Chapter 4
... -MRI: uses magnetic field and radio waves-higher resolution than CT and can visualize smaller brain lesions -PET: uses radioactive material to assess regional brain glucose and to secure images brain function (use in schizophrenia, depression and OCD) -SPECT: similar to PET, poor resolution, less co ...
... -MRI: uses magnetic field and radio waves-higher resolution than CT and can visualize smaller brain lesions -PET: uses radioactive material to assess regional brain glucose and to secure images brain function (use in schizophrenia, depression and OCD) -SPECT: similar to PET, poor resolution, less co ...
the brain - Cloudfront.net
... 4. The more you repeat something the more brain space is dedicated to it. For example, in musicians the part of the brain that controls fingers used to play an instrument is up to 130% larger than in a non-musician. ...
... 4. The more you repeat something the more brain space is dedicated to it. For example, in musicians the part of the brain that controls fingers used to play an instrument is up to 130% larger than in a non-musician. ...
Etiopathogenesis of Alzem - Nursing Powerpoint Presentations
... • The brain has billions of neurons, each with an axon and many dendrites. • To stay healthy, neurons must communicate with each other, carry out metabolism, and repair themselves. • AD disrupts all three of these essential jobs. ...
... • The brain has billions of neurons, each with an axon and many dendrites. • To stay healthy, neurons must communicate with each other, carry out metabolism, and repair themselves. • AD disrupts all three of these essential jobs. ...
Document
... be identified from several factors like eyeblink level, yawning ,gripping force on wheel and so on. But all these measuring techniques will check only the physical activities of the human. In some cases , people will mentally sleep with eyes open for a few seconds. This will make very big accidents ...
... be identified from several factors like eyeblink level, yawning ,gripping force on wheel and so on. But all these measuring techniques will check only the physical activities of the human. In some cases , people will mentally sleep with eyes open for a few seconds. This will make very big accidents ...
Brain Notes Most complex organ in the body It allows us to think
... 3.guiding the body’s response to it II. Types of input (information received): 1. odors 2. light 3. sounds 4. pain III.Preforms vital operations such as 1. breathing 2. maintaining blood pressure 3. releasing hormones IV. Divided into 3 main sections : 1. Hindbrain 2. Limbic System 3. Neocortex A.Ea ...
... 3.guiding the body’s response to it II. Types of input (information received): 1. odors 2. light 3. sounds 4. pain III.Preforms vital operations such as 1. breathing 2. maintaining blood pressure 3. releasing hormones IV. Divided into 3 main sections : 1. Hindbrain 2. Limbic System 3. Neocortex A.Ea ...
Option A Neural Development Study Guide A1 A2
... How the neural tube of embryonic chordates forms How differentiation of the neural tube produces neurons That immature neurons migrate to a final location That chemical stimuli influence the growth of axons to other parts of the body Multiple synapses form with developing neurons Unused synapses are ...
... How the neural tube of embryonic chordates forms How differentiation of the neural tube produces neurons That immature neurons migrate to a final location That chemical stimuli influence the growth of axons to other parts of the body Multiple synapses form with developing neurons Unused synapses are ...
Activity of Spiking Neurons Stimulated by External Signals of
... Spiking neuron systems gained increasing interest in recent years because they represent spatio-temporal relations within simulated systems, unlike the spatial simple neuron models found in artificial neural systems. They are also closer to biophysical models of neurons, synapses, and related elemen ...
... Spiking neuron systems gained increasing interest in recent years because they represent spatio-temporal relations within simulated systems, unlike the spatial simple neuron models found in artificial neural systems. They are also closer to biophysical models of neurons, synapses, and related elemen ...
Chapter Three Study Guide
... --The largest proportion of the human cortex is devoted to integrating and interpreting information gathered from the sensory parts of the brain. Collectively, these regions re known as the association cortex Cerebral Dominance: ...
... --The largest proportion of the human cortex is devoted to integrating and interpreting information gathered from the sensory parts of the brain. Collectively, these regions re known as the association cortex Cerebral Dominance: ...
Neurons - Transcript - the Cassiopeia Project
... neuron's power is a result of its connections to other neurons. Each neuron is connected to as many as a thousand of its neighbors. These trillions of connections provide the playing field upon which the complex activity of the brain takes place. Each neuron can turn its neighbors on or off dependin ...
... neuron's power is a result of its connections to other neurons. Each neuron is connected to as many as a thousand of its neighbors. These trillions of connections provide the playing field upon which the complex activity of the brain takes place. Each neuron can turn its neighbors on or off dependin ...
