Cells - Tuckahoe Common School District
... • Mitosis = cell division that results in two daughter cells that are genetically identical to parent. • Meiosis = cell division that results in 4 daughter cells, each having ½ the chromosomes of the parent. • Asexual reproduction = process where a new individual organism is created from only one pa ...
... • Mitosis = cell division that results in two daughter cells that are genetically identical to parent. • Meiosis = cell division that results in 4 daughter cells, each having ½ the chromosomes of the parent. • Asexual reproduction = process where a new individual organism is created from only one pa ...
Objectives For Chapter 25
... nurtures developing individuals, and gives birth. Humans usually have one child per birth, but multiple births, such as those of twins or triplets, are possible. Human reproduction can be affected by cancer, infertility, and disease. ...
... nurtures developing individuals, and gives birth. Humans usually have one child per birth, but multiple births, such as those of twins or triplets, are possible. Human reproduction can be affected by cancer, infertility, and disease. ...
Document
... 1. A collection of 2 or more tissues that work together to perform a function is called ______________. 2. A person has about 200 different kinds of cells; each specialized to do a particular job. How could you explain the organization levels of this person? 3. Arrange in order from least to most co ...
... 1. A collection of 2 or more tissues that work together to perform a function is called ______________. 2. A person has about 200 different kinds of cells; each specialized to do a particular job. How could you explain the organization levels of this person? 3. Arrange in order from least to most co ...
here - The University of Sydney
... medicinal chemistry, biochemistry and molecular biology; and applies chemical biology approaches to validating therapeutic targets, and elucidating the biological pathways that drive disease. Dr Lessene trained as an organic chemist, completing his PhD at the University of Bordeaux, before undertaki ...
... medicinal chemistry, biochemistry and molecular biology; and applies chemical biology approaches to validating therapeutic targets, and elucidating the biological pathways that drive disease. Dr Lessene trained as an organic chemist, completing his PhD at the University of Bordeaux, before undertaki ...
Intro to Biology
... 3. Cell = the smallest unit of any living thing 4. Cell Theory = Every living thing is made of one or more cells, cells carry out the functions needed to support life, cells can only come from other living cells AND because you are made of cells…duh. 5. 2 types of organisms: unicellular & multicellu ...
... 3. Cell = the smallest unit of any living thing 4. Cell Theory = Every living thing is made of one or more cells, cells carry out the functions needed to support life, cells can only come from other living cells AND because you are made of cells…duh. 5. 2 types of organisms: unicellular & multicellu ...
Asexual and Sexual Reproduction Study Guide
... ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION: OFFSPRING EXACT COPY OF PARENT 8) Describe meiosis: Chromosome copied cell divides much like mitosis, but then divides again without making another copy resulting in 4 daughter cells with ½ the chromosomes of the parent cells. These cells become sex cells and are used in sexual ...
... ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION: OFFSPRING EXACT COPY OF PARENT 8) Describe meiosis: Chromosome copied cell divides much like mitosis, but then divides again without making another copy resulting in 4 daughter cells with ½ the chromosomes of the parent cells. These cells become sex cells and are used in sexual ...
• B2.1.1 Cells and cell structure • B2.1.2 Dissolved substances No
... Adult bone marrow stem cells can also be used umbilical cords and bone marrow. but can’t be made into as many different things but you can give permission to have them taken the operation can be painful! ...
... Adult bone marrow stem cells can also be used umbilical cords and bone marrow. but can’t be made into as many different things but you can give permission to have them taken the operation can be painful! ...
Human Body Systems and Single Cell vs. Multicellular
... ii. Bacteria = decomposer= breaks down decayed/dead material iii. Paramecium=consumer=cilia (little hairs) sweep in food to eat iv. Algae = producer=makes its own food through photosynthesis v. Amoeba = consumer=eats other living organisms (surrounds food as it traps & eats it) 5. Multicellular Orga ...
... ii. Bacteria = decomposer= breaks down decayed/dead material iii. Paramecium=consumer=cilia (little hairs) sweep in food to eat iv. Algae = producer=makes its own food through photosynthesis v. Amoeba = consumer=eats other living organisms (surrounds food as it traps & eats it) 5. Multicellular Orga ...
Curriculum information for Biological sciences and Biology
... Australian curriculum biological sciences and biology – lessons for Years 7 and 10 - 12 Where else would you explore the diversity of plant life, but at the botanic gardens? Your students will create and use dichotomous keys to classify the plants and animals living in the gardens, travel back throu ...
