BamHI - Courses
... Nucleases – break DNA polymers by cleaving the phosphodiester bond Ligases – join DNA molecules together End-modifying enzymes – add labels and make compatible ends for further manipulation http://www.neb.com/nebecomm/products/categories.asp ...
... Nucleases – break DNA polymers by cleaving the phosphodiester bond Ligases – join DNA molecules together End-modifying enzymes – add labels and make compatible ends for further manipulation http://www.neb.com/nebecomm/products/categories.asp ...
Jeffreys - OldForensics 2012-2013
... • After discovering the technique of genetic fingerprinting at the University of Leicester, he continued to work there as a professor in the Department of Genetics. • Sir Alec Jeffreys's methods were soon applied to the public when two young women were raped and murdered in Leicestershire. • One man ...
... • After discovering the technique of genetic fingerprinting at the University of Leicester, he continued to work there as a professor in the Department of Genetics. • Sir Alec Jeffreys's methods were soon applied to the public when two young women were raped and murdered in Leicestershire. • One man ...
File
... GCSE DNA, genes and chromosomes Evolution Classification Genetic disease Enzymes AS 1.1.1 Cell structure 2.1.1 Biological molecules 2.1.2 Nucleic acids 2.1.3 Enzymes ...
... GCSE DNA, genes and chromosomes Evolution Classification Genetic disease Enzymes AS 1.1.1 Cell structure 2.1.1 Biological molecules 2.1.2 Nucleic acids 2.1.3 Enzymes ...
Molecular characterization of individual DNA double strand breaks
... DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) are deadly lesions that can lead to genetic defects and cell apoptosis1. Techniques to directly image DSBs in isolated DNA include scanning electron microscopy2, Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) and single molecule fluorescence microscopy3. While these techniques can be ...
... DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) are deadly lesions that can lead to genetic defects and cell apoptosis1. Techniques to directly image DSBs in isolated DNA include scanning electron microscopy2, Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) and single molecule fluorescence microscopy3. While these techniques can be ...
SNP Discovery Services - Sanger Sequencing
... The concentration of plasmid DNA required is between 100 and 500 ng/µl. The DNA must be of good quality in order to ensure that the sequencing reactions work adequately. The required quantity of plasmid DNA for a project is approximately 2 µl or 4 µl per 600 bases. For example, if the region to be s ...
... The concentration of plasmid DNA required is between 100 and 500 ng/µl. The DNA must be of good quality in order to ensure that the sequencing reactions work adequately. The required quantity of plasmid DNA for a project is approximately 2 µl or 4 µl per 600 bases. For example, if the region to be s ...
Lab Business - Memorial University
... SCOTUS in essence recognized that BRCA genes are ‘products of nature’ and thus on accepted principles not patentable. Such genes include expressed exon and intervening intron regions, as well as upstream and downstream promoters, enhancers, and other paraphernalia by which genes get things done. The ...
... SCOTUS in essence recognized that BRCA genes are ‘products of nature’ and thus on accepted principles not patentable. Such genes include expressed exon and intervening intron regions, as well as upstream and downstream promoters, enhancers, and other paraphernalia by which genes get things done. The ...
Supplemental Figure 3
... representative A. thaliana acccessions. Equivalent amounts of genomic DNA isolated from different accessions were subjected to PCR using the same pair of SCR1 primers (the PseSCR3 and PseSCR5 primers described by Shimizu et al. 2004). Note that DNA from the C24 and Mt-0 accessions, which lack SCR1 ...
... representative A. thaliana acccessions. Equivalent amounts of genomic DNA isolated from different accessions were subjected to PCR using the same pair of SCR1 primers (the PseSCR3 and PseSCR5 primers described by Shimizu et al. 2004). Note that DNA from the C24 and Mt-0 accessions, which lack SCR1 ...
Genetic Engineering
... A. Selective Breeding – allowing only those individuals with desired characteristics to produce the next generation 1. Inbreeding – cross two of the same type of individual to preserve the characteristics (Risky!) 2. Cross-breeding / Hybridization – cross two different types of individuals to get th ...
... A. Selective Breeding – allowing only those individuals with desired characteristics to produce the next generation 1. Inbreeding – cross two of the same type of individual to preserve the characteristics (Risky!) 2. Cross-breeding / Hybridization – cross two different types of individuals to get th ...
DNA/Protein Synthesis Study Guide
... What type of bond attaches a new amino acid to a polypeptide chain? By what process does a tRNA molecule attach onto mRNA during translation? ...