Nerve Notes
... Parasymp often innervate same organs and act in opposition III. Cell Types A. Neurons - transmit nerve impulses B. Neuroglia carry out a variety of functions to aid and protect other components IV. ...
... Parasymp often innervate same organs and act in opposition III. Cell Types A. Neurons - transmit nerve impulses B. Neuroglia carry out a variety of functions to aid and protect other components IV. ...
Chapter 3: The Nervous System
... • GABA secreted by “local” interneurons all over the brain. ▫ Works as an off switch. ...
... • GABA secreted by “local” interneurons all over the brain. ▫ Works as an off switch. ...
Neurotransmitters
... A Neuron is a specialized nerve cell that receives, processes, and transmits information to other cells in the body. We have a fixed number of neurons, which means they do not regenerate. About 10,000 neurons die every day, but since we start out with between ten and 100 billion (Hooper & Teresi, 19 ...
... A Neuron is a specialized nerve cell that receives, processes, and transmits information to other cells in the body. We have a fixed number of neurons, which means they do not regenerate. About 10,000 neurons die every day, but since we start out with between ten and 100 billion (Hooper & Teresi, 19 ...
The Nervous System
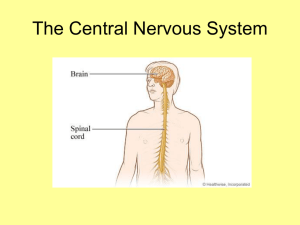
... central nervous system The spinal cord is the main communication link between the brain and the rest of the body. A reflex is a quick automatic response to a stimulus such as SNEEZING and ...
... central nervous system The spinal cord is the main communication link between the brain and the rest of the body. A reflex is a quick automatic response to a stimulus such as SNEEZING and ...
1. Learning Depends on Integration of Brain Structures
... movement of their eyes to follow the the words on a page while listening to stories and attempt to write their names, the earlier they while learn to read. ...
... movement of their eyes to follow the the words on a page while listening to stories and attempt to write their names, the earlier they while learn to read. ...
Sensory Memory
... Short-Term Memory Short-term memory has two characteristics: • Information that enters it is available for only a very limited time unless it is actively processed. • It has limited capacities. ...
... Short-Term Memory Short-term memory has two characteristics: • Information that enters it is available for only a very limited time unless it is actively processed. • It has limited capacities. ...
Memory Lecture/PPT
... Memory misattribution—assigning a recollection or an idea to the wrong source ...
... Memory misattribution—assigning a recollection or an idea to the wrong source ...
Memory notes Explaining memory Learning required memorisation
... neurotransmitter being produced and released by the neurons; that is the specific chemical substance used by neurons to communicate. Second change – to the structure of the slug’ neuron where the number of branches increases as they become bushier through the growth of smaller ‘offshoots’ called den ...
... neurotransmitter being produced and released by the neurons; that is the specific chemical substance used by neurons to communicate. Second change – to the structure of the slug’ neuron where the number of branches increases as they become bushier through the growth of smaller ‘offshoots’ called den ...
SENSATION - Ms. Kelly's AP Psychology Website
... is used to predict when a weak signal will be detected. A new theory that assumes there is no absolute threshold. Detection of a stimulus depends on a combination of actors: stimulus intensity, background noise, a person’s level of experience, motivation & physical condition. ...
... is used to predict when a weak signal will be detected. A new theory that assumes there is no absolute threshold. Detection of a stimulus depends on a combination of actors: stimulus intensity, background noise, a person’s level of experience, motivation & physical condition. ...
Unit 2 Review
... 6. A neuron either fires or it doesn’t. There is no in between. This phenomenon is called _______________________________. 7. Another name for a neural impulse is an ______________________________. 8. Explain how neural communication is both an electrical and chemical process. ...
... 6. A neuron either fires or it doesn’t. There is no in between. This phenomenon is called _______________________________. 7. Another name for a neural impulse is an ______________________________. 8. Explain how neural communication is both an electrical and chemical process. ...
The Brain and Learning Summary Review
... reading and understanding a language. Most of the fifth part of The Brain and Learning is used to describe the actual processes in the brain during these three basic activities. Each article presented ...
... reading and understanding a language. Most of the fifth part of The Brain and Learning is used to describe the actual processes in the brain during these three basic activities. Each article presented ...
The Brain** in Brain Computer Interface - CBMSPC
... Neurological Injury • Injury to the nervous system often causes irreversible damage – results in disability, sometimes devastating – occasionally results in very bizarre symptoms ...
... Neurological Injury • Injury to the nervous system often causes irreversible damage – results in disability, sometimes devastating – occasionally results in very bizarre symptoms ...