refractory period
... The experiment on the next slide shows the singlechannel currents recorded from 7 individual Na+ channels in response to a depolarizing voltage step. Notice how random the behavior is - the different channels open at different times, stay open for different times, and may flicker closed a time or tw ...
... The experiment on the next slide shows the singlechannel currents recorded from 7 individual Na+ channels in response to a depolarizing voltage step. Notice how random the behavior is - the different channels open at different times, stay open for different times, and may flicker closed a time or tw ...
Channels active in the excitability of nerves and skeletal muscles
... Primer on How the Neurotransmitter ACh Activates Muscle ACh is released from the presynaptic motor neuron into the synapse based on excitation-secretion coupling facilitated by P/Q-type voltage-gated Ca2⫹ channels (1). These neurotransmitter molecules diffuse across the 20- to 30-nm synaptic cleft a ...
... Primer on How the Neurotransmitter ACh Activates Muscle ACh is released from the presynaptic motor neuron into the synapse based on excitation-secretion coupling facilitated by P/Q-type voltage-gated Ca2⫹ channels (1). These neurotransmitter molecules diffuse across the 20- to 30-nm synaptic cleft a ...
Notes Chapter 50 Nervous and Sensory Systems
... During an action potential, the polarity of the membrane is reversed briefly as Na+ ions diffuse into the neuron and K+ ions diffuse out of the neuron through gated channels. When an action potential reaches the presynaptic membrane of the next neuron, neurotransmitter molecules diffuse across t ...
... During an action potential, the polarity of the membrane is reversed briefly as Na+ ions diffuse into the neuron and K+ ions diffuse out of the neuron through gated channels. When an action potential reaches the presynaptic membrane of the next neuron, neurotransmitter molecules diffuse across t ...
CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM
... As mentioned above, the sensation of pain is caused by activation of very small diameter nerve endings. When tissue is damaged, chemical substances are released that stimulate these fibers. Many different chemical substances (e.g., aspirin) have an analgesic (pain-killing) effect. Different analgesi ...
... As mentioned above, the sensation of pain is caused by activation of very small diameter nerve endings. When tissue is damaged, chemical substances are released that stimulate these fibers. Many different chemical substances (e.g., aspirin) have an analgesic (pain-killing) effect. Different analgesi ...
New Insights into Neuron-Glia Communication
... pathways linked to G-protein activation afbroadly through the brain through glial cells, and fect synaptic depression, possibly through rethis could, in theory, modulate the efficacy of lease of nitric oxide (14). Together, these nearby synapses. Terminal Schwann cells affect synaptic signaling netw ...
... pathways linked to G-protein activation afbroadly through the brain through glial cells, and fect synaptic depression, possibly through rethis could, in theory, modulate the efficacy of lease of nitric oxide (14). Together, these nearby synapses. Terminal Schwann cells affect synaptic signaling netw ...
Neurodegenerative Diseases of Horses: Equine Motor Neuron
... weakness and tremors, her appetite remained very good. A ravenous appetite with weight loss is often reported in horses with this disease. Aside from these findings on physical examination, there was no evidence of infectious or inflammatory disease observed (complete blood count and fibrinogen were ...
... weakness and tremors, her appetite remained very good. A ravenous appetite with weight loss is often reported in horses with this disease. Aside from these findings on physical examination, there was no evidence of infectious or inflammatory disease observed (complete blood count and fibrinogen were ...
Properties of Primary Sensory (Lemniscal) Synapses in the
... medial lemniscus produced a very short-latency (⬃1 ms), fast-rising EPSP that peaked at ⬃2 ms. When the EPSP reaches firing threshold it produces an action potential at a latency of ⬃2 ms (Fig. 1B). Thus lemniscal synapses are extremely fast (Sabatini and Regehr 1999). Corticothalamic synapses forme ...
