pptx
... • Feedback in networks “clean up” noisy sensory information to make it consistent with what our systems expect • In a very real way, what we see, hear, taste, smell, touch and think is biased by our network’s expectation • A network’s expectation is established by its ...
... • Feedback in networks “clean up” noisy sensory information to make it consistent with what our systems expect • In a very real way, what we see, hear, taste, smell, touch and think is biased by our network’s expectation • A network’s expectation is established by its ...
Neuroscience
... These composite MRI brain scans show the distribution of active areas in the brain of males (left) and females (right) during a verbal task involving rhyming. In males, activation is more lateralized, or confined, to the left hemisphere, whereas in females, activation is bilateralized, that is, occ ...
... These composite MRI brain scans show the distribution of active areas in the brain of males (left) and females (right) during a verbal task involving rhyming. In males, activation is more lateralized, or confined, to the left hemisphere, whereas in females, activation is bilateralized, that is, occ ...
Memory and Recall Training Module File
... of the same brain activity, and neither guarantee that input will be automatically stored. ...
... of the same brain activity, and neither guarantee that input will be automatically stored. ...
7-9_BrainDev_ValaczkaiR
... sensory dorsal root ganglia in the spinal cord. At one end of the neural tube cells divide more rapidly and this part becomes the brain later. Neurons cannot divide freely in contrast to glia cells, therefore proliferation zones are needed along the neural tube where neuroblasts and glioblasts produ ...
... sensory dorsal root ganglia in the spinal cord. At one end of the neural tube cells divide more rapidly and this part becomes the brain later. Neurons cannot divide freely in contrast to glia cells, therefore proliferation zones are needed along the neural tube where neuroblasts and glioblasts produ ...
(Early Period) - Connectionism
... A glance at its history: ● The 1940s: it was pioneered by neurophysiologist Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts. They noted that neurons are either ‘firing’ electrochemical impulses down their lengthy projections (axons) towards junctions with other neurons (synapses) or are inactive. ● Hebb’s rule: D ...
... A glance at its history: ● The 1940s: it was pioneered by neurophysiologist Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts. They noted that neurons are either ‘firing’ electrochemical impulses down their lengthy projections (axons) towards junctions with other neurons (synapses) or are inactive. ● Hebb’s rule: D ...
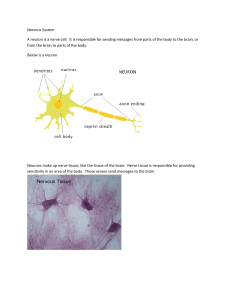
Nervous System A neuron is a nerve cell. It is responsible for
... Below you will find a plastic model of the brain. The brain is responsible for sending and receiving all the signals that make the organs of our bodies function properly. The brain is why we blink, breathe and our hearts beat without thinking about it or being able to really stop it for very long. ...
... Below you will find a plastic model of the brain. The brain is responsible for sending and receiving all the signals that make the organs of our bodies function properly. The brain is why we blink, breathe and our hearts beat without thinking about it or being able to really stop it for very long. ...
THE BRAIN The brain can be divided into three main regions
... 2. Pons: Contains several clusters of cell bodies involved with sleep and arousal. 3. Cerebellum: critical to the coordination of movement and to the sense of equilibrium. One of the structures first depressed by alcohol. MIDBRAIN 1. The midbrain contains an area that is concerned with integrating s ...
... 2. Pons: Contains several clusters of cell bodies involved with sleep and arousal. 3. Cerebellum: critical to the coordination of movement and to the sense of equilibrium. One of the structures first depressed by alcohol. MIDBRAIN 1. The midbrain contains an area that is concerned with integrating s ...
