DNA
... • Made of fatty acids and glycerol • Function- energy storage and insulation • Tests: brown paper test , potato chips on a napkin will leave a greasey residue • Examples: fats and steroids Example: Bears store fat to hibernate ...
... • Made of fatty acids and glycerol • Function- energy storage and insulation • Tests: brown paper test , potato chips on a napkin will leave a greasey residue • Examples: fats and steroids Example: Bears store fat to hibernate ...
Fertilization and Development
... • As embryo grows, the cells begin to sort themselves into layers which give rise to various organs and organ systems • At specific times, each cell type begins to change in order to carry out its specific function ...
... • As embryo grows, the cells begin to sort themselves into layers which give rise to various organs and organ systems • At specific times, each cell type begins to change in order to carry out its specific function ...
6.2 workbook - Fetal Development
... Embryonic development takes place during the first eight weeks after fertilization. During this time, the embryo develops. Its cells divide constantly, and tissues and organs form. During the first week, the single fertilized cell, the zygote, develops into a mass of many cells. This mass of cells t ...
... Embryonic development takes place during the first eight weeks after fertilization. During this time, the embryo develops. Its cells divide constantly, and tissues and organs form. During the first week, the single fertilized cell, the zygote, develops into a mass of many cells. This mass of cells t ...
Biology Standards Checklist
... 2. Diversity of Life: a. Speciation and biological classification based on molecular evidence: Cladograms 2 . Diversity of Life: b. Variation of organisms within a species due to population genetics and gene frequency 2 . Diversity of Life: c. Four ways that populations evolve over time 1. Classific ...
... 2. Diversity of Life: a. Speciation and biological classification based on molecular evidence: Cladograms 2 . Diversity of Life: b. Variation of organisms within a species due to population genetics and gene frequency 2 . Diversity of Life: c. Four ways that populations evolve over time 1. Classific ...
Introduction to Animals
... Found in the embryo of all animals except sponges (have specialized ...
... Found in the embryo of all animals except sponges (have specialized ...
The Tiny Living World Around Us
... Think of cells as living bricks • Bricks are the basic unit that some buildings are made of, cells are the basic unit that living things are made of • A house (organism) gets bigger when more bricks (cells) are added to it • When a brick breaks (or a cell dies) it has to be replaced with a new bric ...
... Think of cells as living bricks • Bricks are the basic unit that some buildings are made of, cells are the basic unit that living things are made of • A house (organism) gets bigger when more bricks (cells) are added to it • When a brick breaks (or a cell dies) it has to be replaced with a new bric ...
AP Biology Unit 9 Plant Structure and Function
... 2. primary growth 3. apical meristem 4. internodes 5. auxins 6. gibberellins 7. gravitropisms 8. photoperiodism 9. ethylene 10.zone of maturation 11.phototropism 12.xylem 13.phloem ...
... 2. primary growth 3. apical meristem 4. internodes 5. auxins 6. gibberellins 7. gravitropisms 8. photoperiodism 9. ethylene 10.zone of maturation 11.phototropism 12.xylem 13.phloem ...
lesson-1-explore-page-217-inheritance-and-traits
... Inherited traits are part of an organism’s phenotype. The phenotype of a trait is how the trait appears, or is expressed. Phenotypes result from the interaction of an organism’s genes and its environment. Light, temperature, moisture, nutrients, and social factors are not constant, but these ...
... Inherited traits are part of an organism’s phenotype. The phenotype of a trait is how the trait appears, or is expressed. Phenotypes result from the interaction of an organism’s genes and its environment. Light, temperature, moisture, nutrients, and social factors are not constant, but these ...
Animal Tissue
... • These cells function in involuntary movements and/or autonomic responses (such as breathing, secretion, ejaculation, birth, and certain reflexes). • spindle shaped cells that form masses. These fibers are components of structures in the digestive system, reproductive tract, and blood vessels. ...
... • These cells function in involuntary movements and/or autonomic responses (such as breathing, secretion, ejaculation, birth, and certain reflexes). • spindle shaped cells that form masses. These fibers are components of structures in the digestive system, reproductive tract, and blood vessels. ...
Unit 3 Review Study Guide
... Background Information: There are many different types of cells in the human body. None of these cells function on their own well. These cells are part of the larger organism that is called – human. Cells work together to form tissues. There are four main types of tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tis ...
... Background Information: There are many different types of cells in the human body. None of these cells function on their own well. These cells are part of the larger organism that is called – human. Cells work together to form tissues. There are four main types of tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tis ...
Human Body Systems Review answers
... 1. Put the following in order starting with the smallest: organs, organisms, organ systems, cells, tissues ...
... 1. Put the following in order starting with the smallest: organs, organisms, organ systems, cells, tissues ...
• B2.1.1 Cells and cell structure • B2.1.2 Dissolved substances No
... Adult bone marrow stem cells can also be used umbilical cords and bone marrow. but can’t be made into as many different things but you can give permission to have them taken the operation can be painful! ...
... Adult bone marrow stem cells can also be used umbilical cords and bone marrow. but can’t be made into as many different things but you can give permission to have them taken the operation can be painful! ...
fly2
... After the activity of four different pathways, the D/V patterning of the ectoderm Is controlled by a conserved Ser/Thr receptor that is dependent on the gradient of its ligand dpp and dpp’s interactors ...
... After the activity of four different pathways, the D/V patterning of the ectoderm Is controlled by a conserved Ser/Thr receptor that is dependent on the gradient of its ligand dpp and dpp’s interactors ...
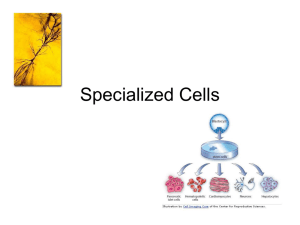
Specialized Cells
... blood cells. - made of specialized cells and fibers that stick to living cells. *exs. Bone, cartilage, and blood. ...
