term 2 cumulative exam review sheet
... Central Concepts: There is a relationship between the organization of cells into tissues and the organization of tissues into organs. The structures and functions of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to perform its normal functions. ...
... Central Concepts: There is a relationship between the organization of cells into tissues and the organization of tissues into organs. The structures and functions of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to perform its normal functions. ...
Slide 1
... ATP, anaerobic (no O2 needed), if O2 is present followed by Kreb’s Cycle Kreb’s Cycle - occurs in matrix (inner cavity of mitochondria), aerobic (O2 needed), net gain 0 ATP Electron Transport Chain – occurs in cristae (mitochondria), aerobic (O2 needed), net gain 34 ATP ...
... ATP, anaerobic (no O2 needed), if O2 is present followed by Kreb’s Cycle Kreb’s Cycle - occurs in matrix (inner cavity of mitochondria), aerobic (O2 needed), net gain 0 ATP Electron Transport Chain – occurs in cristae (mitochondria), aerobic (O2 needed), net gain 34 ATP ...
Homeostasis
... proportional to the surface area over which diffusion can take place. Understand that large organisms have problems with diffusion Say how these problems of size can be overcome such as : a. the body may be flattened, thus reducing the distance between the two surfaces e.g. the leaves of plants b. i ...
... proportional to the surface area over which diffusion can take place. Understand that large organisms have problems with diffusion Say how these problems of size can be overcome such as : a. the body may be flattened, thus reducing the distance between the two surfaces e.g. the leaves of plants b. i ...
The Human Body - bakerbiologykingdoms
... them toward the body cells • Axon: single extension carries impulses away from the cell body toward muscles or glands. ...
... them toward the body cells • Axon: single extension carries impulses away from the cell body toward muscles or glands. ...
Document
... Looking at Table A, determine which type of milk, per serving, will theoretically yield a greater amount of ATP in the human body, and what is the reason for this? a. soymilk, because it contains no cholesterol ...
... Looking at Table A, determine which type of milk, per serving, will theoretically yield a greater amount of ATP in the human body, and what is the reason for this? a. soymilk, because it contains no cholesterol ...
Grade 11 College Biology Unit 4 Test
... 31. With the support of a diagram, explain OSMOSIS? The movement of water that does not require energy across a cell membrane from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration 32. What is CYTOKINESIS? The stage of the Cell Cycle following mitosis when two daughter cells are ...
... 31. With the support of a diagram, explain OSMOSIS? The movement of water that does not require energy across a cell membrane from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration 32. What is CYTOKINESIS? The stage of the Cell Cycle following mitosis when two daughter cells are ...
Cells
... Homologous Structures • Homologous Structures-structures that have different mature forms in different organisms, but develop from the same embryonic tissue ...
... Homologous Structures • Homologous Structures-structures that have different mature forms in different organisms, but develop from the same embryonic tissue ...
Human Body Systems Power Point
... • System: Give the name • Main Job: one sentence description of the job of the system • Organs: list main organs ...
... • System: Give the name • Main Job: one sentence description of the job of the system • Organs: list main organs ...
UNIT 2
... • Extracellular digestion: takes places outside the cells. Can be: • External digestion: takes place outside the body. Many insects • Internal digestion: takes place inside the digestive system. The transformation of food is both mechanical (food is broken down into smaller pieces) and chemical (foo ...
... • Extracellular digestion: takes places outside the cells. Can be: • External digestion: takes place outside the body. Many insects • Internal digestion: takes place inside the digestive system. The transformation of food is both mechanical (food is broken down into smaller pieces) and chemical (foo ...
Unit 6 Human Body & Organ Systems
... Passive immunity – due to the acquisition of antibodies from another organism in which active immunity has been stimulated (placenta or colostrum) Natural immunity – due to infection or from mother Artificial immunity - due to innoculation with vaccine ...
