biological psychologists endorphins neuron morphine dendrite
... 1. How do neuroscientists explore the connection among, brain, mind and behavior? 2. What are the lower-level brain structures, and what are their functions? 3. What is a "reward deficiency syndrome" and how might it explain addictive disorders? 4. How do neural networks within the cerebral cort ...
... 1. How do neuroscientists explore the connection among, brain, mind and behavior? 2. What are the lower-level brain structures, and what are their functions? 3. What is a "reward deficiency syndrome" and how might it explain addictive disorders? 4. How do neural networks within the cerebral cort ...
Mid-Year Review - The Bronx High School of Science
... Reticular formation – controls body arousal and ability to focus Damaged fall into deep coma Forebrain Thalamus – relay information from senses to different parts of brain Hypothalamus – controls body temperature, hunger, thirst, sexual arousal and endocrine system Cerebral Cortex Rece ...
... Reticular formation – controls body arousal and ability to focus Damaged fall into deep coma Forebrain Thalamus – relay information from senses to different parts of brain Hypothalamus – controls body temperature, hunger, thirst, sexual arousal and endocrine system Cerebral Cortex Rece ...
Nervous System - Holy Trinity Diocesan High School
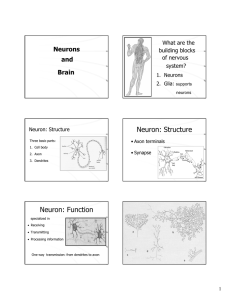
... Relay information between the brain and the body Information is electrical and chemical Receptors: specialized structures that pick up information Negative feedback to the body Stimulus-Response: much faster change but a short lasting effect compared to hormones Structures: 1. Neuron: Nerve cell; ...
... Relay information between the brain and the body Information is electrical and chemical Receptors: specialized structures that pick up information Negative feedback to the body Stimulus-Response: much faster change but a short lasting effect compared to hormones Structures: 1. Neuron: Nerve cell; ...
Document
... - Neural network is a computational model that simulate some properties of the human brain. - The connections and nature of units determine the behavior of a neural network. - Perceptrons are feed-forward networks that can only ...
... - Neural network is a computational model that simulate some properties of the human brain. - The connections and nature of units determine the behavior of a neural network. - Perceptrons are feed-forward networks that can only ...
Abstract n Bio - Prof Arto Nurmikko
... Arto V. Nurmikko, a native of Finland, is a L. Herbert Ballou University Professor of Engineering and Physics at Brown, USA. He received his degrees from University of California, Berkeley, with postdoctoral stays at MIT and Hebrew University. Professor Nurmikko conducts research i ...
... Arto V. Nurmikko, a native of Finland, is a L. Herbert Ballou University Professor of Engineering and Physics at Brown, USA. He received his degrees from University of California, Berkeley, with postdoctoral stays at MIT and Hebrew University. Professor Nurmikko conducts research i ...
Module 23
... series of numbers (a string of digits), S could recall up to 70 if they were presented at three-second intervals in a quiet room. How does our brain pluck information out of the world around us and tuck that information away for later use? Memory is the retention of learning over time. Here, the que ...
... series of numbers (a string of digits), S could recall up to 70 if they were presented at three-second intervals in a quiet room. How does our brain pluck information out of the world around us and tuck that information away for later use? Memory is the retention of learning over time. Here, the que ...
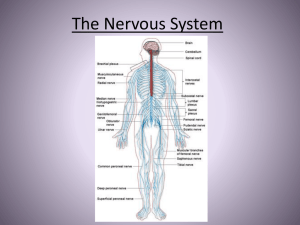
The Nervous System
... • Allows body to respond to stimuli • Structures • 1. Central Nervous System: • - brain • - spinal cord • 2. Peripheral Nervous System - nerves leading away from cns ...
... • Allows body to respond to stimuli • Structures • 1. Central Nervous System: • - brain • - spinal cord • 2. Peripheral Nervous System - nerves leading away from cns ...
Memory kaleidoscope: enhancing memory to improve learning
... signaling process, whereby neurons throughout the cortex with links to the nervous system communicate with each other via synapse interaction. Memories are formed when brain cells make connections at the synapse. Neurons that fire together, “wire together.” Memory is the increased probability of a p ...
... signaling process, whereby neurons throughout the cortex with links to the nervous system communicate with each other via synapse interaction. Memories are formed when brain cells make connections at the synapse. Neurons that fire together, “wire together.” Memory is the increased probability of a p ...
CBRAIN Fact Sheet
... Rotman Research Institute, Baycrest Hospital, Toronto, Ontario University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario Université de Montréal, Quebec University of British Columbia ...
... Rotman Research Institute, Baycrest Hospital, Toronto, Ontario University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario Université de Montréal, Quebec University of British Columbia ...
HP Authorized Customer
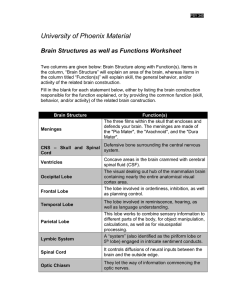
... the column, “Brain Structure” will explain an area of the brain, whereas items in the column titled “Function(s)” will explain skill, the general behavior, and/or activity of the related brain construction. Fill in the blank for each statement below, either by listing the brain construction responsi ...
