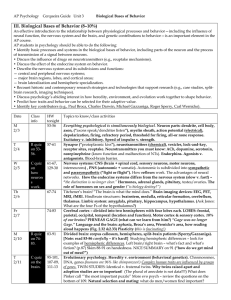
10-5 Infant Biosocial Development
... Germinal, embryonic, and fetal periods Teratogens: critical period, threshold, interaction Birth process ...
... Germinal, embryonic, and fetal periods Teratogens: critical period, threshold, interaction Birth process ...
PSY103_Lecture_CH2_WordScript
... - Involved in regulating hunger, thirst, emotion, sex drive - Also thought to contain "reward centers" because animals will feverishly engage in behavior that results in electrical stimulation of this area. - e.g., rat press bar in cage. ...
... - Involved in regulating hunger, thirst, emotion, sex drive - Also thought to contain "reward centers" because animals will feverishly engage in behavior that results in electrical stimulation of this area. - e.g., rat press bar in cage. ...
Myers` Psychology for AP
... 5. Identify the brain areas involved in language, and explain how these areas coordinate to produce speech. aphasia – 6. Discuss the brain’s plasticity following injury or illness. LO #5 plasticity – neurogenesis – Our Divided Brain LO #6 7. Describe split-brain research, and explain how it helps us ...
... 5. Identify the brain areas involved in language, and explain how these areas coordinate to produce speech. aphasia – 6. Discuss the brain’s plasticity following injury or illness. LO #5 plasticity – neurogenesis – Our Divided Brain LO #6 7. Describe split-brain research, and explain how it helps us ...
Nervous System Exam Review
... Know the 5 types of neuroglia cell --- where are they found, what do they do. Identify neurons by structural classification and functional classification. Explain how an impulse travels and the ions involved. Terms: action potential resting membrane potential repolarization depolarization sodium-pot ...
... Know the 5 types of neuroglia cell --- where are they found, what do they do. Identify neurons by structural classification and functional classification. Explain how an impulse travels and the ions involved. Terms: action potential resting membrane potential repolarization depolarization sodium-pot ...
Unit 3 Cerqueira guide
... • Discuss psychology’s abiding interest in how heredity, environment, and evolution work together to shape behavior. • Predict how traits and behavior can be selected for their adaptive value. • Identify key contributors (e.g., Paul Broca, Charles Darwin, Michael Gazzaniga, Roger Sperry, Carl Wernic ...
... • Discuss psychology’s abiding interest in how heredity, environment, and evolution work together to shape behavior. • Predict how traits and behavior can be selected for their adaptive value. • Identify key contributors (e.g., Paul Broca, Charles Darwin, Michael Gazzaniga, Roger Sperry, Carl Wernic ...
Cognitive information processing
... Connectionistic theory • Information is stored in multiple locations throughout the brain in the form of networks of connections • More connections to a single idea or concept, the more likely it is to be stored and retrieved ...
... Connectionistic theory • Information is stored in multiple locations throughout the brain in the form of networks of connections • More connections to a single idea or concept, the more likely it is to be stored and retrieved ...
File
... and axon. What are the functions of each component? Answer: Cell body- control center (nucleus & cytoplasm). Axons- extends from cell body & produces nerve terminals. Dendrite- receives messages from other neurons. ...
... and axon. What are the functions of each component? Answer: Cell body- control center (nucleus & cytoplasm). Axons- extends from cell body & produces nerve terminals. Dendrite- receives messages from other neurons. ...
Study Guide
... The individual nerve cell is called a neuron. Impulses going to a nerve cell travel along feelers called dendrites. Impulses leaving a nerve cell travel along feelers called axons. Involuntary responses are performed without our brain becoming involved. Voluntary responses are performed when you wan ...
... The individual nerve cell is called a neuron. Impulses going to a nerve cell travel along feelers called dendrites. Impulses leaving a nerve cell travel along feelers called axons. Involuntary responses are performed without our brain becoming involved. Voluntary responses are performed when you wan ...
vocabulary worksheet
... 27. The _______________ is the outermost covering of the brain consisting of densely packed neurons, responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input. 28. The thick band of neurons that connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres is called the _________________ _____ ...
... 27. The _______________ is the outermost covering of the brain consisting of densely packed neurons, responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input. 28. The thick band of neurons that connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres is called the _________________ _____ ...
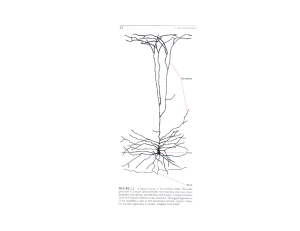
Is Neuronatin mRNA Dendritically localized in Hippocampal Neurons
... modifications of existing proteins, changes in gene expression are necessary for long-lasting effects. One question that arises is how plasticity can occur in a spatially restricted manner, where certain synapses can be altered while surrounding synapses on the same cell are unchanged. The dendritic ...
