) RNA primer, (8) DNA helicase, (9) D ...
... (3-1) Draw a DNA replication fork and identify and label the locations of the following major components: (1) 5’ and 3’ ends of each strand, (2) leading strand, (3) lagging strand, (4) single-stranded binding proteins, (5) DNA polymerase, (6)Okazaki fragments, (7) RNA primer, (8) DNA helicase, (9) D ...
Unit 9 Completed Vocabulary - WAHS
... transformation – process in which one strain of bacteria is changed by a gene or genes from another strain of bacteria. bacteriophage – a virus that infects bacteria. nucleotide – monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. base pairing – principl ...
... transformation – process in which one strain of bacteria is changed by a gene or genes from another strain of bacteria. bacteriophage – a virus that infects bacteria. nucleotide – monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. base pairing – principl ...
AZBio Ch 13
... •Because longer segments move across the gel more slowly, and do not go as far •Based on size, the DNA fragments make a pattern of bands on the gel ...
... •Because longer segments move across the gel more slowly, and do not go as far •Based on size, the DNA fragments make a pattern of bands on the gel ...
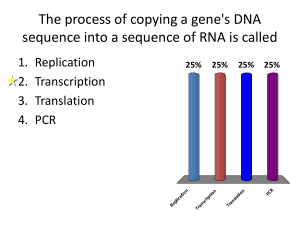
The process of copying a gene`s DNA sequence into a sequence of
... Which of the following statements is true regarding introns? 1. Introns are the parts of mRNA that are translated 2. Introns have no function. 3. In general, human genes have fewer introns than genes of other organisms. 4. Introns may be involved in exon shuffling ...
... Which of the following statements is true regarding introns? 1. Introns are the parts of mRNA that are translated 2. Introns have no function. 3. In general, human genes have fewer introns than genes of other organisms. 4. Introns may be involved in exon shuffling ...
FlyCutTM XmaI - AP
... with T4 DNA ligase at 25°C. Of these ligated fragments, more than 95% can be recut. ...
... with T4 DNA ligase at 25°C. Of these ligated fragments, more than 95% can be recut. ...
Biotechnology Need To Know List
... How to recognize a diagram of DNA cut by a restriction enzyme What DNA analysis by gel electrophoresis allows researchers to do The technique used to make many copies of a gene What genetic engineering involves The technique of DNA sequencing How a recombinant plasmid gets inside a bacterial cell Wh ...
... How to recognize a diagram of DNA cut by a restriction enzyme What DNA analysis by gel electrophoresis allows researchers to do The technique used to make many copies of a gene What genetic engineering involves The technique of DNA sequencing How a recombinant plasmid gets inside a bacterial cell Wh ...
Human Genomic DNA Quality Controls for aCGH and Microarray
... DNA from research laboratories can be of uneven quality. Our DNA comes from immortalized cell lines, where the sequences are validated and the DNA is unchanging. ...
... DNA from research laboratories can be of uneven quality. Our DNA comes from immortalized cell lines, where the sequences are validated and the DNA is unchanging. ...
Chapter 13 Genetic Engineering
... • Gel Electrophoresis- DNA Fragments are placed in certain gel wells and an electric voltage is passed through them. • DNA molecules move toward the opposite end of the gel. • Smaller DNA fragments move faster through the gel. ...
... • Gel Electrophoresis- DNA Fragments are placed in certain gel wells and an electric voltage is passed through them. • DNA molecules move toward the opposite end of the gel. • Smaller DNA fragments move faster through the gel. ...
1 - web.biosci.utexas.edu
... b. contains 13-bp inverted repeat at the termini (TIR) c. forms a two-element system d. first cloned from the waxy locus e. moves via cut-and-paste (gain-and-loss) mechanism 6. Many transposons in plants are inactive, but can be activated. Which mechanism has not been shown to make a major contribut ...
... b. contains 13-bp inverted repeat at the termini (TIR) c. forms a two-element system d. first cloned from the waxy locus e. moves via cut-and-paste (gain-and-loss) mechanism 6. Many transposons in plants are inactive, but can be activated. Which mechanism has not been shown to make a major contribut ...
Gene Technology
... A vector that can carry the gene is used Plasmids are circular DNA that can replicate independently ...
... A vector that can carry the gene is used Plasmids are circular DNA that can replicate independently ...
Lecture_3_2005
... • Hierarchical or contig based sequencing – Clone smaller segments of the genome. – Labor intensive, slow – Not needed for sequencing microbial genomes ...
... • Hierarchical or contig based sequencing – Clone smaller segments of the genome. – Labor intensive, slow – Not needed for sequencing microbial genomes ...
flyer
... WES analyses the total genome, or protein-coding sequence. Most of the known disease causing genes lie within this part of the genome. ...
... WES analyses the total genome, or protein-coding sequence. Most of the known disease causing genes lie within this part of the genome. ...
Worksheet – DNA and Protein Synthesis Biology 11 Name: DNA
... What are the full names of the bases found in DNA? Which ones bond with each other? ...
... What are the full names of the bases found in DNA? Which ones bond with each other? ...
Bisulfite sequencing

Bisulphite sequencing (also known as bisulfite sequencing) is the use of bisulphite treatment of DNA to determine its pattern of methylation. DNA methylation was the first discovered epigenetic mark, and remains the most studied. In animals it predominantly involves the addition of a methyl group to the carbon-5 position of cytosine residues of the dinucleotide CpG, and is implicated in repression of transcriptional activity.Treatment of DNA with bisulphite converts cytosine residues to uracil, but leaves 5-methylcytosine residues unaffected. Thus, bisulphite treatment introduces specific changes in the DNA sequence that depend on the methylation status of individual cytosine residues, yielding single- nucleotide resolution information about the methylation status of a segment of DNA. Various analyses can be performed on the altered sequence to retrieve this information. The objective of this analysis is therefore reduced to differentiating between single nucleotide polymorphisms (cytosines and thymidine) resulting from bisulphite conversion (Figure 1).