* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 3 Review Study Guide
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
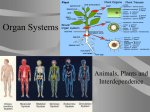
Name ____________________________________ Date __________________ Block _______ Unit 3 Review Study Guide Background Information: There are many different types of cells in the human body. None of these cells function on their own well. These cells are part of the larger organism that is called – human. Cells work together to form tissues. There are four main types of tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tissue, connective tissue and epithelial tissue. These tissues work together to form organs. Each organ belongs to an organ system. Organ systems are composed of two or more different organs that work together to provide a common function. There are eleven major organ systems in your body. The organ systems then work together to make the organism. These levels of organization from the smallest cell to the biggest organism represent a division of labor in your body. The work is divided up among the different parts so everything can get done. Levels of Organization: cell > tissue > organ > organ system > organism Directions: Label each of the following pictures or words with the appropriate level of organization. 1 Directions: Match the human body systems to the functions and key structures. Once sorted, place the information in the graphic organizer below. System Digestive Circulatory Nervous Function Diagram Major Organs Interactions-Working with other Systems 1. w/circulatory – absorb & deliver nutrients to the cells 2. w/muscular – control the contractions of many of the digestive organs to pass food along 3. w/nervous – hypothalamus maintains homeostasis by triggering appetite (stomach growling), digest. 1. w/respiratory – deliver O2 from lungs to cells and drop off CO2 from cells to lungs. 2. w/digestive – absorb and deliver digested nutrients to cells. 3. w/excretory – kidneys filter cellular waste out of blood for removal. 4. w/immune – transports WBCs throughout body to fight diseases. 5. w/nervous – brain controls heartbeat. 6. w/endocrine – transports hormones. Controls all other systems. Hypothalamus – maintains homeostasis by working with all systems. Excretory 1. w/circulatory – filters waste out of blood 2. w/lungs – removes excretory waste 3. w/integumentary – removes excretory waste 2 Respiratory 1. w/circulatory – takes in O2 for delivery to cells and removes CO2 brought from cells. 2. w/excretory – removes excretory waste 3. w/nervous – controls breathing 4. w/muscular – diaphragm controls breathing Skeletal 1. w/muscular – allow movement 2. w/circulatory – produce red blood cells 3. w/immune – produce white blood cells 4. w/circulatory and respiratory – protects its organs Muscular 1. w/skeletal – allow movement 2. w/digestive – allow organs to contract to push food through 3. w/respiratory – diaphragm controls breathing 4. w/circulatory – controls pumping of blood (heart) 5. w/nervous – controls all muscle contractions Endocrine 1. w/circulatory – transports hormones to target organs. 2. w/nervous – maintain homeostasis, hormone release 3. w/reproductive – controlled by hormones 4. w/skeletal – controls growth of bones. 3 Immune 1. w/circulatory – transports WBCs to fight invaders 2. w/lymphatic – has lots of WBCs to fight invaders, spleen filters bacteria/viruses out of blood 3. w/skeletal – WBCs made in bone marrow 4. w/integumentary – prevents invaders from getting in Integumentary 1. w/excretory – removes cellular waste 2. w/nervous – controls body temperature (sweating, goose bumps) 3. w/immune – prevents pathogens from entering Lymphatic 1. w/immune – holds lots of WBCs to fight pathogens 2. w/circulatory – to transport materials to and from cells 4 Correctly color code and identify the name for each part of the cell membrane. Letter Name/Color Letter Name/Color _____ Phospholipid bilayer (no color) _____ Peripheral protein (red) _____ Integral protein (pink) _____ Cholesterol (blue) _____ Fatty acid tails (orange) _____ Phosphate heads (yellow) 5 Directions: Complete the graphic organizer below regarding passive and active transport. 6 OSMOSIS Write the correct type of solution underneath (isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic) ________tonic means there is a GREATER concentration of solute molecules OUTSIDE the cell than inside. _______tonic means there is a LOWER concentration of solute molecules OUTSIDE the cell than inside. ______tonic means there is the SAME concentration of solute molecules outside the cell as inside. Complete the transport terms. Some of the letters have been filled in! 1. Active transport requires _E_______________ to move molecules across membranes. 2. _A_______________ is the molecule that provides the energy for active transport. 3. _D_______________ moves oxygen and carbon dioxide molecules from a high concentration to a low concentration across membranes. 4. The cell organelles that burns glucose and provides ATP for active transport are the _M________________. 5. Water moves across membranes by _O_______________. 6. A small membrane sac used to transport substances during exocytosis & endocytosis = _V_______________ 7. _P_______________ transport does NOT REQUIRE energy. 8. What kind of transport requires energy? A_______________ | 9. A cell placed in an _I_______________ solution neither swells or shrinks because the concentration of molecules outside the cell is the same as inside. 10. A solution in which there is a HIGHER concentration of molecules OUTSIDE the cell than inside = _H_______________ 7 11. A CONCENTRATION _G_______________ forms whenever there is a difference in concentration between one place and another. 12. A solution in which the concentration of molecules outside the cell is LOWER than inside = _H_______________ 13. When molecules move from high to low along a concentration gradient we say they are moving a. “_D_______________” the gradient. 14. _O_______________ pressure is caused by water inside a plant cell pushing against the cell wall. 15. The substance that is dissolved in liquid to make a solution = S_______________ 16. The liquid a substance is dissolved in to make a solution = S_______________ Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration Fill out the chart below: Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Reactants (all) Products (all) *Major Product* Organism Type (plant, animal, or both) Where in cell 8 Directions: Fill in the blanks that show the processes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. 9 Directions: Sort the cards to show the chemical formulas for photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Once sorted, place the formula in the spaces provided. Chemical formula for photosynthesis: _______________ + _______________ + _______________ ---- _______________ + _______________ Chemical formula for cellular respiration: _______________ + _______________ ---- _______________ + _______________ + _______________ 10 Directions: Fill in the boxes below on the process of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. 11