Mitochondrial DNA - Winona Senior High School
... polymerase amplifying the DNA • Taq (Thermus aquaticus): bacteria from hot springs contains enzymes that can withstand the high temperatures of PCR ...
... polymerase amplifying the DNA • Taq (Thermus aquaticus): bacteria from hot springs contains enzymes that can withstand the high temperatures of PCR ...
DNA Sequencing
... DNA Sequencing Steps Synthesis of new strand starts at 3’ end of primer and continues until dideoxyribonucleotide is inserted- stops synthesis Separate labeled strands through a polyacrylamide gel Placed on x-ray film Because of florescent tag, different length fragments are revealed on fi ...
... DNA Sequencing Steps Synthesis of new strand starts at 3’ end of primer and continues until dideoxyribonucleotide is inserted- stops synthesis Separate labeled strands through a polyacrylamide gel Placed on x-ray film Because of florescent tag, different length fragments are revealed on fi ...
CALL FOR PROPOSALS 2008
... Justify the sequencing strategy proposed, but do not provide technical details of manipulations. You can suggest the technology to be used, but the final decision on technology choice will be made by France Génomique. In the case of de novo sequencing, indicate the need for finishing. Because of the ...
... Justify the sequencing strategy proposed, but do not provide technical details of manipulations. You can suggest the technology to be used, but the final decision on technology choice will be made by France Génomique. In the case of de novo sequencing, indicate the need for finishing. Because of the ...
Worksheet for 4/16
... gel electrophoresis. Diagram a gel including electric charge, and labeled fragments. ...
... gel electrophoresis. Diagram a gel including electric charge, and labeled fragments. ...
HigH-THrougHpuT dna sequencing
... HTS overcomes previous limitations to allow millions of bases to be sequenced much quicker and at lower cost compared to conventional methods. This technology can be used to uncover a vast amount of germline (sperm/egg cells) and somatic (all other cells) variation for mutation detection in disease ...
... HTS overcomes previous limitations to allow millions of bases to be sequenced much quicker and at lower cost compared to conventional methods. This technology can be used to uncover a vast amount of germline (sperm/egg cells) and somatic (all other cells) variation for mutation detection in disease ...
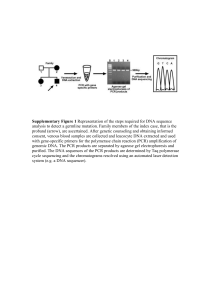
Figure 2 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence
... Supplementary Figure 1 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence analysis to detect a germline mutation. Family members of the index case, that is the proband (arrow), are ascertained. After genetic counseling and obtaining informed consent, venous blood samples are collected and leucocy ...
... Supplementary Figure 1 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence analysis to detect a germline mutation. Family members of the index case, that is the proband (arrow), are ascertained. After genetic counseling and obtaining informed consent, venous blood samples are collected and leucocy ...
Cutting-Edge Forensics
... of victims and/or suspects to establish presence or absence at a scene or familial relationships, among other applications. Traditionally, this sequencing involves older technologies, such as Sanger sequencing, and targets only small portions of the genome. More recently, some forensic scientists ar ...
... of victims and/or suspects to establish presence or absence at a scene or familial relationships, among other applications. Traditionally, this sequencing involves older technologies, such as Sanger sequencing, and targets only small portions of the genome. More recently, some forensic scientists ar ...
Mutation identification by whole genome sequencing
... I. We will continue with SNP mapping, and then move on to: II. Mutation Detection Through Whole Genome Sequencing A. Sequencing Methods 1. Conventional Sanger Sequencing a. dideoxy nucleotide triphosphates (ddNTPs), the key to the Sanger method 1) they terminate DNA polymerization because they lack ...
... I. We will continue with SNP mapping, and then move on to: II. Mutation Detection Through Whole Genome Sequencing A. Sequencing Methods 1. Conventional Sanger Sequencing a. dideoxy nucleotide triphosphates (ddNTPs), the key to the Sanger method 1) they terminate DNA polymerization because they lack ...
DNA sequencing

DNA sequencing is the process of determining the precise order of nucleotides within a DNA molecule. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases—adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine—in a strand of DNA. The advent of rapid DNA sequencing methods has greatly accelerated biological and medical research and discovery.Knowledge of DNA sequences has become indispensable for basic biological research, and in numerous applied fields such as medical diagnosis, biotechnology, forensic biology, virology and biological systematics. The rapid speed of sequencing attained with modern DNA sequencing technology has been instrumental in the sequencing of complete DNA sequences, or genomes of numerous types and species of life, including the human genome and other complete DNA sequences of many animal, plant, and microbial species.The first DNA sequences were obtained in the early 1970s by academic researchers using laborious methods based on two-dimensional chromatography. Following the development of fluorescence-based sequencing methods with a DNA sequencer, DNA sequencing has become easier and orders of magnitude faster.