Netter`s Atlas of Neuroscience - 9780323265119 | US Elsevier
... mainly through axonal terminations on the cell body and dendrites. These synapses are isolated and protected by astrocytic processes. The dendrites usually provide the greatest surface area of the neuron. Some protrusions from dendritic branches (dendritic spines) are sites of specific axo-dendritic ...
... mainly through axonal terminations on the cell body and dendrites. These synapses are isolated and protected by astrocytic processes. The dendrites usually provide the greatest surface area of the neuron. Some protrusions from dendritic branches (dendritic spines) are sites of specific axo-dendritic ...
Neurons and the Brain
... It’s the most common neurotransmitter. It is located in both the central nervous and peripheral nervous system. It acts on basic autonomic and muscular functions Plays an important role in arousal and attention ...
... It’s the most common neurotransmitter. It is located in both the central nervous and peripheral nervous system. It acts on basic autonomic and muscular functions Plays an important role in arousal and attention ...
ángeles garcía pardo
... deletion syndrome, which involves a set of phenotypes including brain abnormalities. Ski shows a dynamic expression pattern during cortical development, and accordingly, the phenotype of Ski-deficient cortices is complex, involving altered cell cycle characteristics of neural progenitors, disturbed ...
... deletion syndrome, which involves a set of phenotypes including brain abnormalities. Ski shows a dynamic expression pattern during cortical development, and accordingly, the phenotype of Ski-deficient cortices is complex, involving altered cell cycle characteristics of neural progenitors, disturbed ...
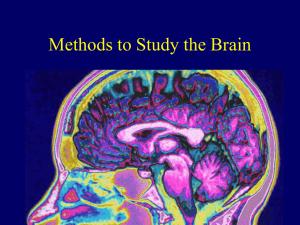
Module 11: Methods to Study the Brain
... • Takes a series of cross-sectional photographs, which are then put together to form a three-dimensional image. ...
... • Takes a series of cross-sectional photographs, which are then put together to form a three-dimensional image. ...
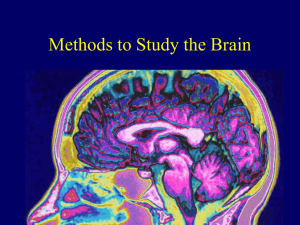
Module 11: Methods to Study the Brain
... • Takes a series of cross-sectional photographs, which are then put together to form a three-dimensional image. ...
... • Takes a series of cross-sectional photographs, which are then put together to form a three-dimensional image. ...
PsychSim5: Neural Messages 1 PsychSim 5: NEURAL MESSAGES
... In an additional experiment, words are flashed briefly to the left or right visual field of the participant. Try to predict the results. For example, when the word appears in the left visual field, will the person be able to read the word? ...
... In an additional experiment, words are flashed briefly to the left or right visual field of the participant. Try to predict the results. For example, when the word appears in the left visual field, will the person be able to read the word? ...
AJA Teaching - Neuroscience
... material of embryos in the early stages of development. The effects of this can still be observed some sixty years later. These alterations are not changes in the genetic code, but a different setting for the code which indicates whether a gene is on or off. This is known as epigenetics. One of the ...
... material of embryos in the early stages of development. The effects of this can still be observed some sixty years later. These alterations are not changes in the genetic code, but a different setting for the code which indicates whether a gene is on or off. This is known as epigenetics. One of the ...
Slide ()
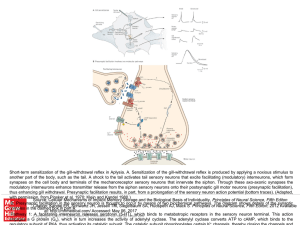
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
Behavioural Neuroscience Lecture 2: History
... • Rejected idea of animal spirits flowing through nerves • Frag experiments: electrical charge applied to frogs legs to make muscles contract • Suggested nerves must be coated in fat (insulation to prevent any leaking) • Inspired books like Frankenstein (electrical happening in brain to allow though ...
... • Rejected idea of animal spirits flowing through nerves • Frag experiments: electrical charge applied to frogs legs to make muscles contract • Suggested nerves must be coated in fat (insulation to prevent any leaking) • Inspired books like Frankenstein (electrical happening in brain to allow though ...
Nerve cells - Spark (e
... In biology are defined dendrites the minor fibers branching from the neuron, they carry nerve signals in centripetal direction. The dendrites are shorter and thinner than the axon. ...
... In biology are defined dendrites the minor fibers branching from the neuron, they carry nerve signals in centripetal direction. The dendrites are shorter and thinner than the axon. ...
Neurons in the Brain
... • newborns demonstrate preference for Mother's voice and native language • as young as 2 months old listen longer to human speech vs. structurally similar nonspeech sounds • between 6-8 mos. they filter out sounds that are not important in their own language ...