... Australian curriculum biological sciences and biology – lessons for Years 7 and 10 - 12 Where else would you explore the diversity of plant life, but at the botanic gardens? Your students will create and use dichotomous keys to classify the plants and animals living in the gardens, travel back throu ...
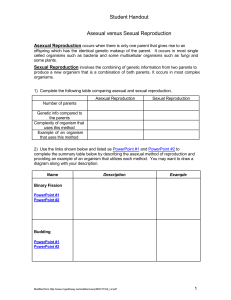
Student Handout Asexual versus Sexual Reproduction
... The ability of plants to asexually reproduce comes from a group of unspecialized cells in the stem and roots called meristem. Meristem cells will at certain points become specialized and turn into root, leaf, and stem cells. The meristems are also the cells that are used when the plant has been inju ...
... The ability of plants to asexually reproduce comes from a group of unspecialized cells in the stem and roots called meristem. Meristem cells will at certain points become specialized and turn into root, leaf, and stem cells. The meristems are also the cells that are used when the plant has been inju ...
Immunology - Bosna Sema
... contacts with them and this triggers phagocyte to engulf. It will wrap around the bacteria. Once time when bacteria find themselves inside phagocyte cells…there are some organelles that we call lysosomes. This little package will merge with bacteria and will dups. his contents into this pathogen and ...
... contacts with them and this triggers phagocyte to engulf. It will wrap around the bacteria. Once time when bacteria find themselves inside phagocyte cells…there are some organelles that we call lysosomes. This little package will merge with bacteria and will dups. his contents into this pathogen and ...
What Makes Something Alive?
... Organisms can be: Unicellular – 1 cell Multicellular – many cells Living things are highly organized: Cells Tissue Organ Organ system Organism ...
... Organisms can be: Unicellular – 1 cell Multicellular – many cells Living things are highly organized: Cells Tissue Organ Organ system Organism ...
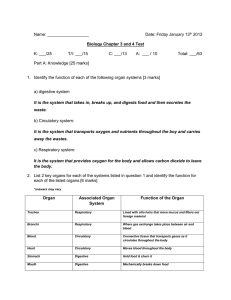
Name: Date: Friday January 13th 2012 Biology Chapter 3 and 4 Test
... -in normal heart, blood that is low in oxygen returns from body to the right filling chamber. It passes a valve into the right pumping chamber, and then travels out to lungs to receive oxygen. The blood then travels to the left filling chamber, across a valve to the left pumping chamber, and out to ...
... -in normal heart, blood that is low in oxygen returns from body to the right filling chamber. It passes a valve into the right pumping chamber, and then travels out to lungs to receive oxygen. The blood then travels to the left filling chamber, across a valve to the left pumping chamber, and out to ...
Animal Development
... Sea Urchin Gastrulation Begins at the vegetal pole where individual cells enter the blastocoel as mesenchyme cells Rest of cells buckle in to form the ...
... Sea Urchin Gastrulation Begins at the vegetal pole where individual cells enter the blastocoel as mesenchyme cells Rest of cells buckle in to form the ...
Lesson 3.3 – Passive and Active Transport
... (and their building blocks) are too large to cross it easily if at all ...
... (and their building blocks) are too large to cross it easily if at all ...
cell differentiation
... Between the upper and lower surface of the leaf is the MESOPHYLL TISSUE (mesomeans middle). Mesophyll tissue consists of PALISADE TISSUE CELLS (perform most of the photosynthesis in the leaf – they are arranged in lines that resemble long poles – the top of these cells are arranged to meet the Sun’s ...
... Between the upper and lower surface of the leaf is the MESOPHYLL TISSUE (mesomeans middle). Mesophyll tissue consists of PALISADE TISSUE CELLS (perform most of the photosynthesis in the leaf – they are arranged in lines that resemble long poles – the top of these cells are arranged to meet the Sun’s ...
TISSUES 1) DEFINITION: A group of cells that are similar in structure
... 1) DEFINITION: A group of cells that are similar in structure and work together to achieve a specific function is called a tissue. 2) IMPORTANCE IN MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS a) Multicellular organisms are complex. Thus, they show division of labour. b) A tissue is arranged and designed to give the hig ...
... 1) DEFINITION: A group of cells that are similar in structure and work together to achieve a specific function is called a tissue. 2) IMPORTANCE IN MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS a) Multicellular organisms are complex. Thus, they show division of labour. b) A tissue is arranged and designed to give the hig ...
chapter28_Sections 1
... through extracellular fluid is limited • Vertebrates developed a circulatory system to transport substances ...
