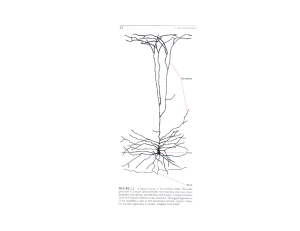
Unit 3 Biology of Behavior The Neuron Dendrites: Tree
... branches, it causes the synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitters into the synapse. b. The neurotransmitters then bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron (like a key fitting into a lock). Some neurotransmitters are excitatory (create a new action potential) while others are inhibitory (s ...
... branches, it causes the synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitters into the synapse. b. The neurotransmitters then bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron (like a key fitting into a lock). Some neurotransmitters are excitatory (create a new action potential) while others are inhibitory (s ...
EDP3004_ch2a
... c) via synapses (electrical inputs) Glial cells = interneurons Outnumber neurons Serve as supportive role Maintain the ideal environment for neurons to flourish Producers of myelin (coating) for axons Transport nutrients Help in immune system ...
... c) via synapses (electrical inputs) Glial cells = interneurons Outnumber neurons Serve as supportive role Maintain the ideal environment for neurons to flourish Producers of myelin (coating) for axons Transport nutrients Help in immune system ...
Chapter 2
... 37. Which of the following is an event that can trigger the initial Na+ influx that can cause the membrane potential to reach threshold? (p 46) 38. Which of the following do NOT occur with the action potential? (p 46) 39. The tiny gap that exists at the junction where two neurons meet is called the ...
... 37. Which of the following is an event that can trigger the initial Na+ influx that can cause the membrane potential to reach threshold? (p 46) 38. Which of the following do NOT occur with the action potential? (p 46) 39. The tiny gap that exists at the junction where two neurons meet is called the ...
Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of
... potential. This indicates that a neuron's reaction is A) inhibited by the myelin sheath. B) delayed by the refractory period. C) an all-or-none response. D) dependent on neurotransmitter molecules. E) primarily electrical rather than chemical. 9. Neurotransmitters are released from vesicles located ...
... potential. This indicates that a neuron's reaction is A) inhibited by the myelin sheath. B) delayed by the refractory period. C) an all-or-none response. D) dependent on neurotransmitter molecules. E) primarily electrical rather than chemical. 9. Neurotransmitters are released from vesicles located ...
The basic unit of computation - Zador Lab
... dynamic element with complex nonlinear behavior8. The output of a synapse depends on its input, because of a host of presynaptic mechanisms, including paired-pulse facilitation, depression, augmentation and post-tetanic potentiation. In many physiological experiments designed to study the properties ...
... dynamic element with complex nonlinear behavior8. The output of a synapse depends on its input, because of a host of presynaptic mechanisms, including paired-pulse facilitation, depression, augmentation and post-tetanic potentiation. In many physiological experiments designed to study the properties ...
The Nervous System
... Anatomy of a Neuron Each neuron contains: - Cell body with nucleus - Dendrites : fibers that receive messages from other neurons - Axons : fibers that send messages to other neurons ...
... Anatomy of a Neuron Each neuron contains: - Cell body with nucleus - Dendrites : fibers that receive messages from other neurons - Axons : fibers that send messages to other neurons ...
European Neuroscience Conference for Doctoral Students
... ventricle layer and they need to migrate to their final destination. The proper dynamics of this process are crucial for the normal formation of the mammalian brain and aberrant neuronal migration may result in devastating consequences as severe brain malformation, mental retardation, epileptic seiz ...
... ventricle layer and they need to migrate to their final destination. The proper dynamics of this process are crucial for the normal formation of the mammalian brain and aberrant neuronal migration may result in devastating consequences as severe brain malformation, mental retardation, epileptic seiz ...
Physical Neural Networks Jonathan Lamont November 16, 2015
... – Average human neocortex contains 150,000 billion connections ...
... – Average human neocortex contains 150,000 billion connections ...
Nervous system slides
... ¾ Somatosensory and motor areas of different lobes directly process info. and association areas integrate info. ¾ Our sensory perceptions are produced by a complicated interchange of signals among receiving centers and association centers. ...
... ¾ Somatosensory and motor areas of different lobes directly process info. and association areas integrate info. ¾ Our sensory perceptions are produced by a complicated interchange of signals among receiving centers and association centers. ...
Ch. 48-49 Nervous System 9e S13
... • Nerves = bundles of neurons – Contains motor neurons +/or sensory neurons ...
... • Nerves = bundles of neurons – Contains motor neurons +/or sensory neurons ...
Chapter 3 PowerPoint Outline
... Loss of interest and pleasure in life Dopamine Found in the brain, inhibitory in nature Motivation, reward, pleasure Regulation of muscle movement Regulation of perception of reality Abnormally low levels linked with Parkinson’s disease [also ADHD] Abnormally high levels linked with sc ...
... Loss of interest and pleasure in life Dopamine Found in the brain, inhibitory in nature Motivation, reward, pleasure Regulation of muscle movement Regulation of perception of reality Abnormally low levels linked with Parkinson’s disease [also ADHD] Abnormally high levels linked with sc ...
Ch. 11: Machine Learning: Connectionist
... Understanding the brain (1) “ Because we do not understand the brain very well we are constantly tempted to use the latest technology as a model for trying to understand it. In my childhood we were always assured that the brain was a telephone switchboard. (“What else could it be?”) I was amused to ...
... Understanding the brain (1) “ Because we do not understand the brain very well we are constantly tempted to use the latest technology as a model for trying to understand it. In my childhood we were always assured that the brain was a telephone switchboard. (“What else could it be?”) I was amused to ...
