* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cbse class – x science solutions
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Living things in culture wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Carbohydrate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Mendelian inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
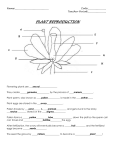
CBSE CLASS – X SCIENCE SOLUTIONS (31/1, 2, 3) Series LRH (ALL INDIA) 19. 19. 20. 20. 21. 21. 22. 22. 23. 23. 24. 24. SET 1 SECTION – B State any one difference between autotrophic and heterotrophic modes of nutrition. Autotrophic nutrition Heterotrophic nutrition Organisms which adopt autotrophic mode of nutrition depend upon inorganic raw materials like CO2, H2O and sunlight for their nutritional requirement. Organisms which adopt heterotrophic nutrition depend upon autotrophs for their nutritional requirements. Give one reason why multicellular organisms require special organs for exchanges of gases between their body and their environment. In multicellular organisms, all the cells are not in direct contact with the environment so direct exchange of gases can not take place and thus they require special organs for exchange of gases. Mention one example of chemotropism. Growth of pollen tube towards the ovule Name the two main organs of our central nervous system. Which one of them plays a major role in sending command to muscles to act without involving thinking process? Name the phenomenon involved. Two main organs of our central nervous system are: Brain and spinal cord. Spinal cord sends the command to muscles to act without involving thinking process. This phenomenon is known as reflex action. With the help of an example show that ‘reuse’ strategy is better than ‘recycling’. Reuse strategy is better than recycling. For example, if plastics are sent for recycling, then they would be subjected to melting; causing additional cost of machinery and an unnecessary strain on the energy sources. Also it will lead to environmental pollution. These all factors are ignored during reuse e.g. using the plastic bottles again for drinking water will save the energy. Construct an aquatic food chain showing four trophic levels. Trophic levels 25. 25. Hydrilla ⎯⎯→ Scorpio ⎯⎯→ Fish ⎯⎯→ Crane 1 2 3 4 Explain the process of breakdown of glucose in a cell (i) in the presence of oxygen, (ii) in the absence of oxygen. Presence of O2 CO2 + H2O + energy (in mitochondria) Glucose In cytoplasm (6-carbon molecule) Pyruvate (3-carbon molecule + energy) Absence of O2 Ethanol + CO2 + energy (In yeast) www.steps.TCYonline.com Page : 1 26. 26. 27. The first step is the break – down of glucose, a six-carbon molecule, into a three-carbon molecule called pyruvate. This process takes place in the cytoplasm. Further, the pyruvate may be converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide. This process take place in yeast during fermentation. Since this process takes place in the absence in air (oxygen), it is called anaerobic respiration. Break-down of pyruvate using oxygen takes place in the mitochondria. This process breaks up the three-carbon pyruvate molecule to give three molecules of carbon dioxide. The other product is water. Since this process takes place in the presence of air (oxygen), it is called aerobic respiration. The release of energy in this aerobic process is a lot greater than in the anaerobic process. Explain the mechanism of sex determination in humans. All human chromosomes are not paired. Most human chromosomes have a maternal and a paternal copy, and we have 22 such pairs. But one pair, called the sex chromosomes, is odd and not always being a perfect pair. Women have a perfect pair of sex chromosomes, both called X. But men have a mismatched pair in which one is a normal-sized X while the other is a short one called Y. So women are XX, while men are XY. As figure shows, half the children will be boys and half will be girls. All children will inherit an X chromosome from their mother regardless of whether they are boys or girls. Thus, the sex of the children will be determined by what they inherit form their father. A child who inherits an X chromosomes from her father will be a girl, and one who inherits a Y chromosome from him will be a boy. (a) (b) (a) (b) Draw a longitudinal section of a flower and label the following parts: (i) Part that produces pollen grain (ii) Part that transfers male gametes to the female gametes (iii) Part that is sticky to trap the pollen grain (iv) Part the develops into a fruit Differentiate between pollination and fertilization. OR Explain the role of placenta in the development of human embryo. Give example of two bacterial and two viral sexually transmitted diseases. Name the most effective contraceptive which prevents spread of such disease. www.steps.TCYonline.com Page : 2 27. (a) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Part that produces pollen grain: anther Part that transfers male gamete to the female gamete: style sticky part to trap pollen grain: stigma Part that develops into fruit: Ovary (b) Pollination Fertilization 1. 