... the column, “Brain Structure” will explain an area of the brain, whereas items in the column titled “Function(s)” will explain skill, the general behavior, and/or activity of the related brain construction. Fill in the blank for each statement below, either by listing the brain construction responsi ...
Nervous System
... • What are the major functions of the nervous system? • What are the 3 major organs in the nervous system? • Which part of the brain controls thought? • Which part of the nervous system control arms and legs? ...
... • What are the major functions of the nervous system? • What are the 3 major organs in the nervous system? • Which part of the brain controls thought? • Which part of the nervous system control arms and legs? ...
GEOTRAN - Life Solutions Institute
... In the human brain, there are more than several hundred million neurons. In these neurons ion currents flow. The ion currents produce the magnetic field. This magnetic field emerges out of the head through the brain, the scalp and the head. ...
... In the human brain, there are more than several hundred million neurons. In these neurons ion currents flow. The ion currents produce the magnetic field. This magnetic field emerges out of the head through the brain, the scalp and the head. ...
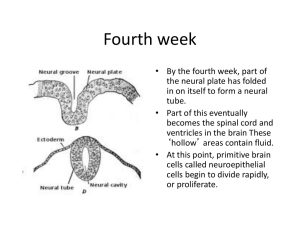
Fourth week
... in short-term memory, and other structures involved in the olfactory pathways Next, the telencephalon produces the basal ganglia, which will eventually contain structures that control movement, sensory information, and some types of learning. The amygdala will eventually help the brain attach emotio ...
... in short-term memory, and other structures involved in the olfactory pathways Next, the telencephalon produces the basal ganglia, which will eventually contain structures that control movement, sensory information, and some types of learning. The amygdala will eventually help the brain attach emotio ...
3.10 notes
... • Procedural memories seem to be stored in the cerebellum • PET scans suggest short-term memories are stored in the prefrontal cortex and temporal lobe • Consolidation – Changes in structure and functioning of neurons when a memory is formed ...
... • Procedural memories seem to be stored in the cerebellum • PET scans suggest short-term memories are stored in the prefrontal cortex and temporal lobe • Consolidation – Changes in structure and functioning of neurons when a memory is formed ...
AP Psychology Exam Review Sheet for “Confusing Pairs” Bottom
... of individual stressed) Structuralism (school of thought that thought the structure (parts of brain) and elements of immediate, conscious experience to be proper subject matter of psychology- Wundt, Titchener (USA) v. Functionalism (school of thought that tried to understand how& why the mind functi ...
... of individual stressed) Structuralism (school of thought that thought the structure (parts of brain) and elements of immediate, conscious experience to be proper subject matter of psychology- Wundt, Titchener (USA) v. Functionalism (school of thought that tried to understand how& why the mind functi ...
Students with Learning Disabilities
... Disabilities • All learning occurs in the brain facilitated by the nervous system • Theory that minimal disorders or abnormalities in the nervous system result in learning problems • Neurology is the medical specialty that focuses on the structure and function of the nervous system ...
... Disabilities • All learning occurs in the brain facilitated by the nervous system • Theory that minimal disorders or abnormalities in the nervous system result in learning problems • Neurology is the medical specialty that focuses on the structure and function of the nervous system ...
Understanding the Gifted Learner`s Brain
... (Growth of Neurons) • During the 9 months of fetal development, neurons grow at the rate of 250,000 per minute. • At birth the brain has approximately 100 billion neurons and weighs about 1 pound. By one year it has doubled and by age 5 or 6 it is 90% of its adult size and weight • This growth is ...
... (Growth of Neurons) • During the 9 months of fetal development, neurons grow at the rate of 250,000 per minute. • At birth the brain has approximately 100 billion neurons and weighs about 1 pound. By one year it has doubled and by age 5 or 6 it is 90% of its adult size and weight • This growth is ...
Biopsychology - WordPress.com
... • Psychophysiology ~ also studies the neural bases of thought, memory, attention, perception ...
... • Psychophysiology ~ also studies the neural bases of thought, memory, attention, perception ...
A Guided Tour of the Brain
... Case studies of individuals with brain damage have provided valuable insights into behavior in such area as memory, speech, emotion, movement, and personality. Lesions- surgically altering, removing, or destroying specific portions of the brain › In humans, lesions are produced for medical reasons, ...
... Case studies of individuals with brain damage have provided valuable insights into behavior in such area as memory, speech, emotion, movement, and personality. Lesions- surgically altering, removing, or destroying specific portions of the brain › In humans, lesions are produced for medical reasons, ...
Chapter 3 – The nerve cell Study Guide Describe an integrate
... Fundamentals of Cognitive Neuroscience: A Beginner’s Guide Bernard J. Baars and Nicole M. Gage 2012 Academic Press ...
... Fundamentals of Cognitive Neuroscience: A Beginner’s Guide Bernard J. Baars and Nicole M. Gage 2012 Academic Press ...
Ch38-Nervous_system
... • The experiences are unique to each individual (i.e. there is no universal association between a certain letter or a certain color), are not made up or learned, and usually remain the same throughout life. ...
... • The experiences are unique to each individual (i.e. there is no universal association between a certain letter or a certain color), are not made up or learned, and usually remain the same throughout life. ...
Puzzle 2A: The Neuron and Nervous System
... Puzzle 2A: The Neuron and Nervous System Created by Don & Sandy Hockenbury ...
... Puzzle 2A: The Neuron and Nervous System Created by Don & Sandy Hockenbury ...