... • newborns demonstrate preference for Mother's voice and native language • as young as 2 months old listen longer to human speech vs. structurally similar nonspeech sounds • between 6-8 mos. they filter out sounds that are not important in their own language ...
WHAT PARTS DO YOU KNOW THAT ARE IN THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
... 2. Vesicles with neurotransmitters move toward the membrane 3. Chemicals are released into the synaptic cleft and diffuse toward the next cell’s plasma membrane 4. The chemicals open up the transport proteins and allow the signal to pass to the next cell ...
... 2. Vesicles with neurotransmitters move toward the membrane 3. Chemicals are released into the synaptic cleft and diffuse toward the next cell’s plasma membrane 4. The chemicals open up the transport proteins and allow the signal to pass to the next cell ...
Ch. 35.3
... computer) CNS relays messages, processes information, and analyzes information PNS relays information from environment to the CNS ...
... computer) CNS relays messages, processes information, and analyzes information PNS relays information from environment to the CNS ...
Students know
... between different parts of the body and the body’s interactions with the environment. • 9d.Students know the functions of the nervous system and the role of neurons in transmitting electrochemical impulses. • 9e.Students know the roles of sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons in sensation ...
... between different parts of the body and the body’s interactions with the environment. • 9d.Students know the functions of the nervous system and the role of neurons in transmitting electrochemical impulses. • 9e.Students know the roles of sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons in sensation ...
Development of the Cerebral Cortex: VI. Growth Factors
... that are secreted by the target nerve cells, bind to specific receptors, and signal to the nearby developing synapse. Within the nervous system, the most extensively studied of these factors is the family of neurotrophins. Almost 50 years ago, Rita Levi-Montalcini and Stanley Cohen isolated and iden ...
... that are secreted by the target nerve cells, bind to specific receptors, and signal to the nearby developing synapse. Within the nervous system, the most extensively studied of these factors is the family of neurotrophins. Almost 50 years ago, Rita Levi-Montalcini and Stanley Cohen isolated and iden ...
Brain Parts Matching Review - District 196 e
... _______ 15. controls language expression – an area of the frontal lobe, usually in the left hemisphere, that directs the muscle movement of speech. _______ 16. directs several maintenance activities like eating, drinking and sleeping. Helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. ______ ...
... _______ 15. controls language expression – an area of the frontal lobe, usually in the left hemisphere, that directs the muscle movement of speech. _______ 16. directs several maintenance activities like eating, drinking and sleeping. Helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. ______ ...
Review - TheThinkSpot
... • Within the autonomic nervous system, the sympathetic system stimulates organs and responds to stress, and the parasympathetic system calms the organs and maintains normal functioning. ...
... • Within the autonomic nervous system, the sympathetic system stimulates organs and responds to stress, and the parasympathetic system calms the organs and maintains normal functioning. ...
Study Guide Solutions - Elsevier: Baars and Gage
... Arrays, maps and hierarchies support spatial coding in neurons. For example the visual thalamus and area V1 (the first visual projection area) can be seen as maps of the retina. Maps represent spatial arrangements in the world. But the brain makes use of temporal coding as well. Figure 3.23 shows an ...
... Arrays, maps and hierarchies support spatial coding in neurons. For example the visual thalamus and area V1 (the first visual projection area) can be seen as maps of the retina. Maps represent spatial arrangements in the world. But the brain makes use of temporal coding as well. Figure 3.23 shows an ...
Chapter 48: The Nervous System
... regulate ion & neurotransmitter concentration; dilation of blood vessels act as stem cells ...
... regulate ion & neurotransmitter concentration; dilation of blood vessels act as stem cells ...
neurotransmitter
... 4. Interaction of NT and protein receptor open post-synaptic membrane ion channel for Na+ 5. After transmission the NT is either degraded by an enzyme or taken back into the pre-synaptic membrane by a transporter or reuptake pump ...
... 4. Interaction of NT and protein receptor open post-synaptic membrane ion channel for Na+ 5. After transmission the NT is either degraded by an enzyme or taken back into the pre-synaptic membrane by a transporter or reuptake pump ...
Mechanisms of response homeostasis during retinocollicular map
... long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD). These Hebbian changes, however, are inherently unstable and can lead to the runaway excitation or depression of a subset of synapses when left unchecked. For example, if LTP is based on the ability of a presynaptic neuron to fire a postsyn ...
... long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD). These Hebbian changes, however, are inherently unstable and can lead to the runaway excitation or depression of a subset of synapses when left unchecked. For example, if LTP is based on the ability of a presynaptic neuron to fire a postsyn ...