1. Fertilization is the process of fusion of male gamete with the female gamete. 2. It takes place by the growth of pollen tube towards the ovary. 2. Pollination is the process of transfer of pollen grains from anther to the stigma of the same or different flower. It takes place with the help of pollinations like wind, water insects etc. OR (a) (b) Placenta is a temporary organ which is formed from the tissues derived from the foetus and the mother. The placenta contains villi on the embryo’s side of tissue and blood spaces on the mother side of tissue. The blood space surrounds the villi. The villi provides a large surface area for glucose and oxygen to pass from the mother to the embryo. Thus, through placenta, the maternal blood passes food (glucose, amino acids, lipids and proteins), oxygen, hormones, water, antibodies to the foetal blood and the foetal metabolic wastes (carbon dioxide, urea) pass into the maternal blood. BACTERIAL INFECTION – which includes gonorrhoea (inflammation of mucus membrane of urinogenital tract) and syphilis (lesions in the mucus membrane of urinogential tract). VIRAL INFECTION – which includes warts, HIV-AIDS, Hepatitis-B. Use of condoms can prevent the spread of these diseases to a great extent 19. SET – 2 SECTION – B Name the process in plants where water is lost as water vapour. 19. The loss of water in the form of water vapour takes place through stomata in the plants and the process is known as transpiration. 20. Mention the function of the hind brain in humans. 20. Main function of hind brain in humans is to maintain the posture and balance of the body. It is responsible for the precision of voluntary actions like walking in straight line, riding a bicycle. 22. Name the hormone secreted by human testes. State its functions. 22. Hormone secreted by human testes. Testosterone function of testosterone is the development of secondary sexual characters in males like growth of hair, hoarse voice, moustaches etc. www.steps.TCYonline.com Page : 3 23. List any four changes you would like to incorporate in your lifestyle in a move towards a sustainable use of available resources in our country. 23. 25. (i) Use of bicycle instead of scooter to go to school. (ii) Switching off the lights, fans etc, when not in use (iii) Pool in the car instead of using individually (iv) Minimizing use of plastics Name the organism Mendel used for his experiments. Explain about F1 and F2 progeny obtained by Mendel when he bred the tall and the short varieties of the organism he experimented with. 25. Mendel used garden pea for his experiments. Parents TT tt Tall short T t Gametes F1 Generation Tt Tall F2 Generation T t T TT Tt t Tt tt TT 1 Tall 3 : : Tt 2 : : : : tt 1 Short 1 All the plants in the F1 progeny came out to be hybrid tall when Mendel bred tall and short varieties of the organisms. In the F2 generation there were 25% per plant as pure tall, 50% the hybrid tall and 25% as the short pea plants. 19. SET – 3 SECTION – B Name the plant hormone that retards growth of the plant. 19. 20. Abscieic acid is the plant hormone which retards plant growth. What is ‘translocation’ in plants? 20. Translocation in plants is the process of movement of the dissolved food to all the parts of the plant through phloem. Name and explain the function of the hormone secreted by the pituitary gland in humans. 22. 22. 23. 23. Growth hormone is secreted by the pituitary gland. This hormone regulates growth and development of the body. If there is a deficiency of this hormone in childhood, it leads to dwarfism and excess of this hormone leads to giant body size. Explain ‘biological magnification’ with the help of an example. We use several pesticides and other chemicals to protect our crops from diseases and pests. These chemicals are either washed down into the soil or into the water bodies. From the soil, these are absorbed by the plants along with water and minerals, and from the water bodies these are taken up by aquatic plants and animals. This is one of the ways in which they enter the food chain. As these chemicals are not degradable, these get accumulated progressively at each trophic level. As human beings occupy the top level in any food chain, the maximum concentration of these chemicals get accumulated in our bodies. This phenomenon is known as biological magnification. www.steps.TCYonline.com Page : 4 25. Name the two homologous structures in vertebrates. Why are they so called? How do such organs help in understanding an evolutionary relationship? 25. Limbs of birds, reptiles and humans are all the examples of homologous structures in the vertebrates. They are called so as the basic structure of the limbs is similar. Though it has been modified to perform different functions in various vertebrates. These are organs which are inherited from a common ancestor. Such a homologous characteristic helps to identify an evolutionary relationship between apparently different species. www.steps.TCYonline.com Page : 5