Neural Coalition and Main Theorem
... •What is memory? How is it physically stored and accessed? • Can the max information rate hypothesis be proved by appealing to a least action principal in chemical statistical mechanics? (Perhaps this can be approached via the fact that the solution of multiphase chemical equilibrium problems is obt ...
... •What is memory? How is it physically stored and accessed? • Can the max information rate hypothesis be proved by appealing to a least action principal in chemical statistical mechanics? (Perhaps this can be approached via the fact that the solution of multiphase chemical equilibrium problems is obt ...
Module 4 Neural and Hormonal Systems
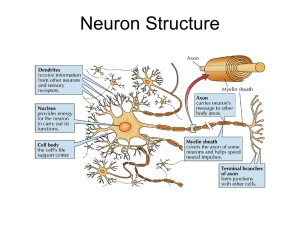
... understanding the rest of the course. Action potentials travel down the axon until reaching a tiny junction, the synapse. Then, the action potential stimulates the release of neurotransmitter molecules. They cross the synaptic gap and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron. This allows ions ...
... understanding the rest of the course. Action potentials travel down the axon until reaching a tiny junction, the synapse. Then, the action potential stimulates the release of neurotransmitter molecules. They cross the synaptic gap and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron. This allows ions ...
Chapter 2
... • Action potential occurs when the membrane potential rapidly shifts from -70 to +40 mV – Ion channels open in the membrane, allowing sodium ions to enter the axon – Sodium entry shifts the membrane potential toward a ...
... • Action potential occurs when the membrane potential rapidly shifts from -70 to +40 mV – Ion channels open in the membrane, allowing sodium ions to enter the axon – Sodium entry shifts the membrane potential toward a ...
Unit 01 Biology and the Brain_Part 2
... Hippocampus • Involved in the processing and storage of memories. ...
... Hippocampus • Involved in the processing and storage of memories. ...
THE DOGMA OF AN AGING BRAIN
... IMPORTANT WARNING Please note that this PowerPoint Presentation contains animations. In order to view the content properly, an add-in function must be installed into the PowerPoint software. The add-in function is downloadable from the following hyperlink. Swiff Point Player ...
... IMPORTANT WARNING Please note that this PowerPoint Presentation contains animations. In order to view the content properly, an add-in function must be installed into the PowerPoint software. The add-in function is downloadable from the following hyperlink. Swiff Point Player ...
Students know
... (nerve impulses) that are generated. • Stimulants-drugs that increase the number of action potentials (nerve impulses) that neurons generate by increasing the amount of neurotransmitters in the synapses. ...
... (nerve impulses) that are generated. • Stimulants-drugs that increase the number of action potentials (nerve impulses) that neurons generate by increasing the amount of neurotransmitters in the synapses. ...
Secrets of the Teen Brain
... developed by 12 years of age. • Piaget research in cognitive development, stages and ~12 years was start of formal ...
... developed by 12 years of age. • Piaget research in cognitive development, stages and ~12 years was start of formal ...
Ch 2 Biology and Behavior
... • 2 hemispheres cooperate naturally and neither is dominant over the other. • They both have their talents and they are used when needed. ...
... • 2 hemispheres cooperate naturally and neither is dominant over the other. • They both have their talents and they are used when needed. ...
File
... The brainstem consists of the midbrain, pons and the medulla oblongata The midbrain receives and integrates several types of sensory information and sends it to specific regions of the forebrain A major function of the pons and medulla is to transfer information between the PNS and the midbrain and ...
... The brainstem consists of the midbrain, pons and the medulla oblongata The midbrain receives and integrates several types of sensory information and sends it to specific regions of the forebrain A major function of the pons and medulla is to transfer information between the PNS and the midbrain and ...
-Louie Klaire Kat SAQ Outline Explain how biological factors may
... biological, as well as cognitive, process of memory. Recent research by Kandel (2000) has given more insight into the relationship between biology and memory on a neuronal level. He studied snails and looked into the synaptic changes in brain structure, which correlate with memory. However, it is th ...
... biological, as well as cognitive, process of memory. Recent research by Kandel (2000) has given more insight into the relationship between biology and memory on a neuronal level. He studied snails and looked into the synaptic changes in brain structure, which correlate with memory. However, it is th ...
3-7_DiversityOfDendriticTree_RabNóra
... The shape of the dendrites reflects both the necessity of accommodating inputs from specific locations and the requirement that these inputs be processed in a specific way. The characteristic shape of dendrites is often clue to the way neurons process information. For example, the horizontal cell in ...
... The shape of the dendrites reflects both the necessity of accommodating inputs from specific locations and the requirement that these inputs be processed in a specific way. The characteristic shape of dendrites is often clue to the way neurons process information. For example, the horizontal cell in ...