... What type of bond attaches a new amino acid to a polypeptide chain? By what process does a tRNA molecule attach onto mRNA during translation? ...
The Human Genome Analysis Variable Number Tandem Repeats
... EACH patient has a chip and microarray containing “candidate” genes ...
... EACH patient has a chip and microarray containing “candidate” genes ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR CHAPTER 12 – DNA Two Main Processes for
... Why would DNA need to be replicated? (2 reasons – be specific) What enzyme reads one side of the DNA and makes a complementary strands? What enzyme unzips the double helix? What enzyme acts as “glue” to make sure the new DNA strands are complete? DNA is a double helix, a small portion of one side of ...
... Why would DNA need to be replicated? (2 reasons – be specific) What enzyme reads one side of the DNA and makes a complementary strands? What enzyme unzips the double helix? What enzyme acts as “glue” to make sure the new DNA strands are complete? DNA is a double helix, a small portion of one side of ...
DNA Fingerprinting of Bacterial Communities
... – Some so variable they can be used to distinguish between very closely related organisms (different strains of same species) ...
... – Some so variable they can be used to distinguish between very closely related organisms (different strains of same species) ...
8.1-8.2 TAKE DOWN NOTES AND SKETCH MOLECULES
... that would be identified by Avery as DNA. Deoxyribonucleic Acid– DNA has two strands and is a double helix. Hershey & Chase confirmed that DNA is the material that passes on traits. ...
... that would be identified by Avery as DNA. Deoxyribonucleic Acid– DNA has two strands and is a double helix. Hershey & Chase confirmed that DNA is the material that passes on traits. ...
DNA and RNA study guide Answer Key
... 7. Before a cell divides, it must duplicate its own DNA in a process known as… DNA Replication 8. The genetic code in DNA depends upon the order or sequence of… Nitrogenous Bases 9. If one strand of DNA has the nitrogenous base sequence ATCGT, the sequence of bases on the COMPLEMENTARY STRAND of DNA ...
... 7. Before a cell divides, it must duplicate its own DNA in a process known as… DNA Replication 8. The genetic code in DNA depends upon the order or sequence of… Nitrogenous Bases 9. If one strand of DNA has the nitrogenous base sequence ATCGT, the sequence of bases on the COMPLEMENTARY STRAND of DNA ...
DNA Replication
... breaking the hydrogen bonds between nucleotides Replication Fork: point where DNA strands separate. ...
... breaking the hydrogen bonds between nucleotides Replication Fork: point where DNA strands separate. ...
DNA: The Genetic Material
... DNA polymerase proofreads DNA during its replication so that very few errors occur http://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=zdDkiRw1PdU ...
... DNA polymerase proofreads DNA during its replication so that very few errors occur http://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=zdDkiRw1PdU ...
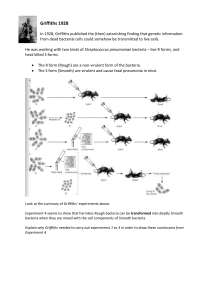
DNA experiments exercise
... Experiment 4 seems to show that harmless Rough bacteria can be transformed into deadly Smooth bacteria when they are mixed with the cell components of Smooth bacteria. Explain why Griffiths needed to carry out experiments 1 to 3 in order to draw these conclusions from Experiment 4. ...
... Experiment 4 seems to show that harmless Rough bacteria can be transformed into deadly Smooth bacteria when they are mixed with the cell components of Smooth bacteria. Explain why Griffiths needed to carry out experiments 1 to 3 in order to draw these conclusions from Experiment 4. ...
DNA sequencing

DNA sequencing is the process of determining the precise order of nucleotides within a DNA molecule. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases—adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine—in a strand of DNA. The advent of rapid DNA sequencing methods has greatly accelerated biological and medical research and discovery.Knowledge of DNA sequences has become indispensable for basic biological research, and in numerous applied fields such as medical diagnosis, biotechnology, forensic biology, virology and biological systematics. The rapid speed of sequencing attained with modern DNA sequencing technology has been instrumental in the sequencing of complete DNA sequences, or genomes of numerous types and species of life, including the human genome and other complete DNA sequences of many animal, plant, and microbial species.The first DNA sequences were obtained in the early 1970s by academic researchers using laborious methods based on two-dimensional chromatography. Following the development of fluorescence-based sequencing methods with a DNA sequencer, DNA sequencing has become easier and orders of magnitude faster.