WHO AM I
... •Discovered a 1:1 ratio of adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine in DNA samples from a variety of organisms. ...
... •Discovered a 1:1 ratio of adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine in DNA samples from a variety of organisms. ...
The data were obtained from a study of the length of time spent in
... After DNA replication, results in each DNA strand having 1 original + 1 copy of DNA ...
... After DNA replication, results in each DNA strand having 1 original + 1 copy of DNA ...
ANSWERS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS – CHAPTER 13
... DNA molecules in living cells are no longer thought to be inert molecules in terms of possessing an unchanging DNA sequence. Why is this? (pp. 269–273) A typical DNA sequence is not invariant, and many things can influence the DNA sequence of a normal cell including the replication and relocation of ...
... DNA molecules in living cells are no longer thought to be inert molecules in terms of possessing an unchanging DNA sequence. Why is this? (pp. 269–273) A typical DNA sequence is not invariant, and many things can influence the DNA sequence of a normal cell including the replication and relocation of ...
Packet - MsOttoliniBiology
... 1) The enzyme ________________ unwinds and separates the 2 DNA strands by breaking the weak ________________ bonds between bases. It “unzips” the double helix. 2) ________________ gathers _______________ and brings them into the replication fork. A ________________ is created to start the new strand ...
... 1) The enzyme ________________ unwinds and separates the 2 DNA strands by breaking the weak ________________ bonds between bases. It “unzips” the double helix. 2) ________________ gathers _______________ and brings them into the replication fork. A ________________ is created to start the new strand ...
Unit 4 Objectives
... o Define helicase and DNA polymerase and describe their functions o Identify a replication fork and describe how it enables DNA to be copied Determine the complementary strand of DNA when given the original strand ...
... o Define helicase and DNA polymerase and describe their functions o Identify a replication fork and describe how it enables DNA to be copied Determine the complementary strand of DNA when given the original strand ...
DNA Flipbook Objective: You will create an informational Flipbook
... Objective: You will create an informational Flipbook explaining in words and pictures the parts of DNA, DNA replication, Transcription, and Translation. As you complete each task, place a check to keep track of your progress. Label each flip as outlined below. Directions: Each page should be titled ...
... Objective: You will create an informational Flipbook explaining in words and pictures the parts of DNA, DNA replication, Transcription, and Translation. As you complete each task, place a check to keep track of your progress. Label each flip as outlined below. Directions: Each page should be titled ...
Study Questions for Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... 1 Purine pairs w/ 1 pyrimidine; purines have 2 rings (A, G) and pyrimidines have 1 ring (C and T); pair with each other 2 keep consistent distance between Sugar-Phosphate backbones 4) Describe the semiconservative model of DNA replication. ...
... 1 Purine pairs w/ 1 pyrimidine; purines have 2 rings (A, G) and pyrimidines have 1 ring (C and T); pair with each other 2 keep consistent distance between Sugar-Phosphate backbones 4) Describe the semiconservative model of DNA replication. ...
Chapter 12 Study Guide
... 1.) Describe Griffith’s experiment and the conclusions he drew from it. - took heat killed disease causing bacteria and mixed it with harmless bacteria, transforming it then injecting it in a mouse which died of pneumonia. - Conclusion was the disease causing bacteria transferred their ability to ca ...
... 1.) Describe Griffith’s experiment and the conclusions he drew from it. - took heat killed disease causing bacteria and mixed it with harmless bacteria, transforming it then injecting it in a mouse which died of pneumonia. - Conclusion was the disease causing bacteria transferred their ability to ca ...
Semester Test Practice Test
... A repressor protein… • a. blocks movement of RNA polymerase • b. prevents DNA synthesis • c. attaches to ribosomes during translation • d. is encoded by one of the structural genes. ...
... A repressor protein… • a. blocks movement of RNA polymerase • b. prevents DNA synthesis • c. attaches to ribosomes during translation • d. is encoded by one of the structural genes. ...
DNA functions worksheet
... 9. The role of ribosomes in protein synthesis is to A. split the two strands of DNA apart. B. check for and replace faulty codons. C. carry amino acids to the site of translation. D. provide a site for mRNA and tRNA to join together. 10. What is the DNA sequence that would produce the following amin ...
... 9. The role of ribosomes in protein synthesis is to A. split the two strands of DNA apart. B. check for and replace faulty codons. C. carry amino acids to the site of translation. D. provide a site for mRNA and tRNA to join together. 10. What is the DNA sequence that would produce the following amin ...
Rita Levi Montalcini was born on April 22nd, 1909
... psychological traits and was first identified in 1869. His structure, which was discovered by Francis Crick and James Watson in the middle of the last century, has a sort of double helix shape. It is made of different nucleid acids. Acids are made up from nucleotide molecules that have three parts: ...
... psychological traits and was first identified in 1869. His structure, which was discovered by Francis Crick and James Watson in the middle of the last century, has a sort of double helix shape. It is made of different nucleid acids. Acids are made up from nucleotide molecules that have three parts: ...
