Proein Synthesis Note Fill-in
... 50. A ribosome is made of _____________% of rRNA and _____________% of proteins. 51. A ribosome contains 2 sites for tRNA to bind called _____ and ______. 52. Sketch and label a ribosome. Include the attachment sites and the mRNA in your drawing. 53. What is the purpose of translation? 54. What 4 th ...
... 50. A ribosome is made of _____________% of rRNA and _____________% of proteins. 51. A ribosome contains 2 sites for tRNA to bind called _____ and ______. 52. Sketch and label a ribosome. Include the attachment sites and the mRNA in your drawing. 53. What is the purpose of translation? 54. What 4 th ...
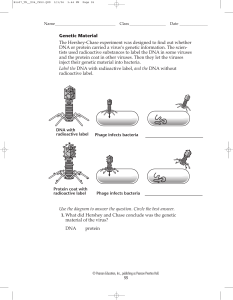
Genetic Material The Hershey-Chase experiment was designed to
... 1. What did Hershey and Chase conclude was the genetic material of the virus? DNA ...
... 1. What did Hershey and Chase conclude was the genetic material of the virus? DNA ...
DNA Crossword Puzzle
... 1. One of the four nitrogenous bases in the double helix of DNA. It always bonds to adenine in DNA. It does not occur in RNA. [THYMINE] 2. A molecule that along with a sugar forms the legs of the ladder of DNA. [PHOSPHATE] 4. A molecule composed of strings of nucleotides. They act as the genetic mat ...
... 1. One of the four nitrogenous bases in the double helix of DNA. It always bonds to adenine in DNA. It does not occur in RNA. [THYMINE] 2. A molecule that along with a sugar forms the legs of the ladder of DNA. [PHOSPHATE] 4. A molecule composed of strings of nucleotides. They act as the genetic mat ...
Molecular Biotechnology Programme Rolling circle transcription on
... RNA polymerase T7 is utilized as a component of motor complexes in DNA nanotechnology due to its high promotor specificity, the lack of external transcription factors and its very high processivity, but there is no experience of its application on small double stranded DNA circles. Circular template ...
... RNA polymerase T7 is utilized as a component of motor complexes in DNA nanotechnology due to its high promotor specificity, the lack of external transcription factors and its very high processivity, but there is no experience of its application on small double stranded DNA circles. Circular template ...
DNA transcription
... Label the DNA and RNA. Then, label the missing nucleotides marked on the diagram. ...
... Label the DNA and RNA. Then, label the missing nucleotides marked on the diagram. ...
Molecular Genetics Study Guide
... What are the 4 nitrogen bases located in DNA? How do they pair up? What happens in replication and where does it occur? When does it occur? What does semi-conservative replication mean? What are the 3 main stages of replication and what enzymes are involved? What are Okazaki fragments and why do the ...
... What are the 4 nitrogen bases located in DNA? How do they pair up? What happens in replication and where does it occur? When does it occur? What does semi-conservative replication mean? What are the 3 main stages of replication and what enzymes are involved? What are Okazaki fragments and why do the ...
DNA
... The bases pair up (A-T & G-C) forming the DOUBLE HELIX first described by Watson and Crick ...
... The bases pair up (A-T & G-C) forming the DOUBLE HELIX first described by Watson and Crick ...
Cancer - EurekAlert!
... In summary, our data are consistent with the interpretation that the variant forms of Pol beta found in tumors have a direct link to cancer. When the DNA of a cell is damaged, the damage is removed, leaving a single-stranded gap in the double helix. One function of Pol beta is to fill that gap by c ...
... In summary, our data are consistent with the interpretation that the variant forms of Pol beta found in tumors have a direct link to cancer. When the DNA of a cell is damaged, the damage is removed, leaving a single-stranded gap in the double helix. One function of Pol beta is to fill that gap by c ...
From DNA to Proteins Unit Crossword
... 9. - The bases of both DNA and RNA are almost always found as paired bases. In DNA Adenine pairs with Thymine and Guanine pairs with Cytosine. The pairing is the same in RNA except Uracil replaces Thymine 11. - (DNA) a molecule composed of a deoxyribose sugar, a phosphorus group and a nitrogen base. ...
... 9. - The bases of both DNA and RNA are almost always found as paired bases. In DNA Adenine pairs with Thymine and Guanine pairs with Cytosine. The pairing is the same in RNA except Uracil replaces Thymine 11. - (DNA) a molecule composed of a deoxyribose sugar, a phosphorus group and a nitrogen base. ...
Word Definition Synonym 1 DNA replication the
... an organism that always produces an offspring with the same form of a trait as the purebred parent trait a characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes allele the different forms of a gene Rosalind Franklin famous woman scientist who used x-rays to photograph DNA mo ...
