* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Connective Tissues
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Nerve guidance conduit wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
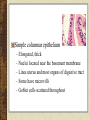
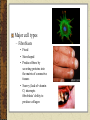
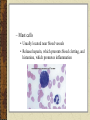
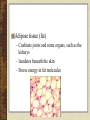
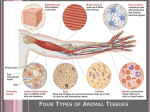
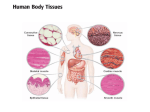
Tissues Chapter 5 Epithelial tissue Covers organs, forms the inner lining of body cavities, lines hollow organs Anchored to connective tissue by basement membrane Lacks blood vessels Cells readily divide; injuries heal quickly Simple squamous epithelium – Single layer of thin, flattened cells – Fit together like tiles – Nuclei are broad and thin – Site of diffusion – Line air sacs of lungs, walls of capillaries – Easily damaged Simple cuboidal epithelium – Single layer of cube shaped cells – Centrally located spherical nuclei – Covers ovaries, lines kidney tubules, ducts of glands – Functions in the kidneys in secretion and absorption – Functions in the glands in secretion of glandular products Simple columnar epithelium – – – – – Elongated, thick Nuclei located near the basement membrane Lines uterus and most organs of digestive tract Some have microvilli Goblet cells scattered throughout Pseudostratified columnar epithelium – Appear layered – Cell nuclei are at two or more levels in the row of aligned cells – Cilia – Lines passages of the respiratory system Stratified squamous epithelium – Thick – Cells divide in deeper layers, and newer cells push older ones farther outward where they flatten – Forms outer layer of the skin – As skin cells age, they accumulate a protein called keratin and then harden and die – Prevents water loss and blocks substances from entering – (not keratinzed) Lining of mouth, throat, vaginal, and anal canal Stratified cuboidal epithelium – – – – Two or three layers Form the lining of a lumen Provides protection Lines mammary glands, sweat glands, salivary glands, pancreas, developing ovarian follicles and seminiferous tubules Stratified columnar epithelium – – – – – Several layers Superficial cells are elongated Basal layers are cuboidal Male urethra and vas deferens Parts of the pharynx Transitional epithelium – Specialized to change in response to increased tension – Inner lining of urinary bladder, ureters, and part of the urethra Tissue Engineering Video Homework Review Exercises p. 111 #1-5 (omit i.) Write the questions and answers Connective Tissues Bind structures Provide support and protection Serve as frameworks Fill spaces Store fat Produce blood cells Protect against infections Help repair tissue damage Major cell types – Fibroblasts • Fixed • Star-shaped • Produce fibers by secreting proteins into the matrix of connective tissues • Scurvy (lack of vitamin C) interrupts fibroblasts’ ability to produce collagen – Macrophages • Originate as white blood cells • Carry on phagocytosis – Mast cells • Usually located near blood vessels • Release heparin, which prevents blood clotting, and histamine, which promotes inflammation Connective tissue fibers produced by fibroblasts – Collagenous • Great tensile strangth • Compose ligaments and tendons • White fibers – Elastic • Composed of elastin • Found in vocal cords • Yellow fibers – Reticular • Very thin collagenous fiers • Delicate support Loose connective tissue (areolar) – Composed of fibroblasts – Binds the skin to the underlying organs – Fills spaces between muscles Adipose tissue (fat) – Cushions joints and some organs, such as the kidneys – Insulates beneath the skin – Stores energy in fat molecules Dense connective tissue – Consists of thick collagenous fibers and network of elastic fibers – Very strong – Found in tendons, ligaments, white layer of eyeball, and deeper skin layer Cartilage – Provides support and protection – Chondrocytes occupy small chambers called lacunae – Three types • Hyaline (nose) • Elastic (ears) • Fibrocartilage (intervertebral disks) Bone – Hardness due to mineral salts and collagen – Supports and protects – Attachment for muscle – Contains red marrow (forms blood cells) – Osteocytes concentrically clustered around osteonic canal, form a cylinder-shaped unit called an osteon Blood – Transports – RBCs, WBCs, platelets, plasma Muscle Tissue Contractile muscle fibers lengthen and shorten Skeletal muscle – Attached to bone – Can control by conscious effort (voluntary) – Alternating light and dark cross-markings called striations – Each cell has many nuclei – Move the head, trunk, and limbs Smooth muscle tissue – – – – – Cells lack striations Shorter than skeletal muscle tissue Spindle-shaped Single, centrally located nucleus Makes up walls of hollow internal organs, such as the stomach, intestines, urinary bladder, uterus, and blood vessels – involuntary Cardiac muscle tissue – – – – Only in the heart Striated cells are joined end to end Cells touch each other an intercalated disk Controlled involuntarily Nervous Tissue Found in the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves Sense changes in their surroundings Includes neurons (nerve cells) and neuroglial cells Types of membranes 1. Serous – Line body cavities that lack openings to the outside – inner lining of thorax and abdomen, cover organs within cavity – Simple squamous epithelium, loose connective tissue – Secrete serous fluid, a lubricant 2. Mucous – Line cavities and tubes that open to the outside of the body – Oral and nasal cavities and the tubes of the digestive, respiratory, urinary, and reproductive systems – Epithelium, loose connective tissue – Secrete mucus 3. Synovial – Inner linings of joint cavities between the ends of bones – Dense connective tissue, loose connective tissue, adipose tissue – Secrete synovial fluid, lubricant 4. Cutaneous – skin http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/ap/holeessenti als/student/olc/chap05out.html