... medial lemniscus produced a very short-latency (⬃1 ms), fast-rising EPSP that peaked at ⬃2 ms. When the EPSP reaches firing threshold it produces an action potential at a latency of ⬃2 ms (Fig. 1B). Thus lemniscal synapses are extremely fast (Sabatini and Regehr 1999). Corticothalamic synapses forme ...
Structural and Functional areas of the Medulla Oblongata
... the unconscious autonomic functions c. Facilitating memory storage and retrieval ...
... the unconscious autonomic functions c. Facilitating memory storage and retrieval ...
Role of Astrocytes, Soluble Factors, Cells Adhesion Molecules and
... which possess multiple defining characteristics that make them attractive as research tools, such as the ability to maintain unlimited proliferation while retaining the ability to differentiate in vitro and in vivo into cell types of all three germ layers [1]. In addition, hESCs are also amenable to ...
... which possess multiple defining characteristics that make them attractive as research tools, such as the ability to maintain unlimited proliferation while retaining the ability to differentiate in vitro and in vivo into cell types of all three germ layers [1]. In addition, hESCs are also amenable to ...
Document
... 1. (I know this questions are for chapter 7 problems, I have forgotten to put in Chapter 7 practice questions). Now indicate whether the following events would stimulate or inhibit skeletal muscle activity. stimulate Acetylcholine binds nicotinic receptors on the muscle cell membrane. inhibit Calciu ...
... 1. (I know this questions are for chapter 7 problems, I have forgotten to put in Chapter 7 practice questions). Now indicate whether the following events would stimulate or inhibit skeletal muscle activity. stimulate Acetylcholine binds nicotinic receptors on the muscle cell membrane. inhibit Calciu ...
神经系统传导通路
... The giant pyramidal cell of paracentral lobule’s anterior part and precentral gyrus and the pyramidal cells of other type as well as the axon of pyramidal cell which lie at the frontal lobe and apical lobe constitute pyramidal tract. ...
... The giant pyramidal cell of paracentral lobule’s anterior part and precentral gyrus and the pyramidal cells of other type as well as the axon of pyramidal cell which lie at the frontal lobe and apical lobe constitute pyramidal tract. ...
Evolution of Animal Neural Systems
... Molecular details of five molecular modules of neurons for which extensive evolutionary information is available. Most channels, pumps and exchangers are evolutionarily ancient, whereas certain sub-modules in synapses are more recent innovations. ...
... Molecular details of five molecular modules of neurons for which extensive evolutionary information is available. Most channels, pumps and exchangers are evolutionarily ancient, whereas certain sub-modules in synapses are more recent innovations. ...
Slide 1
... FIGURE 15-8: Serotonin neurons and receptors are targets for a wide variety of therapeutic drugs. Drugs that act as agonists to activate receptors are indicated by solid-line arrows, whereas antagonists or inhibitors are shown with broken-line arrows. The 5-HT1A receptor acts as both the somatodend ...
... FIGURE 15-8: Serotonin neurons and receptors are targets for a wide variety of therapeutic drugs. Drugs that act as agonists to activate receptors are indicated by solid-line arrows, whereas antagonists or inhibitors are shown with broken-line arrows. The 5-HT1A receptor acts as both the somatodend ...
File
... 77-78. Neurons are slightly permeable to sodium ions. a. In which direction is the chemical force for sodium? Why? The direction of the chemical force is into the cell because it has a higher concentration outside the cell and diffuses down its concentration gradient. b. In which direction is the el ...
... 77-78. Neurons are slightly permeable to sodium ions. a. In which direction is the chemical force for sodium? Why? The direction of the chemical force is into the cell because it has a higher concentration outside the cell and diffuses down its concentration gradient. b. In which direction is the el ...
Ph.D. THESIS THE NEUROMODULATOR AND
... distinguish chemical, electrical and combined synapses. In the case of chemical synapses, a presynaptic neuron releases chemical signal compounds, neurotransmitters. These transmitters interact with specific receptor proteins located at the surface of post-synaptic neurons and hence induce cellular ...