... through extracellular fluid is limited • Vertebrates developed a circulatory system to transport substances ...
Cells The cell theory: All living things are made up of cells. Cells are
... accomplish similar functions, and are very diverse. For instance, there are over 200 types of cells in the human body that vary greatly in size, shape, and function. PROKARIOTIC: The simplest types of cells were most likely the first type of cells that formed on Earth. These are called prokaryotic c ...
... accomplish similar functions, and are very diverse. For instance, there are over 200 types of cells in the human body that vary greatly in size, shape, and function. PROKARIOTIC: The simplest types of cells were most likely the first type of cells that formed on Earth. These are called prokaryotic c ...
1. - OHIO SI
... reproduce, increase in number or frequency, and therefore, are able to transmit and perpetuate their essential genotypic qualities to succeeding generations. 7. Natural forces that promote the reproductive success of some individuals more than others are called ___________________ __________________ ...
... reproduce, increase in number or frequency, and therefore, are able to transmit and perpetuate their essential genotypic qualities to succeeding generations. 7. Natural forces that promote the reproductive success of some individuals more than others are called ___________________ __________________ ...
Unit 2 Review Answers
... 11. Figure 3 (p. 154 of the Student Text) shows conjugation, a sexual form of reproduction. Genetic information is exchanged; new organisms are genetically different from their parents. In binary fission, the usual form of reproduction in protists, one mother cell produces two genetically identical ...
... 11. Figure 3 (p. 154 of the Student Text) shows conjugation, a sexual form of reproduction. Genetic information is exchanged; new organisms are genetically different from their parents. In binary fission, the usual form of reproduction in protists, one mother cell produces two genetically identical ...
Asexual Reproduction Notes Asexual Reproduction • Reproduction
... A form of Asexual Reproduction in which a new organism grows by mitosis and cell division on the body of its parent Occurs in Hydra ...
... A form of Asexual Reproduction in which a new organism grows by mitosis and cell division on the body of its parent Occurs in Hydra ...
Homeostasis
... surrounding environment Perform chemical reactions that provide energy for the cell Synthesize cellular components Sense and respond to changes in surrounding environment (receptors) Reproduce (divide) Cell physiology, biochemistry and molecular biology allows us to further assess function of subcel ...
... surrounding environment Perform chemical reactions that provide energy for the cell Synthesize cellular components Sense and respond to changes in surrounding environment (receptors) Reproduce (divide) Cell physiology, biochemistry and molecular biology allows us to further assess function of subcel ...
LESSON 1. CELLS & TISSUES Lesson Aim
... or Amoeba). In an amoeba all the vital processes of the animal take place inside a single cell. Cells are capable of digesting food, growing, respiring, excreting, secreting, reproducing and responding to stimuli. All these things happen in a single-celled animal. At the other end of the scale, ther ...
... or Amoeba). In an amoeba all the vital processes of the animal take place inside a single cell. Cells are capable of digesting food, growing, respiring, excreting, secreting, reproducing and responding to stimuli. All these things happen in a single-celled animal. At the other end of the scale, ther ...
BIOLOGY20SOL20REVIEW20SHEET2020131
... 47. What is a food chain and a food web? Know how to read one. What happens to the population #, energy, and biomass as you move through a food chain? Which level has the highest # and which has the lowest #? 48. Define consumer, producer, carnivore, omnivore, herbivore, heterotroph, and autotroph. ...
... 47. What is a food chain and a food web? Know how to read one. What happens to the population #, energy, and biomass as you move through a food chain? Which level has the highest # and which has the lowest #? 48. Define consumer, producer, carnivore, omnivore, herbivore, heterotroph, and autotroph. ...
Developmental biology

Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop, and is synonymous with ontogeny. In animals most development occurs in embryonic life, but it is also found in regeneration, asexual reproduction and metamorphosis, and in the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. In plants, development occurs in embryos, during vegetative reproduction, and in the normal outgrowth of roots, shoots and flowers.Practical outcomes from the study of animal developmental biology have included in vitro fertilization, now widely used in fertility treatment, the understanding of risks from substances that can damage the fetus (teratogens), and the creation of various animal models for human disease which are useful in research. Developmental Biology has also help to generate modern stem cell biology which promises a number of important practical benefits for human health.Many of the processes of development are now well understood, and some major textbooks of the subject are