DevelopmentII
... in the brain • Human brain consists of 1011 neurons that form a network with 1014 connections • The number and specificity of synaptic connection needs to be precisely controlled • Changes of synaptic connections and synaptic strength are the basis of information processing and memory formation ...
... in the brain • Human brain consists of 1011 neurons that form a network with 1014 connections • The number and specificity of synaptic connection needs to be precisely controlled • Changes of synaptic connections and synaptic strength are the basis of information processing and memory formation ...
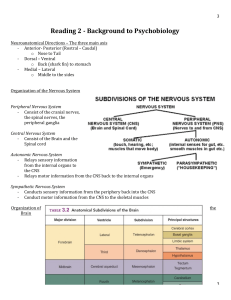
Reading 2 - Background to Psychobiology
... - Sulcus (plural) – The space between the folds of the cerebral cortex - Fissure – A space that is not created by a fold of the brain - The white matter mostly consist of axons o You can think of the brain as many servers that are interconnected (subcortical and cerebral cortex/different area ...
... - Sulcus (plural) – The space between the folds of the cerebral cortex - Fissure – A space that is not created by a fold of the brain - The white matter mostly consist of axons o You can think of the brain as many servers that are interconnected (subcortical and cerebral cortex/different area ...
Synapse Formation in the Peripheral and Central Nervous System
... Synaptic differentiation and signaling between nerve cells • Refinement of circuits and experiencedependent modifications ...
... Synaptic differentiation and signaling between nerve cells • Refinement of circuits and experiencedependent modifications ...
Firing Rate Models
... Figure showing simulated noisy leaky-integrate-and-fire neuron with output to a saturating (NMDA) synapse. ...
... Figure showing simulated noisy leaky-integrate-and-fire neuron with output to a saturating (NMDA) synapse. ...
Molecular basis of learning in the hippocampus and the amygdala
... The hippocampus and the amygdala are structures of mammalian brain both involved in memorizing. However, they are responsible for different types of memory: the hippocampus is involved in creating and storing declarative engrams and the amygdala is engaged in some of non-declarative learning. During ...
... The hippocampus and the amygdala are structures of mammalian brain both involved in memorizing. However, they are responsible for different types of memory: the hippocampus is involved in creating and storing declarative engrams and the amygdala is engaged in some of non-declarative learning. During ...
Lecture 08
... When presynaptic spike (action potential, AP) arrives at the presynaptic terminal, voltage-gated ion channels for calcium in the terminal’s membrane open and let ions of Ca2+ enter to the terminal. ...
... When presynaptic spike (action potential, AP) arrives at the presynaptic terminal, voltage-gated ion channels for calcium in the terminal’s membrane open and let ions of Ca2+ enter to the terminal. ...
In Pursuit of Ecstasy - Heartland Community College
... • Interferes with removal of chemical messenger (serotonin) used by nervous system ...
... • Interferes with removal of chemical messenger (serotonin) used by nervous system ...
chapter_8_powerpoint_le07
... calculations at synapses, the sites at which neurons interact. While hundreds of neurotransmitters and receptors have been identified, they can be functionally classified into two types: excitatory and inhibitory. Excitatory neurotransmitters increase the likelihood that the postsynaptic neuron will ...
... calculations at synapses, the sites at which neurons interact. While hundreds of neurotransmitters and receptors have been identified, they can be functionally classified into two types: excitatory and inhibitory. Excitatory neurotransmitters increase the likelihood that the postsynaptic neuron will ...
unit 2: biological bases of behavior
... Parts of the Brain (p.69-73): Describe the function of each part of the brain and generate a symbol or mnemonic device to assist in remembering this function. ...
... Parts of the Brain (p.69-73): Describe the function of each part of the brain and generate a symbol or mnemonic device to assist in remembering this function. ...
COURSE: 7065
... Pituitary gland---releases hormones that control metabolism and sexual development Spinal cord---controls simple reflexes that do not involve the brain Thalamus---controls the way emotions are expressed How the brain works Neurons---nerve cells in the brain that control body functions Dend ...
