B1 Glossary - physicsinfo.co.uk
... carcinogen cataracts cell membrane cell wall central nervous system (CNS) characteristics chemical defence ...
... carcinogen cataracts cell membrane cell wall central nervous system (CNS) characteristics chemical defence ...
1-2 Notes
... • All living things are mainly water, but with other chemicals too, such as DNA • All living things need energy, some make their own, others must eat things • All organisms grow and develop, some more complex than others • All living things reproduce, some sexually, some asexually ...
... • All living things are mainly water, but with other chemicals too, such as DNA • All living things need energy, some make their own, others must eat things • All organisms grow and develop, some more complex than others • All living things reproduce, some sexually, some asexually ...
Science4CE Biology notes
... The skeleton performs 3 major functions: • Support - it is the frame that body organs hang off • Protection - parts of the skeleton protect vital organs e.g. skull protects the brain, ribs protect heart & lungs • Movement - the skeleton is attached to muscles via tendons which pull on the bones to m ...
... The skeleton performs 3 major functions: • Support - it is the frame that body organs hang off • Protection - parts of the skeleton protect vital organs e.g. skull protects the brain, ribs protect heart & lungs • Movement - the skeleton is attached to muscles via tendons which pull on the bones to m ...
EOCT REVIEW
... SB5 Students will evaluate the role of natural selection in the development of the theory of evolution. a. Trace the history of the theory. b. Explain the history of life in terms of biodiversity, ancestry, and the rates of evolution. c. Explain how fossil and biochemical evidence support the theory ...
... SB5 Students will evaluate the role of natural selection in the development of the theory of evolution. a. Trace the history of the theory. b. Explain the history of life in terms of biodiversity, ancestry, and the rates of evolution. c. Explain how fossil and biochemical evidence support the theory ...
Evidence for Evolution
... Molds and castings form when the hard shell or exoskeleton of an organism is buried in sediment. • The sediment hardens around the body, then the body dissolves or decomposes, leaving a void or mold. • The mold can fill with minerals to form a cast in the shape of the mold. ...
... Molds and castings form when the hard shell or exoskeleton of an organism is buried in sediment. • The sediment hardens around the body, then the body dissolves or decomposes, leaving a void or mold. • The mold can fill with minerals to form a cast in the shape of the mold. ...
1 IMMUNE SYSTEM WORKSHEET KEY CONCEPT: The immune
... 6. ____ Eosinophils ____ are white blood cells that help rid the body of parasites by injecting them with toxic substances. 7. __ Antibodies ____ help fight infection by binding to a pathogen’s membrane proteins, clumping pathogen cells so they can be engulfed by phagocytes, or activating proteins t ...
... 6. ____ Eosinophils ____ are white blood cells that help rid the body of parasites by injecting them with toxic substances. 7. __ Antibodies ____ help fight infection by binding to a pathogen’s membrane proteins, clumping pathogen cells so they can be engulfed by phagocytes, or activating proteins t ...
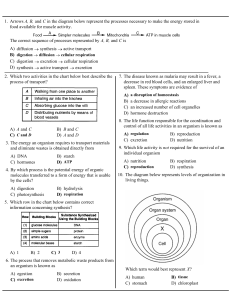
1. Arrows A, B, and C in the diagram below represent the processes
... 26. Base your answer to the following question on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. A solution of an enzyme normally found in the human body was added to a flask containing a solution of proteins in distilled water, and then the flask was stoppered. This mixture was then mainta ...
... 26. Base your answer to the following question on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. A solution of an enzyme normally found in the human body was added to a flask containing a solution of proteins in distilled water, and then the flask was stoppered. This mixture was then mainta ...
Word Roots - Jennifer`s e
... auto- = self; troph- = food, nourishment (autotroph: an organism that obtains organic food molecules without eating other organisms) aux- = grow, enlarge (auxins: a class of plant hormones, including indoleacetic acid, having a variety of effects, such as phototropic response through the stimulation ...
... auto- = self; troph- = food, nourishment (autotroph: an organism that obtains organic food molecules without eating other organisms) aux- = grow, enlarge (auxins: a class of plant hormones, including indoleacetic acid, having a variety of effects, such as phototropic response through the stimulation ...
