Laboratory Exercise 10: Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord
... The withdrawal or flexor reflex has an interneuron between the sensory and motor neuron. Due to the interneuron, it brings the stimulus to the level of consciousness. This reflex has at least two synapses. The withdrawal reflex draws a body part away from a harmful stimulus to prevent damage to the ...
... The withdrawal or flexor reflex has an interneuron between the sensory and motor neuron. Due to the interneuron, it brings the stimulus to the level of consciousness. This reflex has at least two synapses. The withdrawal reflex draws a body part away from a harmful stimulus to prevent damage to the ...
The Nervous System
... • If VM reaches threshold, Na+ channels open and Na+ influx ensues, depolarizing the cell and causing the VM to increase. This is the rising phase of an AP. • Eventually, the Na+ channel will have inactivated and the K+ channels will be open. Now, K+ effluxes and repolarization occurs. This is the f ...
... • If VM reaches threshold, Na+ channels open and Na+ influx ensues, depolarizing the cell and causing the VM to increase. This is the rising phase of an AP. • Eventually, the Na+ channel will have inactivated and the K+ channels will be open. Now, K+ effluxes and repolarization occurs. This is the f ...
23. Parasympathetic nervous system
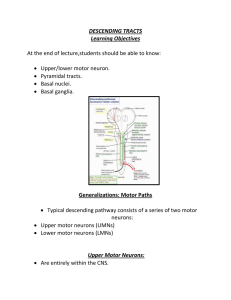
... Basic anatomical difference between the motor pathways of the voluntary somatic nervous system (to skeletal muscles) and those of the autonomic nervous system ...
... Basic anatomical difference between the motor pathways of the voluntary somatic nervous system (to skeletal muscles) and those of the autonomic nervous system ...
Dalibor Sames Tuesday, June 21, 2016, 10:30am
... In this lecture I will discuss our progress on the pursuit of two interconnected longterm goals: visualization and repair of synaptic function with chemical tools. First, I will describe how this overarching theme led us to the development of conceptually new imaging agents, termed fluorescent false ...
... In this lecture I will discuss our progress on the pursuit of two interconnected longterm goals: visualization and repair of synaptic function with chemical tools. First, I will describe how this overarching theme led us to the development of conceptually new imaging agents, termed fluorescent false ...
Cortical Control of Motor Function-L18
... Primary motor cortex - loss of voluntary control of discrete movement of the distal segments of the ...
... Primary motor cortex - loss of voluntary control of discrete movement of the distal segments of the ...
muscle power point - bhshecurriculumwork2011
... In tensile strength bone is rather like cast iron, although around 1/3 of the weight, in bending stress it behaves like steel, although only half as strong and in compression it can withstand the forces exerted by a running man ( approximately equivalent to a dead weight of 594 pounds). ...
... In tensile strength bone is rather like cast iron, although around 1/3 of the weight, in bending stress it behaves like steel, although only half as strong and in compression it can withstand the forces exerted by a running man ( approximately equivalent to a dead weight of 594 pounds). ...
cns structure - Department of Physiology
... dorsal root ganglia, are small bumps that contain the cell bodies of the dorsal roots. Dorsal and ventral roots combine to form a spinal nerve on each side of the spinal cord. There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves: •8 cervical: associated with the neck, shoulders, arms, hands. ...
... dorsal root ganglia, are small bumps that contain the cell bodies of the dorsal roots. Dorsal and ventral roots combine to form a spinal nerve on each side of the spinal cord. There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves: •8 cervical: associated with the neck, shoulders, arms, hands. ...
Nervous system Lab - Sonoma Valley High School
... Describe three factors that determine the speed of the impulse along a neuron. Explain how size of the nerve fiber determines speed and which size is myelinated and which is not. ...
... Describe three factors that determine the speed of the impulse along a neuron. Explain how size of the nerve fiber determines speed and which size is myelinated and which is not. ...
This article was originally published in a journal published by
... short-term working memory and for encoding of information into long-term memory. Detailed computational simulations of the entorhinal cortex [52] demonstrate how the cholinergic activation of intrinsic mechanisms for persistent spiking could underlie spiking activity during the delay period of delay ...
... short-term working memory and for encoding of information into long-term memory. Detailed computational simulations of the entorhinal cortex [52] demonstrate how the cholinergic activation of intrinsic mechanisms for persistent spiking could underlie spiking activity during the delay period of delay ...
Nerve Cells, Neural Circuitry, and Behavior
... periphery (to sensory receptors in the skin, joints, and muscle) and another to the spinal cord (Figure 2–3C). Multipolar neurons predominate in the nervous system of vertebrates. They typically have a single axon and many dendritic structures emerging from various points around the cell body (Figur ...