Nervous System
... Myelinated nerves – have a coat of white fatty material, interrupted along the length of the nerve at regularly spaced intervals -found mostly in the CNS Nonmyelinated nerves – have a thin coat of myelin – found in the autonomic nervous system ...
... Myelinated nerves – have a coat of white fatty material, interrupted along the length of the nerve at regularly spaced intervals -found mostly in the CNS Nonmyelinated nerves – have a thin coat of myelin – found in the autonomic nervous system ...
hendrick
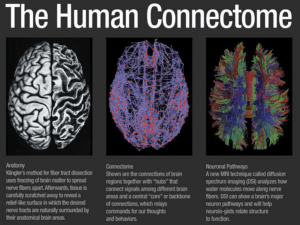
... + 9 + 93 bits = 176 per connection. That multiplies out to over 13 PB for the whole brain. Although my brain weighs just 2% of my body, the ‘informational weight’ of my brain – dominated by the connectivity map – might well come in at 95% or higher! Let’s work with those numbers. Remember, the 13 PB ...
... + 9 + 93 bits = 176 per connection. That multiplies out to over 13 PB for the whole brain. Although my brain weighs just 2% of my body, the ‘informational weight’ of my brain – dominated by the connectivity map – might well come in at 95% or higher! Let’s work with those numbers. Remember, the 13 PB ...
No Slide Title
... 1. carries messages to & from Brain Sensory Neurons Sensory info to CNS Motor Neurons from CNS to muscles and glands ...
... 1. carries messages to & from Brain Sensory Neurons Sensory info to CNS Motor Neurons from CNS to muscles and glands ...
Lecture 2_101_blanks
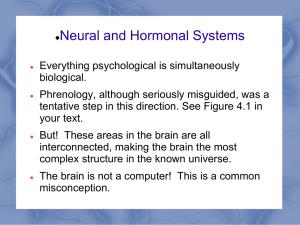
... How does the brain work? How is the brain organized? Is it one working whole? Is it a bunch of different parts that work separately? Phrenology Created by Franz Joseph Gall Different parts of the brain do __________________________________ A Phrenology Guide How correct was Phrenology? Phrenology w ...
... How does the brain work? How is the brain organized? Is it one working whole? Is it a bunch of different parts that work separately? Phrenology Created by Franz Joseph Gall Different parts of the brain do __________________________________ A Phrenology Guide How correct was Phrenology? Phrenology w ...
Nervous System
... homeostasis & processes information Accepts sensory signals & channels them to cerebrum for interpretation (e.g. thalmus may have a consciousness of pain but does not know the location of the pain – the cerebrum interprets the signal and we know where it hurts) ...
... homeostasis & processes information Accepts sensory signals & channels them to cerebrum for interpretation (e.g. thalmus may have a consciousness of pain but does not know the location of the pain – the cerebrum interprets the signal and we know where it hurts) ...
Relating too much information without enough time to
... attention and only 10 minutes to keep it.” ...
... attention and only 10 minutes to keep it.” ...
Confusing Pairs
... 35. Broca’s Area (part of the brain that makes words) v. Wernicke’s Area (part of the brain that comprehends words) 36. Identical Twins (comes from the same fertilized egg) v. Fraternal Twins (comes from two separate eggs) 37. Sensory neurons (body to brain neurons) v. Motor neurons (brain to body n ...
... 35. Broca’s Area (part of the brain that makes words) v. Wernicke’s Area (part of the brain that comprehends words) 36. Identical Twins (comes from the same fertilized egg) v. Fraternal Twins (comes from two separate eggs) 37. Sensory neurons (body to brain neurons) v. Motor neurons (brain to body n ...
xpx tampa bay
... XPX TAMPA BAY The Self Aware Advisor: The Key to Seeing and influencing Others September 11, 2013 ...
... XPX TAMPA BAY The Self Aware Advisor: The Key to Seeing and influencing Others September 11, 2013 ...
Human Physiology
... 9b.Students know how the nervous system mediates communication between different parts of the body and the body’s interactions with the environment. 9d.Students know the functions of the nervous system and the role of neurons in transmitting electrochemical impulses. 9e.Students know the roles of se ...
... 9b.Students know how the nervous system mediates communication between different parts of the body and the body’s interactions with the environment. 9d.Students know the functions of the nervous system and the role of neurons in transmitting electrochemical impulses. 9e.Students know the roles of se ...
Cognitive Neuroscience
... All of the nerve cells except those of the brain and the spinal cord Consists of: • Somatic voluntary part (sensory and motor nerves) • Autonomic involuntary part • Sympathetic (activated under stress) • Parasympathetic (maintains body functions) ...
... All of the nerve cells except those of the brain and the spinal cord Consists of: • Somatic voluntary part (sensory and motor nerves) • Autonomic involuntary part • Sympathetic (activated under stress) • Parasympathetic (maintains body functions) ...