CRT Review Term 2 - Science Page of Mystery
... A. It contains sweat and oil glands B. The hair follicles contain rapidly dividing cells C. The skin contains a rich supply of blood vessels D. It is composed of several cell layers 46) Which part of grass plants absorb most of the minerals needed by this plant? A. flowers B. leaves C. stems D. root ...
... A. It contains sweat and oil glands B. The hair follicles contain rapidly dividing cells C. The skin contains a rich supply of blood vessels D. It is composed of several cell layers 46) Which part of grass plants absorb most of the minerals needed by this plant? A. flowers B. leaves C. stems D. root ...
Program
... Yoram Groner, Weizmann Institute of Science, Israel Molecular insights into cell type specification during Dorsal Root Ganglia (DRG) development ...
... Yoram Groner, Weizmann Institute of Science, Israel Molecular insights into cell type specification during Dorsal Root Ganglia (DRG) development ...
Body Systems - Mrs Physics
... Respiratory System Includes Nose, mouth, trachea (windpipe), lungs ...
... Respiratory System Includes Nose, mouth, trachea (windpipe), lungs ...
Bell Work: 4/8/13
... circulatory system? A)delivering oxygen and nutrients to cells B)carrying carbon dioxide away from cells C)removing solid waste from the body D)pumping blood throughout the body ...
... circulatory system? A)delivering oxygen and nutrients to cells B)carrying carbon dioxide away from cells C)removing solid waste from the body D)pumping blood throughout the body ...
Exam review F14
... 12. Name and describe the stages of mitosis. 13. Name and describe the stages of meiosis. 14. What is non-disjunction and describe a disorder caused by it. 15. In cats striped fur is recessive to plain fur. If a striped cat is mated with a heterozygous cat, give the genotypic and phenotypic percent ...
... 12. Name and describe the stages of mitosis. 13. Name and describe the stages of meiosis. 14. What is non-disjunction and describe a disorder caused by it. 15. In cats striped fur is recessive to plain fur. If a striped cat is mated with a heterozygous cat, give the genotypic and phenotypic percent ...
Developmental Biology
... Textbook: “Developmental Biology” By Scott Gilbert, 10th Edition, Sinauer Associates, Inc Course description (Undergraduates enrolled in Cell 416/Graduate students enrolled in Cell 616): Vertebrate animal development is discussed in a lecture style, with focus on initiation and construction of an or ...
... Textbook: “Developmental Biology” By Scott Gilbert, 10th Edition, Sinauer Associates, Inc Course description (Undergraduates enrolled in Cell 416/Graduate students enrolled in Cell 616): Vertebrate animal development is discussed in a lecture style, with focus on initiation and construction of an or ...
4 - Bulldogbiology.com
... o Fertilization- the second stage, starts when a sperm’s plasma membrane fuses with an egg’s plasma membrane Fertilization is over when the sperm nucleus (haploid) and egg nucleus (haploid) fuse and form a zygote- (diploid; 2n) Fertilization- The process of a sperm joining an egg o A fertilized eg ...
... o Fertilization- the second stage, starts when a sperm’s plasma membrane fuses with an egg’s plasma membrane Fertilization is over when the sperm nucleus (haploid) and egg nucleus (haploid) fuse and form a zygote- (diploid; 2n) Fertilization- The process of a sperm joining an egg o A fertilized eg ...
Connective Tissues
... Stratified squamous epithelium – Thick – Cells divide in deeper layers, and newer cells push older ones farther outward where they flatten – Forms outer layer of the skin – As skin cells age, they accumulate a protein called keratin and then harden and die – Prevents water loss and blocks substance ...
... Stratified squamous epithelium – Thick – Cells divide in deeper layers, and newer cells push older ones farther outward where they flatten – Forms outer layer of the skin – As skin cells age, they accumulate a protein called keratin and then harden and die – Prevents water loss and blocks substance ...
cbse class – x science solutions
... The first step is the break – down of glucose, a six-carbon molecule, into a three-carbon molecule called pyruvate. This process takes place in the cytoplasm. Further, the pyruvate may be converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide. This process take place in yeast during fermentation. Since this proc ...