... Pituitary gland---releases hormones that control metabolism and sexual development Spinal cord---controls simple reflexes that do not involve the brain Thalamus---controls the way emotions are expressed How the brain works Neurons---nerve cells in the brain that control body functions Dend ...
Document
... receive input from other neurons are called: A. dendrites B. axons C. vesicles D. myelins ...
... receive input from other neurons are called: A. dendrites B. axons C. vesicles D. myelins ...
Intro-biological
... The axon terminal of one neuron reaches the dendrites of another. Dendrites surround the nucleus which is connected to a long extension called an axon, which reaches the axon terminal. On one side, at the dendrites, there are receptors of a certain shape, prepared to receive the neurotransmitter fro ...
... The axon terminal of one neuron reaches the dendrites of another. Dendrites surround the nucleus which is connected to a long extension called an axon, which reaches the axon terminal. On one side, at the dendrites, there are receptors of a certain shape, prepared to receive the neurotransmitter fro ...
3-7_DiversityOfDendriticTree_RabNóra
... separately in the two regions, with little information passing between them. They integrate and regulate the input from multiple photoreceptor cells. One of their function is allowing eyes to adjust to see well under both bright and dim light condition. The dendritic tree takes part in neuronal plas ...
... separately in the two regions, with little information passing between them. They integrate and regulate the input from multiple photoreceptor cells. One of their function is allowing eyes to adjust to see well under both bright and dim light condition. The dendritic tree takes part in neuronal plas ...
LSU Seminar Neuroscience Center of Excellence
... Brandeis University, Waltham, MA The fine-tuning of circuits in sensory cortex requires sensory experience during an early critical period. Visual deprivation (VD) during the critical period has atastrophic effects on visual function, including loss of visual responsiveness to the deprived eye, redu ...
... Brandeis University, Waltham, MA The fine-tuning of circuits in sensory cortex requires sensory experience during an early critical period. Visual deprivation (VD) during the critical period has atastrophic effects on visual function, including loss of visual responsiveness to the deprived eye, redu ...
1 - Kvalley Computers and Internet
... You are walking down the street and someone approaches you with a gun. You panic, turn around and run the other way. Describe the parts of the brain that are involved, beginning with “walking down the street”. (You’ll need to continue on another sheet of paper.) ...
... You are walking down the street and someone approaches you with a gun. You panic, turn around and run the other way. Describe the parts of the brain that are involved, beginning with “walking down the street”. (You’ll need to continue on another sheet of paper.) ...
NEUROSCIENCE REVIEW
... What is the level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse? THRESHOLD ...
... What is the level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse? THRESHOLD ...
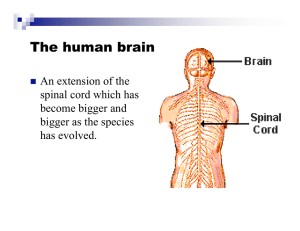
The human brain
... What changes in maturation is the connections between the neurons. On average, we lose about 20% of our neurons by the time we die. ...
... What changes in maturation is the connections between the neurons. On average, we lose about 20% of our neurons by the time we die. ...
the brain: anatomical regions
... CEREBRUM is the largest portion of the brain Cerebellum is the second largest portion of the brain. Its function is for balance. ...
... CEREBRUM is the largest portion of the brain Cerebellum is the second largest portion of the brain. Its function is for balance. ...
Long-term memory
... and retrieval of information. • All animals learn things from their interaction with the environment • Human brain forms memories more effectively than others • Maximum behavioural flexibility and most efficiently adaptation to environment. ...
... and retrieval of information. • All animals learn things from their interaction with the environment • Human brain forms memories more effectively than others • Maximum behavioural flexibility and most efficiently adaptation to environment. ...
Neurons` Short-Term Plasticity Amplifies Signals
... synaptic mechanisms of short-term plasticity in this context have not been fully described. A new study takes a step forward in understanding the most basic level of this process: the short-term plasticity at hippocampal synapses that result from processing incoming signals resembling place-field res ...
... synaptic mechanisms of short-term plasticity in this context have not been fully described. A new study takes a step forward in understanding the most basic level of this process: the short-term plasticity at hippocampal synapses that result from processing incoming signals resembling place-field res ...