... blood cells. - made of specialized cells and fibers that stick to living cells. *exs. Bone, cartilage, and blood. ...
sexual reproduction - Mrs. Maxey`s Science
... All animal sex cells are unique. Humans, as we said, have 23 chromosomes in their sex cells. Goldfish cells have 92 chromosomes which means they have 46 chromosomes in their sex cells. We previously discussed that plants reproduce asexually, but can they also reproduce sexually? Yes, they can. This ...
... All animal sex cells are unique. Humans, as we said, have 23 chromosomes in their sex cells. Goldfish cells have 92 chromosomes which means they have 46 chromosomes in their sex cells. We previously discussed that plants reproduce asexually, but can they also reproduce sexually? Yes, they can. This ...
Pre-AP Bio 8-29
... traffic going in both directions across the cell membrane) • C. A cell must be large enough to contain DNA, Ribosomes, and some cytoplasm. They can only be so big because we have to be able to move enough “Food” into and “waste” out of a cell efficiently. If it is too large the cell becomes ineffici ...
... traffic going in both directions across the cell membrane) • C. A cell must be large enough to contain DNA, Ribosomes, and some cytoplasm. They can only be so big because we have to be able to move enough “Food” into and “waste” out of a cell efficiently. If it is too large the cell becomes ineffici ...
Unit 2 Biology Test Chapter 31.2
... easier for phagocytes to engulf and destroy. Other antibodies activate complement proteins that weaken the pathogen’s cell membrane. ...
... easier for phagocytes to engulf and destroy. Other antibodies activate complement proteins that weaken the pathogen’s cell membrane. ...
What is the function of a red blood cell? A.Transport of gases B
... Which body system provides a structural support for the body and its muscles? ...
... Which body system provides a structural support for the body and its muscles? ...
Mitosis r egulation2008print
... Cyclin & Cyclin-dependent kinases CDKs & cyclin drive cell from one phase to next in cell cycle proper regulation of cell cycle is so key to life that the genes for these regulatory proteins have been highly conserved through evolution the genes are basically the same in yeast, insects, plants ...
... Cyclin & Cyclin-dependent kinases CDKs & cyclin drive cell from one phase to next in cell cycle proper regulation of cell cycle is so key to life that the genes for these regulatory proteins have been highly conserved through evolution the genes are basically the same in yeast, insects, plants ...
Chapter 3 The Basic Structure of a Cell
... • Unicellular organisms are made of one cell only • The cells of multicellular organisms are specialized to perform different functions ...
... • Unicellular organisms are made of one cell only • The cells of multicellular organisms are specialized to perform different functions ...
Page 1 Edexcel 2011 Biology B2 Topic 1 The building blocks of
... synthesis, including transcription and translation: a the production of complementary mRNA strand in the nucleus b the attachment of the mRNA to the ribosome c the coding by triplets of bases (codons) in the mRNA for specific amino acids d the transfer of amino acids to the ribosome by tRNA e the li ...
... synthesis, including transcription and translation: a the production of complementary mRNA strand in the nucleus b the attachment of the mRNA to the ribosome c the coding by triplets of bases (codons) in the mRNA for specific amino acids d the transfer of amino acids to the ribosome by tRNA e the li ...
Platyhelminthes: The Flatworms
... a) Adult C. elegans have exactly 959 cells and the fate of every single cell has been mapped (1) E.g. there are 302 nerve cells, 172 digestive cells etc. (2) The development of each of these cells is entirely described (3) Can figure out exactly what happens when certain genes are turned on through ...
... a) Adult C. elegans have exactly 959 cells and the fate of every single cell has been mapped (1) E.g. there are 302 nerve cells, 172 digestive cells etc. (2) The development of each of these cells is entirely described (3) Can figure out exactly what happens when certain genes are turned on through ...
Test Review Sheet: Biology Final – 09 The Answer are under each
... To genetically engineer organism such as making insulin 35. How is the particular gene that is needed for research isolated from the rest of the DNA? Restriction enzymes cut the DNA at certain places 36. What is the DNA from two different sources? Recombinant DNA 37. What are some reasons for genet ...
... To genetically engineer organism such as making insulin 35. How is the particular gene that is needed for research isolated from the rest of the DNA? Restriction enzymes cut the DNA at certain places 36. What is the DNA from two different sources? Recombinant DNA 37. What are some reasons for genet ...
lossary
... Embryo: A plant in its earliest stages of development. In see bearing plants, the embryo is contained within the seed. Endangered: A plant or animal is said to be endangered when it is in danger of becoming extinct. Energy: The ability to do work, this has many different forms, eg. Heat, sound, ligh ...
... Embryo: A plant in its earliest stages of development. In see bearing plants, the embryo is contained within the seed. Endangered: A plant or animal is said to be endangered when it is in danger of becoming extinct. Energy: The ability to do work, this has many different forms, eg. Heat, sound, ligh ...
Developmental biology

Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop, and is synonymous with ontogeny. In animals most development occurs in embryonic life, but it is also found in regeneration, asexual reproduction and metamorphosis, and in the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. In plants, development occurs in embryos, during vegetative reproduction, and in the normal outgrowth of roots, shoots and flowers.Practical outcomes from the study of animal developmental biology have included in vitro fertilization, now widely used in fertility treatment, the understanding of risks from substances that can damage the fetus (teratogens), and the creation of various animal models for human disease which are useful in research. Developmental Biology has also help to generate modern stem cell biology which promises a number of important practical benefits for human health.Many of the processes of development are now well understood, and some major textbooks of the subject are