* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Body Systems and Single Cell vs. Multicellular
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Acquired characteristic wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
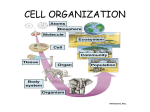
Types of Organisms/Human Body Systems Study Guide 5th Grade 1. Life Processes: basic life functions that need to be performed for all organisms to stay alive a. Require Nutrition- Getting Energy By: i. Producing- making its own food (algae/plants) ii. Consuming- eating another living thing (amoeba, horse) iii. Decomposing –breaking down dead material (Bacteria, mushroom) b. Obtaining Air for Respiration (some organisms use oxygen, others use carbon dioxide or other gases) c. Movement – by the action of muscles in animals, slow growth movements in plants, wiggling flagella or cilia in single cell organisms d. Reproducing- making more of its kind/offspring e. Grow and develop- increase in size and mass, using materials from their food f. Getting Rid of Waste Material –called excretion 2. Cell- the smallest unit of life, microscopic (only seen with a microscope, very tiny) 3. Organism: any living thing a. All Living Things are grouped in 2 Categories based on the NUMBER and Type of Cells i. Unicellular/Single Cell/Complete Organism ii. Multicellular 4. Unicellular/Single Cell Organism: a complete organism made of only 1 cell that controls all of the living thing’s life processes including reproducing and obtaining energy. a. survives on its own without other cells. b. Examples: i. Euglena= producer=makes its own food ii. Bacteria = decomposer= breaks down decayed/dead material iii. Paramecium=consumer=cilia (little hairs) sweep in food to eat iv. Algae = producer=makes its own food through photosynthesis v. Amoeba = consumer=eats other living organisms (surrounds food as it traps & eats it) 5. Multicellular Organism: an organism with more than 1 cell that work together to carry out life processes, multicellular organisms are more complex (have many parts) a. Transport System: a system that moves nutrients, gases, or substances to another place in an organism, i. to transport means to travel from one place to another b. Most multicellular organisms need transport systems because they are not able to exchange gases (carbon dioxide/oxygen) with the outside environment. c. Specialized Cells: Cells that perform a “special” job and cannot survive on their own i. Blood cells= blood cells do not stay alive outside your body ii. Nerve cells iii. Skin cells= skin cells die as they flake off of your body 6. Tissue: a group of specialized cells working together in a multicellular organism 7. Organ: a group of tissues working together in a multicellular organism 8. Body System: a group of organs working together in a multicellular organism to perform a function (job or task) 9. Nervous System: Function: sends electrical signals (messages) to all other body systems i. Parts/Organs 1. Brain= control center 2. spinal cord=like a highway that messages travel to/from your brain to the rest of your body 3. nerves=receive or send messages back to your brain b. Interacts (works with): all other body systems to control them including sending messages to your heart to beat involuntarily, without you telling it (circulatory system) and voluntarily move muscles like your arm to raise your hand (muscular system) 10. Digestive System: a. Function: processes (breaks down) foods into a useable source of energy i. Parts/Organs 1. mouth 2. esophagus= tube running from your mouth to your stomach 3. stomach=organ that uses acids to break down food into nutrients 4. small intestine 5. large intestine =nutrients are absorbed into your bloodstream b. Interacts (works with): circulatory/cardiovascular system to transport or move nutrients through your blood to all other parts of your body 11. Skeletal System: a. Function: protects organs in the other body systems, gives your body structure/shape/support to stand erect, produces or makes red blood cells i. Parts/Organs 1. 206 bones in adult human a. Skull= protects brain b. Teeth= used to break food into smaller pieces c. rib cage= protects heart (circulatory), lungs (respiratory) b. Interacts (works with): muscular system to help body move because muscle is attached to the bones, protects organs in other body systems such as the spine bones protect your spinal cord (nervous system) 12. Muscular System: a. Function: facilitates or helps with movement i. Parts/Organs 1. muscles b. Interacts (works with): skeletal system to help move (MUSCLES CONTRACT AND PULL ON BONE IT IS CONNECTED TO, TO MAKE IT MOVE), heart (is the strongest muscle) in your circulatory system , cardiovascular system delivers oxygen for muscle energy. 13. Circulatory/Cardiovascular System: (CARDIO MEANS HEART, VASCULAR MEANING VESSELS) a. Function/Task: transports or moves (nutrients/useable energy) and oxygen to cells throughout your body by your blood in a circle. Also, transports carbon dioxide (waste product/materials) back to your lungs i. Parts/Organs 1. heart (a muscle that pumps blood and connects to the lungs to get oxygen ) 2. blood 3. vessels (veins and arteries) b. Interacts (works with or combines with): respiratory system to get oxygen and then transports carbon dioxide back to the lungs via the blood, distributes or carries nutrients through the blood after the digestive system breaks down the food into nutrients, the nervous system tells the heart (muscle) to pump the blood through the body. Skeletal system produces red blood cells and the circulatory system transports these cells where they need to go in the blood stream. 14. Respiratory System: a. Function: To BREATH -supplies or provides oxygen (gas from the environment) to cells and releases/gets rid of carbon dioxide as a waste product puts it back into the environment. This results in an exchange of gases outside of the human body. i. Parts/Organs 1. mouth 2. nose 3. trachea= tube from mouth and nose to the lungs (also called wind pipe) 4. lungs b. Interacts (works with): closely with the circulatory (cardiovascular) system to move oxygen to the cells through the blood stream and gets rid of carbon dioxide by releasing it through the lungs up to through the trachea and then to the mouth or nose to the outside environment