... The first step is the break – down of glucose, a six-carbon molecule, into a three-carbon molecule called pyruvate. This process takes place in the cytoplasm. Further, the pyruvate may be converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide. This process take place in yeast during fermentation. Since this proc ...
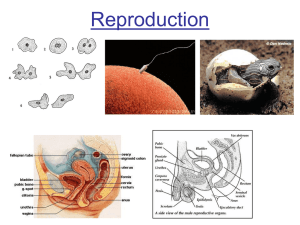
Ovary
... With in the next 2 weeks, the zygote will become an EMBRYO, and continue to divide The embryo implants itself into the uterine lining and GASTRULATES (hollows out) The embryo starts to form distinctive specialized layers, beginning the process of DIFFERENTIATION & GROWTH ...
... With in the next 2 weeks, the zygote will become an EMBRYO, and continue to divide The embryo implants itself into the uterine lining and GASTRULATES (hollows out) The embryo starts to form distinctive specialized layers, beginning the process of DIFFERENTIATION & GROWTH ...
AHSGE Biology Review
... 59. crossing over – exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes (chromosomes that code for the same things) 60. cross-pollination – transferring the pollen from one flower to a flower on a different plant 61. cystic fibrosis – genetic disorder that is inherited in a recessive disorde ...
... 59. crossing over – exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes (chromosomes that code for the same things) 60. cross-pollination – transferring the pollen from one flower to a flower on a different plant 61. cystic fibrosis – genetic disorder that is inherited in a recessive disorde ...
Respiratory System
... deficiency in premature infants Complicated by seepage of fibrin and other proteins from the capillaries into are spaces, forming a hyaline membrane ...
... deficiency in premature infants Complicated by seepage of fibrin and other proteins from the capillaries into are spaces, forming a hyaline membrane ...
The Human Body Quest: The Circulatory System
... CONTAINED IN CYTOPLASM OR PLASMA BACK TO THE LUNGS AND OUT OF THE BODY •T H E C I R C U L A T O R Y S Y S T E M H E L P S C L E A N S E T H E ...
... CONTAINED IN CYTOPLASM OR PLASMA BACK TO THE LUNGS AND OUT OF THE BODY •T H E C I R C U L A T O R Y S Y S T E M H E L P S C L E A N S E T H E ...
Biology Objective 3
... • Prey are the animals that are eaten as a food source for the . . . • Predator This is the hunter animal. The population of the predator must be less than the prey or they do not have enough food. ...
... • Prey are the animals that are eaten as a food source for the . . . • Predator This is the hunter animal. The population of the predator must be less than the prey or they do not have enough food. ...
Developmental Biology
... Textbook: “Developmental Biology” By Scott Gilbert, 9th Edition, 2010, Sinauer Associates, Inc Course description (Undergraduates enrolled in Cell 416/Graduate students enrolled in Cell 616): Vertebrate animal development is discussed in a lecture style, with focus on initiation and construction of ...
... Textbook: “Developmental Biology” By Scott Gilbert, 9th Edition, 2010, Sinauer Associates, Inc Course description (Undergraduates enrolled in Cell 416/Graduate students enrolled in Cell 616): Vertebrate animal development is discussed in a lecture style, with focus on initiation and construction of ...
Developmental biology

Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop, and is synonymous with ontogeny. In animals most development occurs in embryonic life, but it is also found in regeneration, asexual reproduction and metamorphosis, and in the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. In plants, development occurs in embryos, during vegetative reproduction, and in the normal outgrowth of roots, shoots and flowers.Practical outcomes from the study of animal developmental biology have included in vitro fertilization, now widely used in fertility treatment, the understanding of risks from substances that can damage the fetus (teratogens), and the creation of various animal models for human disease which are useful in research. Developmental Biology has also help to generate modern stem cell biology which promises a number of important practical benefits for human health.Many of the processes of development are now well understood, and some major textbooks of the subject are