... modifications of existing proteins, changes in gene expression are necessary for long-lasting effects. One question that arises is how plasticity can occur in a spatially restricted manner, where certain synapses can be altered while surrounding synapses on the same cell are unchanged. The dendritic ...
Overview and Integration
... Composite radioisotope brain scan for patients with each type of aphasia. Darker regions indicate areas where the lesions of many individual patients overlap. The isotope scans operate on the principle that the labeled compound can cross the blood-brain barrier in damaged tissue but not in healthy c ...
... Composite radioisotope brain scan for patients with each type of aphasia. Darker regions indicate areas where the lesions of many individual patients overlap. The isotope scans operate on the principle that the labeled compound can cross the blood-brain barrier in damaged tissue but not in healthy c ...
CNS: Spinal Cord Function
... • Cerebrum: largest portion; last to receive sensory input and integrate it before commanding voluntary motor response; coordinates other areas of the brain; and carries out higher thought processes, memory, language, speech, and learning. ...
... • Cerebrum: largest portion; last to receive sensory input and integrate it before commanding voluntary motor response; coordinates other areas of the brain; and carries out higher thought processes, memory, language, speech, and learning. ...
Central Nervous System
... digestive, cardiovascular, excretory and the endocrine systems ( involuntary ). ...
... digestive, cardiovascular, excretory and the endocrine systems ( involuntary ). ...
Check Yourself
... 3. Space between two neurons 5. Cause for tobacco dependence 7. Brain part for integration of information, planning 8. Chemical signal carried through the blood 9. Amount of drug given 11. Fastest way to get a drug to the brain 12. Agency responsible for regulating pharmaceuticals 15. Where most dru ...
... 3. Space between two neurons 5. Cause for tobacco dependence 7. Brain part for integration of information, planning 8. Chemical signal carried through the blood 9. Amount of drug given 11. Fastest way to get a drug to the brain 12. Agency responsible for regulating pharmaceuticals 15. Where most dru ...
Ch.02
... Central nervous system ◦ Brain and spinal column Peripheral nervous system ◦ Links central nervous system (spinal cord) to sense receptors, muscles and glands ...
... Central nervous system ◦ Brain and spinal column Peripheral nervous system ◦ Links central nervous system (spinal cord) to sense receptors, muscles and glands ...
Nervous system slides
... and arousal, such as the reticular system that filters sensory input sent to the cortex. ¾The two hemispheres of the brain are specialized for different functions; the left hemisphere contains processes supporting speech, language, & analytical ability, while spatial perception and artistic ability ...
... and arousal, such as the reticular system that filters sensory input sent to the cortex. ¾The two hemispheres of the brain are specialized for different functions; the left hemisphere contains processes supporting speech, language, & analytical ability, while spatial perception and artistic ability ...
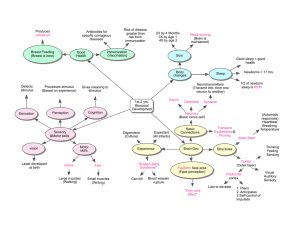
05-First 2 years - Biosocial
... • If starving, the body stops growing, but not the brain • The brain is the last part of the body to be damaged by malnutrition ...
... • If starving, the body stops growing, but not the brain • The brain is the last part of the body to be damaged by malnutrition ...
10.1 Encoding for memories
... • Encoding – transformation of information so the nervous system can process it. • Sensations from hearing, taste, sights, touch, temperature, etc, are encoded to form memories. ...
... • Encoding – transformation of information so the nervous system can process it. • Sensations from hearing, taste, sights, touch, temperature, etc, are encoded to form memories. ...
Module 24
... that our memory capacity was limited, much as a small empty room or attic can hold only so much furniture before it overflows. Contemporary psychologists now believe that our ability to store long-term memories is basically without any limit. ...
... that our memory capacity was limited, much as a small empty room or attic can hold only so much furniture before it overflows. Contemporary psychologists now believe that our ability to store long-term memories is basically without any limit. ...
The nervous system
... system Dendrites- carry impulses towards the cell Axon-carry impulses away from the cell Myelin sheath-insulation Synapse-space between neurons Neurotransmitters-chemical messengers sent across the synapse ...
... system Dendrites- carry impulses towards the cell Axon-carry impulses away from the cell Myelin sheath-insulation Synapse-space between neurons Neurotransmitters-chemical messengers sent across the synapse ...
UsabilityPs3
... Yakking drivers are four times more likely to crash their cars. Using a hands-free headset instead of handheld phone made no difference at all. The brain can be intensely aware of what is coming through either the eyes or the ears but not both at the same time. (Certain brain regions were activate ...
... Yakking drivers are four times more likely to crash their cars. Using a hands-free headset instead of handheld phone made no difference at all. The brain can be intensely aware of what is coming through either the eyes or the ears but not both at the same time. (Certain brain regions were activate ...