... Passive immunity – due to the acquisition of antibodies from another organism in which active immunity has been stimulated (placenta or colostrum) Natural immunity – due to infection or from mother Artificial immunity - due to innoculation with vaccine ...
STAAR Review Day Five Independent Practice 3. In humans, the
... a. Epithelial cells fight invading bacteria and viruses by entering them and destroying their DNA b. Epithelial cells provide oxygen to organ cells so that the organs can repair any damage they sustain c. Epithelial cells form a barrier between the external environment and the internal structures of ...
... a. Epithelial cells fight invading bacteria and viruses by entering them and destroying their DNA b. Epithelial cells provide oxygen to organ cells so that the organs can repair any damage they sustain c. Epithelial cells form a barrier between the external environment and the internal structures of ...
Why do we need a circulatory system?
... The same blood that run to your toes one minute, is re-circulated to your head the next ...
... The same blood that run to your toes one minute, is re-circulated to your head the next ...
The Cell in Action
... a layer of gelatin. At first, it is easy to see where the dye ends and the gelatin begins. But over time, the line between the two layers will blur. The tiny moving particles (which everything is made of) travel from where they are crowded to where they are less crowded. ...
... a layer of gelatin. At first, it is easy to see where the dye ends and the gelatin begins. But over time, the line between the two layers will blur. The tiny moving particles (which everything is made of) travel from where they are crowded to where they are less crowded. ...
6 Kingdoms of Life Part 2: Plants and Animals
... • Recall that all organisms reproduce either sexually or asexually – Sexual- there is a combining of genes from 2 parents but NOT always with egg and sperm (meiosis followed by fertilization) – Asexual- the offspring are reproduced by copying the DNA of one parent (binary fission or budding) ...
... • Recall that all organisms reproduce either sexually or asexually – Sexual- there is a combining of genes from 2 parents but NOT always with egg and sperm (meiosis followed by fertilization) – Asexual- the offspring are reproduced by copying the DNA of one parent (binary fission or budding) ...
AP Biology Unit 10 Animal Structure and Function
... The major histocompatibility complex, or MHC, is the mechanism by which the immune system is able to differentiate between self and nonself cells. The MHC is a collection of glycoproteins that exists on the membranes of all body cells. The proteins of a single individual are unique, originating from ...
... The major histocompatibility complex, or MHC, is the mechanism by which the immune system is able to differentiate between self and nonself cells. The MHC is a collection of glycoproteins that exists on the membranes of all body cells. The proteins of a single individual are unique, originating from ...
Sexual Reproduction
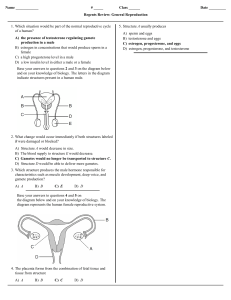
... the upper 1/3 o the oviduct. If the egg is not fertilized within 24 hours after ovulation, it deteriorates. If fertilization occurs, cleavage of the zygote begins in the oviduct, and six to ten days later the resulting embryo may be implanted in the uterine lining. At this stage of development, the ...
... the upper 1/3 o the oviduct. If the egg is not fertilized within 24 hours after ovulation, it deteriorates. If fertilization occurs, cleavage of the zygote begins in the oviduct, and six to ten days later the resulting embryo may be implanted in the uterine lining. At this stage of development, the ...
File
... Base your answers to questions 73 through 76 on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. All organisms need to reproduce for the continuation of their species. Discuss the process of reproduction in humans. 73. Identify one action by the mother that can influence the development of th ...
... Base your answers to questions 73 through 76 on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. All organisms need to reproduce for the continuation of their species. Discuss the process of reproduction in humans. 73. Identify one action by the mother that can influence the development of th ...
EOCT Review Sheet
... Ancestors of the koala lived on the ground, but modern koalas live in trees and eat eucalyptus leaves, which are poisonous to most other animals. The difference between the ancestor and modern koalas was caused by A the presence of homologous structures B the presence of vestigial organs C selective ...