... periphery (to sensory receptors in the skin, joints, and muscle) and another to the spinal cord (Figure 2–3C). Multipolar neurons predominate in the nervous system of vertebrates. They typically have a single axon and many dendritic structures emerging from various points around the cell body (Figur ...
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
... potassium ions to rush out of the neuron. The potassium ions, which have a positive charge as well, create a negatively charged cell interior by their absence. This event stops the depolarization process. The sodium ions are pumped more slowly to the cell exterior by active transport, resulting in t ...
... potassium ions to rush out of the neuron. The potassium ions, which have a positive charge as well, create a negatively charged cell interior by their absence. This event stops the depolarization process. The sodium ions are pumped more slowly to the cell exterior by active transport, resulting in t ...
action potential
... Ranvier, gaps in the myelin sheath where voltagegated Na+ channels are found Action potentials in myelinated axons jump between the nodes of Ranvier in a process called saltatory ...
... Ranvier, gaps in the myelin sheath where voltagegated Na+ channels are found Action potentials in myelinated axons jump between the nodes of Ranvier in a process called saltatory ...
NFPT Study Questions update
... 3. What are the three skeletal muscle fibers? 4. What are the characteristics of white fast twitch fibers? 5. What are the characteristics of red slow twitch fibers? 6. What is a motor unit? 7. Only a minimum number of motor units required to move a given weight, will contract in performing work (Tr ...
... 3. What are the three skeletal muscle fibers? 4. What are the characteristics of white fast twitch fibers? 5. What are the characteristics of red slow twitch fibers? 6. What is a motor unit? 7. Only a minimum number of motor units required to move a given weight, will contract in performing work (Tr ...
Drugs Acting on the Central and Peripheral Nervous
... Neurotransmitters stimulate postsynaptic cells either by exciting or by inhibiting them. The reaction that occurs when a neurotransmitter stimulates a receptor site depends on the specific neurotransmitter that it releases and the receptor site it activates. A nerve may produce only one type of neur ...
... Neurotransmitters stimulate postsynaptic cells either by exciting or by inhibiting them. The reaction that occurs when a neurotransmitter stimulates a receptor site depends on the specific neurotransmitter that it releases and the receptor site it activates. A nerve may produce only one type of neur ...
Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Lecture Outline
... occipital bone and coccyx by coccygeal ligament. Surrounded by the epidural space which contains blood vessels and adipose ...
... occipital bone and coccyx by coccygeal ligament. Surrounded by the epidural space which contains blood vessels and adipose ...
Biology - Chpt 14- The Nervous System
... Where two neurons meet, there is a tiny gap called a synapse. Signals cross this gap using chemicals. One neuron releases the chemical into the gap. The chemical diffuses across the gap and makes the next neuron transmit an electrical signal. ...
... Where two neurons meet, there is a tiny gap called a synapse. Signals cross this gap using chemicals. One neuron releases the chemical into the gap. The chemical diffuses across the gap and makes the next neuron transmit an electrical signal. ...
D22 - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... facilitation) – more muscle fibers are responding. – postactivation facilitation is followed by longer-lasting period of depression, maximal between 2 and 4 min after conditioning exercise period and lasting for 10 min (postactivation exhaustion). miniature endplate potentials have subnormal ampli ...
... facilitation) – more muscle fibers are responding. – postactivation facilitation is followed by longer-lasting period of depression, maximal between 2 and 4 min after conditioning exercise period and lasting for 10 min (postactivation exhaustion). miniature endplate potentials have subnormal ampli ...
Neuromuscular junction

A neuromuscular junction (sometimes called a myoneural junction) is a junction between nerve and muscle; it is a chemical synapse formed by the contact between the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron and the postsynaptic membrane of a muscle fiber. It is at the neuromuscular junction that a motor neuron is able to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.Muscles require innervation to function—and even just to maintain muscle tone, avoiding atrophy. Synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction begins when an action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron, which activates voltage-dependent calcium channels to allow calcium ions to enter the neuron. Calcium ions bind to sensor proteins (synaptotagmin) on synaptic vesicles, triggering vesicle fusion with the cell membrane and subsequent neurotransmitter release from the motor neuron into the synaptic cleft. In vertebrates, motor neurons release acetylcholine (ACh), a small molecule neurotransmitter, which diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) on the cell membrane of the muscle fiber, also known as the sarcolemma. nAChRs are ionotropic receptors, meaning they serve as ligand-gated ion channels. The binding of ACh to the receptor can depolarize the muscle fiber, causing a cascade that eventually results in muscle contraction.Neuromuscular junction diseases can be of genetic and autoimmune origin. Genetic disorders, such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, can arise from mutated structural proteins that comprise the neuromuscular junction, whereas autoimmune diseases, such as myasthenia gravis, occur when antibodies are produced against nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on the sarcolemma.