Memory - mskamburov
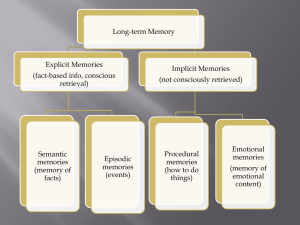
... Information Processing Model Compares our mind to a computer Information is encoded when sensory receptors send impulses to neurons in the brain We store (retain) information for a period of time ...
... Information Processing Model Compares our mind to a computer Information is encoded when sensory receptors send impulses to neurons in the brain We store (retain) information for a period of time ...
Lesson 7:
... - memories - sense of smell 3. occipital lobe – visual info 4. parietal lobe – sensory info (temperature, pressure, touch, pain) Each side focus’s on certain tasks: Left side Right side Math, logic. Language creative (art and music) Gray matter – outer surface of the brain, grayish in color - contai ...
... - memories - sense of smell 3. occipital lobe – visual info 4. parietal lobe – sensory info (temperature, pressure, touch, pain) Each side focus’s on certain tasks: Left side Right side Math, logic. Language creative (art and music) Gray matter – outer surface of the brain, grayish in color - contai ...
A neuron receives input from other neurons
... make decisions, and take action. It allows us to learn a whole lifetime of experiences, and gives us the ability for language and abstract thought. ...
... make decisions, and take action. It allows us to learn a whole lifetime of experiences, and gives us the ability for language and abstract thought. ...
How human memories are formed
... process utilizes a phenomenon called long-term potentiation, which allows a synapse (Figure 3), a complex membrane junction used to transmit signals between cells, to increase in strength as the number of signals between neurons increases. Potentiation is the process by which synchronous firing ...
... process utilizes a phenomenon called long-term potentiation, which allows a synapse (Figure 3), a complex membrane junction used to transmit signals between cells, to increase in strength as the number of signals between neurons increases. Potentiation is the process by which synchronous firing ...
LO: Explain how biological factors may affect one cognitive process.
... It also explains why people suffering from post-traumatic stress disorder have problems forgetting emotional memories. ...
... It also explains why people suffering from post-traumatic stress disorder have problems forgetting emotional memories. ...
Chapter 3
... Neuroscience Deals with the biological bases of our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors Where are memories stored in the brain? How do we experience joy, anger, or desire? Why do drug addictions occur? Are there parts of the brain that have specialized functions? What causes mental illnesses ...
... Neuroscience Deals with the biological bases of our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors Where are memories stored in the brain? How do we experience joy, anger, or desire? Why do drug addictions occur? Are there parts of the brain that have specialized functions? What causes mental illnesses ...
Einstein`s Brain
... Einstein’s Brain • Einstein died in 1955 at age 76. His brain was stored by Dr Thomas Harvey, pathologist, who performed the autopsy. Harvey cut the brain into 240 pieces, which he kept in jars at his house. Harvey moved around the country but he always brought the brain with him. He eventually sen ...
... Einstein’s Brain • Einstein died in 1955 at age 76. His brain was stored by Dr Thomas Harvey, pathologist, who performed the autopsy. Harvey cut the brain into 240 pieces, which he kept in jars at his house. Harvey moved around the country but he always brought the brain with him. He eventually sen ...
einsteins-brain
... Einstein’s Brain • Einstein died in 1955 at age 76. His brain was stored by Dr Thomas Harvey, pathologist, who performed the autopsy. Harvey cut the brain into 240 pieces, which he kept in jars at his house. Harvey moved around the country but he always brought the brain with him. He eventually sen ...
... Einstein’s Brain • Einstein died in 1955 at age 76. His brain was stored by Dr Thomas Harvey, pathologist, who performed the autopsy. Harvey cut the brain into 240 pieces, which he kept in jars at his house. Harvey moved around the country but he always brought the brain with him. He eventually sen ...
Brain Plasticity and Pruning Learning causes growth of brain cells
... Learning causes growth of brain cells. For a long time, scientists held a misconception about brain growth: they believed it stopped at birth and was followed by a lifetime of brain cell death. Now we know that although most of the neurons where information is stored are present at birth, there is a ...
... Learning causes growth of brain cells. For a long time, scientists held a misconception about brain growth: they believed it stopped at birth and was followed by a lifetime of brain cell death. Now we know that although most of the neurons where information is stored are present at birth, there is a ...
Lecture Note
... A: The synthesized proteins are transported to various synapses, but the synapses that are stimulated by serotonins receive the proteins and grow the axon terminals. ...
... A: The synthesized proteins are transported to various synapses, but the synapses that are stimulated by serotonins receive the proteins and grow the axon terminals. ...
Project Description Student: Arvind Ravichandran Title: Examining
... Title: Examining the Mechanisms of the Human Brain with Computer Science Background: The object of all artificial intelligence studies is to simulate the capabilities of the Human brain. No project thus far has even been mildly successful in this endeavor. However, in this project, I seek to instead ...
... Title: Examining the Mechanisms of the Human Brain with Computer Science Background: The object of all artificial intelligence studies is to simulate the capabilities of the Human brain. No project thus far has even been mildly successful in this endeavor. However, in this project, I seek to instead ...
The brain is the body`s most complex organ. Neurons communicate
... scales ranging from milliseconds to months. ...
... scales ranging from milliseconds to months. ...
KEY STUDY - Milner (1966) – HM Case study and
... one of the most important case studies in the history of neuropsychology. It has contributed enormously to the knowledge of how memory processes are related to distinct brain regions. HM died in December 2008 and his brain was donated to science. The brain has been slized up for further anatomical s ...
... one of the most important case studies in the history of neuropsychology. It has contributed enormously to the knowledge of how memory processes are related to distinct brain regions. HM died in December 2008 and his brain was donated to science. The brain has been slized up for further anatomical s ...
The Brain - cloudfront.net
... • Receives auditory, somatosensory and visual sensory signals, sorts data and relays it to proper area in brain ...
... • Receives auditory, somatosensory and visual sensory signals, sorts data and relays it to proper area in brain ...
Brain Chips
... Fromherz researches led to the growth of three or four neurons on a 180x180 transistor array Max Planck Institute grew snail neuron on a CMOS chip with 128x128 Transistors ...
... Fromherz researches led to the growth of three or four neurons on a 180x180 transistor array Max Planck Institute grew snail neuron on a CMOS chip with 128x128 Transistors ...
The Nervous System
... The Nervous System: • is a rapid communication system using electrical signals. • enables movement, perception, thought, emotion and learning. • consists of a network of specialized cells called neurons. ...
... The Nervous System: • is a rapid communication system using electrical signals. • enables movement, perception, thought, emotion and learning. • consists of a network of specialized cells called neurons. ...
Computer Research II Drugs and Mind
... 6b. Draw a normal neuron. 7b. Neurons can be classified by the direction they send information: ...
... 6b. Draw a normal neuron. 7b. Neurons can be classified by the direction they send information: ...