... Ancestors of the koala lived on the ground, but modern koalas live in trees and eat eucalyptus leaves, which are poisonous to most other animals. The difference between the ancestor and modern koalas was caused by A the presence of homologous structures B the presence of vestigial organs C selective ...
Cells, tissues and organs
... In early development embryos are composed of stem cells. This allows the embryo to develop all the different parts of the body and the different cell types needed to form a fully functional body. Through embryonic and foetal development the number of stem cells steadily decreases until very few stem ...
... In early development embryos are composed of stem cells. This allows the embryo to develop all the different parts of the body and the different cell types needed to form a fully functional body. Through embryonic and foetal development the number of stem cells steadily decreases until very few stem ...
Cells and tissues
... • cells are basic units of life • are required for nutrition to the body, supply of oxygen and removal of waste • need to be able to reproduce, called mitosis • tissues are groups of similar cells with specialised function • types are epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous ...
... • cells are basic units of life • are required for nutrition to the body, supply of oxygen and removal of waste • need to be able to reproduce, called mitosis • tissues are groups of similar cells with specialised function • types are epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous ...
Human Body Systems
... Sperm produced in the testes are moved into the epididymis, where sperm mature & are stored. The sperm move into the vas deferens. The vas deferens merges with the urethra the tube that leads to the outside of the body through the penis. The glands lining the reproductive tract including the seminal ...
... Sperm produced in the testes are moved into the epididymis, where sperm mature & are stored. The sperm move into the vas deferens. The vas deferens merges with the urethra the tube that leads to the outside of the body through the penis. The glands lining the reproductive tract including the seminal ...
Biology SOL Review Packet
... D. Cellular Organelles: Word Bank: nucleus, mitochondria, vacuole, ribosomes, golgi body or apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, nucleolus, centriole, cell wall, cytoplasm, chloroplast, lysosomes, cell membrane 1. _____________________- command center of the cell; DNA in the form of chromosomes is her ...
... D. Cellular Organelles: Word Bank: nucleus, mitochondria, vacuole, ribosomes, golgi body or apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, nucleolus, centriole, cell wall, cytoplasm, chloroplast, lysosomes, cell membrane 1. _____________________- command center of the cell; DNA in the form of chromosomes is her ...
Grade 7 Course Description – Life Science UNIT 1 Cell
... Many organisms (for example yeast, algae) are single-celled, and many organisms (for example plants, fungi and animals) are made of millions of cells that work in coordination. 7.2.a.3. All cells come from other cells and they hold the genetic information needed for cell division and growth. When a ...
... Many organisms (for example yeast, algae) are single-celled, and many organisms (for example plants, fungi and animals) are made of millions of cells that work in coordination. 7.2.a.3. All cells come from other cells and they hold the genetic information needed for cell division and growth. When a ...
Document
... 27. In the female reproductive system, what is the function of the ovaries? _______________ _____________________________________________________________________ 28. What connects the embryo to the placenta, what does it contain, and what is its function? ____________________________________________ ...
... 27. In the female reproductive system, what is the function of the ovaries? _______________ _____________________________________________________________________ 28. What connects the embryo to the placenta, what does it contain, and what is its function? ____________________________________________ ...
Developmental biology

Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop, and is synonymous with ontogeny. In animals most development occurs in embryonic life, but it is also found in regeneration, asexual reproduction and metamorphosis, and in the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. In plants, development occurs in embryos, during vegetative reproduction, and in the normal outgrowth of roots, shoots and flowers.Practical outcomes from the study of animal developmental biology have included in vitro fertilization, now widely used in fertility treatment, the understanding of risks from substances that can damage the fetus (teratogens), and the creation of various animal models for human disease which are useful in research. Developmental Biology has also help to generate modern stem cell biology which promises a number of important practical benefits for human health.Many of the processes of development are now well understood, and some major textbooks of the subject are