... an organism that always produces an offspring with the same form of a trait as the purebred parent trait a characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes allele the different forms of a gene Rosalind Franklin famous woman scientist who used x-rays to photograph DNA mo ...
DNA webquest!!
... What is the name for the genetic material in living organisms? __________________________ What is the shape of DNA usually called? ___________________ What are the “rungs” of the ladder in DNA made up of? ________________________________ How are these rungs put together? ____________________________ ...
... What is the name for the genetic material in living organisms? __________________________ What is the shape of DNA usually called? ___________________ What are the “rungs” of the ladder in DNA made up of? ________________________________ How are these rungs put together? ____________________________ ...
No Slide Title
... • DNA sequence represents 'genotype' • expressed genes (ie, mRNA and protein) represent 'phenotype' • generally analysis of DNA is easier than RNA or protein ...
... • DNA sequence represents 'genotype' • expressed genes (ie, mRNA and protein) represent 'phenotype' • generally analysis of DNA is easier than RNA or protein ...
Chapter 16 notes
... • Radioactively labeled T2 with 35S mixed with bacteria, agitated in blender to separate outer ...
... • Radioactively labeled T2 with 35S mixed with bacteria, agitated in blender to separate outer ...
Life Science Vocabulary.xlsx
... an organism that always produces an offspring with the same form of a trait as the purebred parent trait a characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes allele the different forms of a gene Rosalind Franklin famous woman scientist who used x-rays to photograph DNA mo ...
... an organism that always produces an offspring with the same form of a trait as the purebred parent trait a characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes allele the different forms of a gene Rosalind Franklin famous woman scientist who used x-rays to photograph DNA mo ...
NOTES: CH 16 part 1
... *in every species he studied, there was a regularity in base ratios where: the # of A residues equaled the # of T residues, and the # of G equaled the # of C ...
... *in every species he studied, there was a regularity in base ratios where: the # of A residues equaled the # of T residues, and the # of G equaled the # of C ...
DNA Discovery and Structure
... *in every species he studied, there was a regularity in base ratios where: the # of A residues equaled the # of T residues, and the # of G equaled the # of C ...
... *in every species he studied, there was a regularity in base ratios where: the # of A residues equaled the # of T residues, and the # of G equaled the # of C ...
DNA - The Double Helix
... DNA - The Double Helix Recallthat the nucleus is a small spherical, dense body in a cell. lt is often called the "control center" because it controls allthe activities of the cell including cell reproduction, and heredity. How does it do this? The nucleus controls these activities by the chromosomes ...
... DNA - The Double Helix Recallthat the nucleus is a small spherical, dense body in a cell. lt is often called the "control center" because it controls allthe activities of the cell including cell reproduction, and heredity. How does it do this? The nucleus controls these activities by the chromosomes ...
timeline ppt
... Who were they (full names)? Where were they from? When did they do their work? What were these scientists investigating? What is a bacteriophage? What is a radioactive isotope? Describe how these scientists labeled DNA and proteins to determine which was the molecule of heredity. What did these scie ...
... Who were they (full names)? Where were they from? When did they do their work? What were these scientists investigating? What is a bacteriophage? What is a radioactive isotope? Describe how these scientists labeled DNA and proteins to determine which was the molecule of heredity. What did these scie ...
Name
... d. each new double helix consists of 1 old & 1 new strand. 12. In E. coli the error rate of DNA replication is approximately a. 1 per 1,000 nucleotides. b. 1 per 1,000,000 nucleotides. c. 1 per 1,000,000,000 nucleotides. d. 1 per 1,000,000,000,000 nucleotides. 13. Eukaryotic replication bubbles open ...
... d. each new double helix consists of 1 old & 1 new strand. 12. In E. coli the error rate of DNA replication is approximately a. 1 per 1,000 nucleotides. b. 1 per 1,000,000 nucleotides. c. 1 per 1,000,000,000 nucleotides. d. 1 per 1,000,000,000,000 nucleotides. 13. Eukaryotic replication bubbles open ...
DNA polymerase

The DNA polymerases are enzymes that create DNA molecules by assembling nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA. These enzymes are essential to DNA replication and usually work in pairs to create two identical DNA strands from a single original DNA molecule. During this process, DNA polymerase “reads” the existing DNA strands to create two new strands that match the existing ones.Every time a cell divides, DNA polymerase is required to help duplicate the cell’s DNA, so that a copy of the original DNA molecule can be passed to each of the daughter cells. In this way, genetic information is transmitted from generation to generation.Before replication can take place, an enzyme called helicase unwinds the DNA molecule from its tightly woven form. This opens up or “unzips” the double-stranded DNA to give two single strands of DNA that can be used as templates for replication.