Unit 3 Cerqueira guide
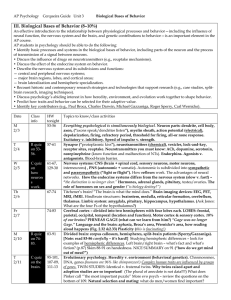
... III. Biological Bases of Behavior (8–10%) An effective introduction to the relationship between physiological processes and behavior—including the influence of neural function, the nervous system and the brain, and genetic contributions to behavior—is an important element in the AP course. AP studen ...
... III. Biological Bases of Behavior (8–10%) An effective introduction to the relationship between physiological processes and behavior—including the influence of neural function, the nervous system and the brain, and genetic contributions to behavior—is an important element in the AP course. AP studen ...
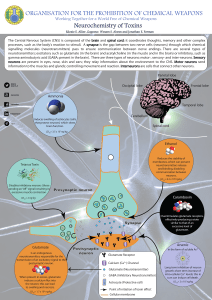
Working Together for a World Free of Chemical Weapons
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord; it coordinates thoughts, memory and other complex processes, such as the body’s reaction to stimuli. A synapse is the gap between two nerve cells (neurons) through which chemical signalling molecules (neurotransmitters) pass ...
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord; it coordinates thoughts, memory and other complex processes, such as the body’s reaction to stimuli. A synapse is the gap between two nerve cells (neurons) through which chemical signalling molecules (neurotransmitters) pass ...
The Neural Control of Behavior
... chord •PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: the entire set of cranial and spinal nerves that connect the central nervous system (brain and spinal chord) to the body’s sensory organs, muscles, and glands. •NERVE: a large bundle containing the axons of many neurons. Located in the PNS, nerves connect the CNS wi ...
... chord •PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: the entire set of cranial and spinal nerves that connect the central nervous system (brain and spinal chord) to the body’s sensory organs, muscles, and glands. •NERVE: a large bundle containing the axons of many neurons. Located in the PNS, nerves connect the CNS wi ...
science guide 2016-Final2.indd
... something new, anticipate the future or recall a memory, a unique set of electrical signals sweeps through your brain. How do these pulses contain all the information necessary to form a thought or memory? The sheer quantity of the billions of cells—and exponentially more routes that a signal can ta ...
... something new, anticipate the future or recall a memory, a unique set of electrical signals sweeps through your brain. How do these pulses contain all the information necessary to form a thought or memory? The sheer quantity of the billions of cells—and exponentially more routes that a signal can ta ...
Cellular Mechanisms of Learning and Memory
... • Short-term facilitation (lasting minutes to hours), resulting from a single tail shock or a single pulse of serotonin, leads to short-term modification of preexisting proteins (like phosphorylation). • Long-term facilitation (lasting one or more days) involves the synthesis of new proteins. PKA r ...
... • Short-term facilitation (lasting minutes to hours), resulting from a single tail shock or a single pulse of serotonin, leads to short-term modification of preexisting proteins (like phosphorylation). • Long-term facilitation (lasting one or more days) involves the synthesis of new proteins. PKA r ...
“Describe the neuroanatomy of and neural processes related to
... way in which that information or those abilities are stored. It is important to note from the outset that there are certainly different kinds of memory, such as procedural memory (remembering how to do something) and declarative memory (remembering some actual semantic information), and that the two ...
... way in which that information or those abilities are stored. It is important to note from the outset that there are certainly different kinds of memory, such as procedural memory (remembering how to do something) and declarative memory (remembering some actual semantic information), and that the two ...
X Period- Review for Brain test
... Upper brain- controls all human functions, example—thinking, personality ...
... Upper brain- controls all human functions, example—thinking, personality ...
document
... mental abilities and our character traits. Through observations of people, Gall pinpointed areas of the brain responsible for 37 traits. ...
... mental abilities and our character traits. Through observations of people, Gall pinpointed areas of the brain responsible for 37 traits. ...
sensory neurons
... • Consist of the neurons (receptor and motor) which lead to and from the central ...
... • Consist of the neurons (receptor and motor) which lead to and from the central ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 7
... 15. The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and __________________________. 16. Stimulating a nerve cell increases the permeability of the membrane to _____________________ ions. 17. The movement of sodium through the membrane into the cell creates a ________________ charge inside and ...
... 15. The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and __________________________. 16. Stimulating a nerve cell increases the permeability of the membrane to _____________________ ions. 17. The movement of sodium through the membrane into the cell creates a ________________ charge inside and ...
The Nervous System WS-11A Review Quest
... 2. What are the two primary cells of the nervous system, and what do they do? The two primary cells of the nervous system are neurons, that actually carry and store information, and glial cells that support the neurons. 3. What protects the brain? The brain is protected by the bones of the skull and ...
... 2. What are the two primary cells of the nervous system, and what do they do? The two primary cells of the nervous system are neurons, that actually carry and store information, and glial cells that support the neurons. 3. What protects the brain? The brain is protected by the bones of the skull and ...
THE SYNAPSE
... aldehyde-fixed tissue, asymmetric synapses include axons that contain predominantly round or spherical vesicles and form synapses that are distinguished by a thickened, postsynaptic density. In contrast, symmetric synapses involve axons that contain clusters of vesicles that are predominantly flatte ...
... aldehyde-fixed tissue, asymmetric synapses include axons that contain predominantly round or spherical vesicles and form synapses that are distinguished by a thickened, postsynaptic density. In contrast, symmetric synapses involve axons that contain clusters of vesicles that are predominantly flatte ...