Molecular Bio Questions2
... a) Four bases on the mRNA that is read by the ribosome in the 3’ to 5’ direction. b) Four bases on the mRNA that is read by the ribosome in the 5’ to 3’ direction. c) Three bases on the mRNA that is read by the ribosome in the 3’ to 5’ direction. d) Three bases on the mRNA that is read by the riboso ...
... a) Four bases on the mRNA that is read by the ribosome in the 3’ to 5’ direction. b) Four bases on the mRNA that is read by the ribosome in the 5’ to 3’ direction. c) Three bases on the mRNA that is read by the ribosome in the 3’ to 5’ direction. d) Three bases on the mRNA that is read by the riboso ...
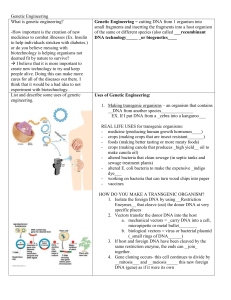
Genetic Engineering Guied Notes
... deemed fit by nature to survive? I believe that it is more important to create new technology to try and keep people alive. Doing this can make more cures for all of the diseases out there. I think that it would be a bad idea to not experiment with biotechnology. List and describe some uses of gen ...
... deemed fit by nature to survive? I believe that it is more important to create new technology to try and keep people alive. Doing this can make more cures for all of the diseases out there. I think that it would be a bad idea to not experiment with biotechnology. List and describe some uses of gen ...
Untitled
... Rosalind Franklin contributed with an X-ray image looking down a double helix 3 hydrogen bonds when G-C 2 Hydrogen bonds when A-T ...
... Rosalind Franklin contributed with an X-ray image looking down a double helix 3 hydrogen bonds when G-C 2 Hydrogen bonds when A-T ...
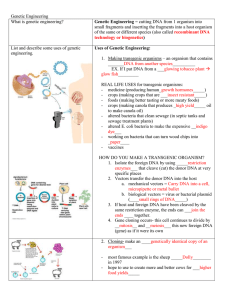
Genetic Engineering
... 1. Isolate the foreign DNA by using _____restriction enzymes___ that cleave (cut) the donor DNA at very specific places 2. Vectors transfer the donor DNA into the host a. mechanical vectors = Carry DNA into a cell, micropipette or metal bullet b. biological vectors = virus or bacterial plasmid (____ ...
... 1. Isolate the foreign DNA by using _____restriction enzymes___ that cleave (cut) the donor DNA at very specific places 2. Vectors transfer the donor DNA into the host a. mechanical vectors = Carry DNA into a cell, micropipette or metal bullet b. biological vectors = virus or bacterial plasmid (____ ...
Worksheet for videos below
... DNA Replication 1. During which cell cycle phase do eukaryotes copy their DNA? ____________________________________ 2. Which theory of DNA replication is the correct theory as determined by the Meselson-Stahl experiment? _______________________________________________________________________________ ...
... DNA Replication 1. During which cell cycle phase do eukaryotes copy their DNA? ____________________________________ 2. Which theory of DNA replication is the correct theory as determined by the Meselson-Stahl experiment? _______________________________________________________________________________ ...
Ch 12 RNO
... Nitrogenous bases: describe them, list them, discuss their arrangement in the DNA molecule. Describe how covalent bonds play a role in the DNA molecule. What is Chargaff’s rule? Describe how Franklin used x-ray diffraction to learn about DNA. a. What did Franklin observe about the structure of the D ...
... Nitrogenous bases: describe them, list them, discuss their arrangement in the DNA molecule. Describe how covalent bonds play a role in the DNA molecule. What is Chargaff’s rule? Describe how Franklin used x-ray diffraction to learn about DNA. a. What did Franklin observe about the structure of the D ...
TIP Translation - dna
... a. amino acid, base, and protein c. mRNA, tRNA, and a ribosome b. sugar, phosphate, and base d. chromosomes and genes ____ 2. DNA is made of subunits called what? a. deoxyribonucleic acids c. proteins b. nucleotides d. traits ____ 3. ...
... a. amino acid, base, and protein c. mRNA, tRNA, and a ribosome b. sugar, phosphate, and base d. chromosomes and genes ____ 2. DNA is made of subunits called what? a. deoxyribonucleic acids c. proteins b. nucleotides d. traits ____ 3. ...
DNA polymerase

The DNA polymerases are enzymes that create DNA molecules by assembling nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA. These enzymes are essential to DNA replication and usually work in pairs to create two identical DNA strands from a single original DNA molecule. During this process, DNA polymerase “reads” the existing DNA strands to create two new strands that match the existing ones.Every time a cell divides, DNA polymerase is required to help duplicate the cell’s DNA, so that a copy of the original DNA molecule can be passed to each of the daughter cells. In this way, genetic information is transmitted from generation to generation.Before replication can take place, an enzyme called helicase unwinds the DNA molecule from its tightly woven form. This opens up or “unzips” the double-stranded DNA to give two single strands of DNA that can be used as templates for replication.