1-nervous_system
... Holds neurons in place Speeds up transmission Can repair if damaged Keeps messages from being scrambled ...
... Holds neurons in place Speeds up transmission Can repair if damaged Keeps messages from being scrambled ...
Types of neurons
... Controls protein manufacturing Directs metabolism No role in neural signaling ...
... Controls protein manufacturing Directs metabolism No role in neural signaling ...
Neurons – A whistle-stop Tour
... http://www.google.co.nz/imgres?imgurl=http://cwx.prenhall.com/bookbind/pubbooks/morris5/medialib/images/F02_01.jpg&imgrefurl=http://http://www.google.co.nz/images?q=neuron&oe=utf8&rls=org.mozilla http://www.google.co.nz/imgres?imgurl=http://www.faqs.org/photo-dict/photofiles/list/667/1077neuron.jpg ...
... http://www.google.co.nz/imgres?imgurl=http://cwx.prenhall.com/bookbind/pubbooks/morris5/medialib/images/F02_01.jpg&imgrefurl=http://http://www.google.co.nz/images?q=neuron&oe=utf8&rls=org.mozilla http://www.google.co.nz/imgres?imgurl=http://www.faqs.org/photo-dict/photofiles/list/667/1077neuron.jpg ...
Neuroscience
... ears, tongue, eyes, and skin) and internal organs to brain. Motor Neurons: Transmit info from the brain to muscles. Interneurons: Communicate between sensory and motor neurons. ...
... ears, tongue, eyes, and skin) and internal organs to brain. Motor Neurons: Transmit info from the brain to muscles. Interneurons: Communicate between sensory and motor neurons. ...
7-9_BrainDev_ValaczkaiR
... sensory dorsal root ganglia in the spinal cord. At one end of the neural tube cells divide more rapidly and this part becomes the brain later. Neurons cannot divide freely in contrast to glia cells, therefore proliferation zones are needed along the neural tube where neuroblasts and glioblasts produ ...
... sensory dorsal root ganglia in the spinal cord. At one end of the neural tube cells divide more rapidly and this part becomes the brain later. Neurons cannot divide freely in contrast to glia cells, therefore proliferation zones are needed along the neural tube where neuroblasts and glioblasts produ ...
Unit 3A: Neural Processing and the Endocrine System Introduction
... it to not fire. When the excitatory signals outweigh the inhibitory signals by a certain amount, the neuron fires. This is called the threshold. How neurons communicate 1. A synapse is the place where the axon of one neuron meets the dendrites of another. There is a very slight gap in between (the “ ...
... it to not fire. When the excitatory signals outweigh the inhibitory signals by a certain amount, the neuron fires. This is called the threshold. How neurons communicate 1. A synapse is the place where the axon of one neuron meets the dendrites of another. There is a very slight gap in between (the “ ...
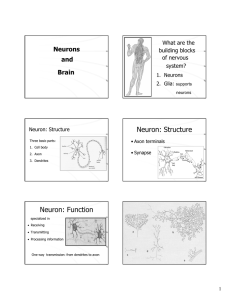
Neuron: Structure Neuron: Function
... How Neurons Communicate One way transmission: from dendrites to axon. 1. Electrical 2. Chemical ...
... How Neurons Communicate One way transmission: from dendrites to axon. 1. Electrical 2. Chemical ...
CNS Introduction
... Binding of a neurotransmitter to its receptor initiates a signal transduction event. Termination of action. -hydrolysis (for acetylcholine and peptides) -reuptake into neurons by specific transporters such as NET, SERT, and DAT (for NE, 5-HT, DA). -Inhibitors of NET, SERT, and DAT increase the dwell ...
... Binding of a neurotransmitter to its receptor initiates a signal transduction event. Termination of action. -hydrolysis (for acetylcholine and peptides) -reuptake into neurons by specific transporters such as NET, SERT, and DAT (for NE, 5-HT, DA). -Inhibitors of NET, SERT, and DAT increase the dwell ...
chapter3Weiten
... The Synapse: Chemicals as Signal Couriers Synaptic cleft Presynaptic neuron ...
... The Synapse: Chemicals as Signal Couriers Synaptic cleft Presynaptic neuron ...
The Biological Bases of Behavior
... biochemical bases of genetic inheritance – Genetic mapping – locating specific genes The Human Genome Project ...
... biochemical bases of genetic inheritance – Genetic mapping – locating specific genes The Human Genome Project ...
Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior
... dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron is called the SYNAPSE Synaptic gap or cleft-a tiny gap between the receiving neuron and sending neuron ...
... dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron is called the SYNAPSE Synaptic gap or cleft-a tiny gap between the receiving neuron and sending neuron ...
Module 4 Neural and Hormonal Systems
... recieving neuron and excite or inhibit a new action potential. The sender neuron reabsorbs excess neurotransmitters. This is reuptake. ...
... recieving neuron and excite or inhibit a new action potential. The sender neuron reabsorbs excess neurotransmitters. This is reuptake. ...
Introduction to Psychology
... Biological Psychology Biological Psychology Branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior Areas of study include neuroscience, the endocrine system and the relative contribution of genetics and evolution The Brain ...
... Biological Psychology Biological Psychology Branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior Areas of study include neuroscience, the endocrine system and the relative contribution of genetics and evolution The Brain ...
Look at brain imaging article.
... narrowly on the shapes of molecules in order to provide insights into how proteins such as channels, enzymes, and transcription factors do their jobs. The x-ray crystallography approach commonly used in structural biology does not generate images per se (producing instead diffraction patterns), but ...
... narrowly on the shapes of molecules in order to provide insights into how proteins such as channels, enzymes, and transcription factors do their jobs. The x-ray crystallography approach commonly used in structural biology does not generate images per se (producing instead diffraction patterns), but ...
Sam Wangdescribes some of the physics of our most complex organ
... Brains have long been compared to the most advanced existing technology – including, at one point, telephone switchboards. Today, people often talk about brains as if they were a sort of biological computer, with pink mushy “hardware” and “software” generated by life experiences. However, any compar ...
... Brains have long been compared to the most advanced existing technology – including, at one point, telephone switchboards. Today, people often talk about brains as if they were a sort of biological computer, with pink mushy “hardware” and “software” generated by life experiences. However, any compar ...
E.4 Neurotransmitters and Synapses
... which is another reason why motor coordination is impaired when under the influence of marijuana ...
... which is another reason why motor coordination is impaired when under the influence of marijuana ...
brainy tests - WordPress.com
... One estimate puts the human brain at about 100 billion neurons and 100 trillion synapses. True ...
... One estimate puts the human brain at about 100 billion neurons and 100 trillion synapses. True ...
Brain Function and Organization via Imaging
... Micro Anatomy: The Neuron Components: 1. Cell body (gray matter) 2. Dendrites 3. Axon (white matter – from myelin sheathes) Axons may be very long e.g. front to back of brain or length of spinal chord ...
... Micro Anatomy: The Neuron Components: 1. Cell body (gray matter) 2. Dendrites 3. Axon (white matter – from myelin sheathes) Axons may be very long e.g. front to back of brain or length of spinal chord ...
Ch. 48 - 49
... and the PNS? Describe the main parts of a neuron. Describe what happens in a Reflex Arc. How are Nodes of Ranvier and Saltatory conduction related? What occurs at the synapse? ...
... and the PNS? Describe the main parts of a neuron. Describe what happens in a Reflex Arc. How are Nodes of Ranvier and Saltatory conduction related? What occurs at the synapse? ...
Ch 3 biology and Behavioir Notes
... New information is received by the senses, and it is processed in the frontal lobe into short term memory for about 5-20 seconds. Most new information is never remembered If it is deemed important, it is sent to the ...
... New information is received by the senses, and it is processed in the frontal lobe into short term memory for about 5-20 seconds. Most new information is never remembered If it is deemed important, it is sent to the ...
research Nerve Cells, Axons, Dendrites, and Synapses: The
... system responds and Structure makes the synaptic Cell contact stronger. This Body response also causes the neuron to expand its receptive connections, the dendrites, and it Dendrite creates more axon contacts for association. These are real physical changes and they can be demonstrated in experiment ...
... system responds and Structure makes the synaptic Cell contact stronger. This Body response also causes the neuron to expand its receptive connections, the dendrites, and it Dendrite creates more axon contacts for association. These are real physical changes and they can be demonstrated in experiment ...
1. The main function of myelin is to a. form a protective coating over
... Q: Neurons send signals to…. A: the brain, muscles, and glands Q: Write the definition for the following neurons.. -Sensory Neurons ...
... Q: Neurons send signals to…. A: the brain, muscles, and glands Q: Write the definition for the following neurons.. -Sensory Neurons ...