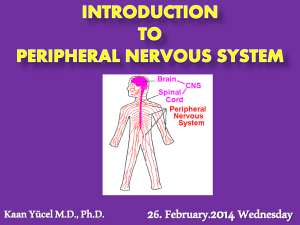
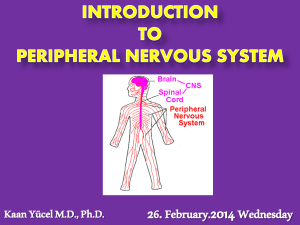
The Nervous Systeminofnotes
... • 4. The motor neuron sends the message to the muscles to carry out your response. ...
... • 4. The motor neuron sends the message to the muscles to carry out your response. ...
Chapter 12
... sensory inputs and determines which of these signals to forward to the cerebral cortex Hypothalamus - regulates the pituitary gland, body T, food intake, emotion, sleep-wake cycle and memory; controls autonomic functions (heart rate, respiration, blood pressure) ...
... sensory inputs and determines which of these signals to forward to the cerebral cortex Hypothalamus - regulates the pituitary gland, body T, food intake, emotion, sleep-wake cycle and memory; controls autonomic functions (heart rate, respiration, blood pressure) ...
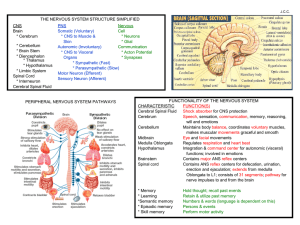
CNS Brain * Cerebrum * Cerebellum * Brain Stem * Diencephalon
... erection and ejaculation; extends from medulla Oblongata to L1; consists of 31 segments; pathway for nerve impulses to and from the brain * Memory * Learning *Semantic memory * Episodic memory * Skill memory ...
... erection and ejaculation; extends from medulla Oblongata to L1; consists of 31 segments; pathway for nerve impulses to and from the brain * Memory * Learning *Semantic memory * Episodic memory * Skill memory ...
Long-term memory
... and retrieval of information. • All animals learn things from their interaction with the environment • Human brain forms memories more effectively than others • Maximum behavioural flexibility and most efficiently adaptation to environment. ...
... and retrieval of information. • All animals learn things from their interaction with the environment • Human brain forms memories more effectively than others • Maximum behavioural flexibility and most efficiently adaptation to environment. ...
SRCD Abstract 01 - University of Illinois Archives
... development are called teratogens). In humans, developmentally-acquired characteristics such as communication skills, social skills, cognitive skills and motor skills all depend heavily upon experience. The genetically-guided processes of neural development are designed to capture information from e ...
... development are called teratogens). In humans, developmentally-acquired characteristics such as communication skills, social skills, cognitive skills and motor skills all depend heavily upon experience. The genetically-guided processes of neural development are designed to capture information from e ...
06powerpoint
... for which there is no known solution, another system is needed. • The Supervisory Attentional System (SAS) has more general flexible strategies that can be applied to any problem situation. • The SAS monitors schemas and can suppress or ...
... for which there is no known solution, another system is needed. • The Supervisory Attentional System (SAS) has more general flexible strategies that can be applied to any problem situation. • The SAS monitors schemas and can suppress or ...
Ch 3 biology and Behavioir Notes
... A system of nerves connects your brain to the rest of your body • communication can occur in split ...
... A system of nerves connects your brain to the rest of your body • communication can occur in split ...
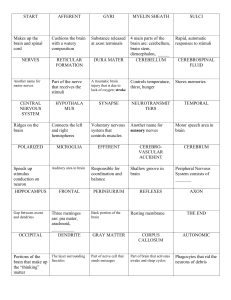
6th Study Guide D1w:ans
... 2. A neuron is a nerve cell. 3. The gap or space between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another is called a synapse. 4. The part of the brain that allows you to think is the cerebrum. 5. The sense of smell is closely linked to the sense of taste. 6. The cones are the part of the eye that ...
... 2. A neuron is a nerve cell. 3. The gap or space between the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another is called a synapse. 4. The part of the brain that allows you to think is the cerebrum. 5. The sense of smell is closely linked to the sense of taste. 6. The cones are the part of the eye that ...