... distinguish chemical, electrical and combined synapses. In the case of chemical synapses, a presynaptic neuron releases chemical signal compounds, neurotransmitters. These transmitters interact with specific receptor proteins located at the surface of post-synaptic neurons and hence induce cellular ...
Cardiac Pharmacology
... (Sodium potassium exchange pump) • Results in increased quantity of Ca in ...
... (Sodium potassium exchange pump) • Results in increased quantity of Ca in ...
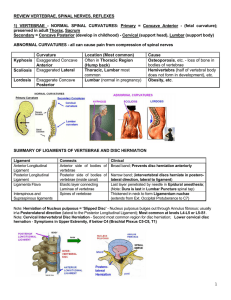
REVIEW VERTEBRAE, SPINAL NERVES, REFLEXES 1
... 7. ____ A 24-year-old-patient is seen for a routine neurological exam. The patient is a medical student who has been studying intensely for Step 1 board (or Final) examinations. Testing of patellar tendon reflexes (deep tendon reflex) shows bilateral, mild hyperreflexia (scored 3). The physician sus ...
... 7. ____ A 24-year-old-patient is seen for a routine neurological exam. The patient is a medical student who has been studying intensely for Step 1 board (or Final) examinations. Testing of patellar tendon reflexes (deep tendon reflex) shows bilateral, mild hyperreflexia (scored 3). The physician sus ...
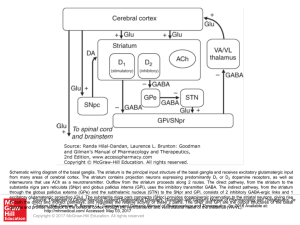
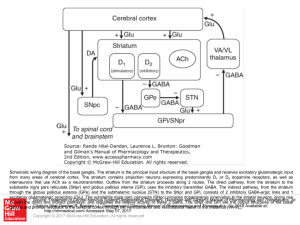
Slide ()
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
Spinal_Cord_Power_Point
... provides sensory input to the CNS via one pair of spinal nerves or the trigeminal nerve. ...
... provides sensory input to the CNS via one pair of spinal nerves or the trigeminal nerve. ...
Smooth Muscle - OpenStax CNX
... it lls, the mechanical stress of the stretching will trigger contraction, but this is immediately followed by relaxation so that the organ does not empty its contents prematurely. This is important for hollow organs, such as the stomach or urinary bladder, which continuously expand as they ll. The ...
... it lls, the mechanical stress of the stretching will trigger contraction, but this is immediately followed by relaxation so that the organ does not empty its contents prematurely. This is important for hollow organs, such as the stomach or urinary bladder, which continuously expand as they ll. The ...
Neuromuscular junction

A neuromuscular junction (sometimes called a myoneural junction) is a junction between nerve and muscle; it is a chemical synapse formed by the contact between the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron and the postsynaptic membrane of a muscle fiber. It is at the neuromuscular junction that a motor neuron is able to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.Muscles require innervation to function—and even just to maintain muscle tone, avoiding atrophy. Synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction begins when an action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron, which activates voltage-dependent calcium channels to allow calcium ions to enter the neuron. Calcium ions bind to sensor proteins (synaptotagmin) on synaptic vesicles, triggering vesicle fusion with the cell membrane and subsequent neurotransmitter release from the motor neuron into the synaptic cleft. In vertebrates, motor neurons release acetylcholine (ACh), a small molecule neurotransmitter, which diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) on the cell membrane of the muscle fiber, also known as the sarcolemma. nAChRs are ionotropic receptors, meaning they serve as ligand-gated ion channels. The binding of ACh to the receptor can depolarize the muscle fiber, causing a cascade that eventually results in muscle contraction.Neuromuscular junction diseases can be of genetic and autoimmune origin. Genetic disorders, such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, can arise from mutated structural proteins that comprise the neuromuscular junction, whereas autoimmune diseases, such as myasthenia gravis, occur when antibodies are produced against nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on the sarcolemma.