* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download STAAR Review Day Five Independent Practice 3. In humans, the
Survey
Document related concepts
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Induced pluripotent stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
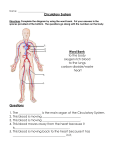
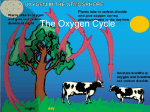
STAAR Review Day Five Independent Practice 1. Cells of the epithelial tissue are packed closely together in layers. How do epithelial cells protect organs within the human body? a. Epithelial cells fight invading bacteria and viruses by entering them and destroying their DNA b. Epithelial cells provide oxygen to organ cells so that the organs can repair any damage they sustain c. Epithelial cells form a barrier between the external environment and the internal structures of the body d. Epithelial cells can change into organ cells through cellular differentiation. 2. Photosynthesis occurs in the leaves of the plant. Leaves absorb light. They take in carbon dioxide during photosynthesis and take in oxygen during respiration. What specialized role do guard cells have in photosynthesis? a. Guard cells contain chloroplasts in which photosynthesis occurs b. Guard cells convert carbon dioxide into oxygen and water c. Guard cells store excess food made during photosynthesis d. Guard cells regulate the opening and closing of the stoma to prevent water loss. 3. In humans, the respiratory system allows for the release of carbon dioxide produced during cellular respiration and for the intake of oxygen for use during that same process. This process is similar to which structure in plants? a. The release of oxygen and intake of carbon dioxide for cellular respiration from the roots b. The release of oxygen and intake of carbon dioxide for cellular respiration from the stomata c. The release of oxygen and intake of carbon dioxide for photosynthesis from the roots d. The release of oxygen and intake of carbon dioxide for photosynthesis from the stomata 4. During a game of tag, how are human body systems interacting to maintain homeostasis a. The endocrine system is increasing the heart rate which will increase blood flow to muscles, the nervous is releasing sweat to cool down body, integumentary is sending messages around the body, and respiratory is increasing in rate to help bring in more oxygen/release more CO 2 b. The endocrine system is producing hormones to increase heart rate which will increase blood flow to muscles (circulatory), the nervous is not involved during this process, and the integumentary is increasing in rate to help bring in more oxygen/release more CO2 c. The endocrine system is producing hormones to increase heart rate which will increase blood flow to muscles (circulatory), the nervous is sending messages to the body to move faster and move away from “danger”, integumentary is releasing sweat to cool down body, and respiratory is increasing in rate to help bring in more oxygen/release more CO2 5. A neurologist that specializes in neuroanatomy does several experiments to determine how the structure of a neuron affects its function. In one of her experiments, she uses a microscalpel to cut off a neurons dendrites. How do you think this experiment will change the function of a neuron? The neuron will no longer be able to receive messages because it is missing its dendrites therefore it will not be able to function at all 6. Sickle cell anemia is a condition caused by a mutation in the gene that encodes for red blood cells. This point mutation causes red blood cells to be sickle shaped instead of disk shaped. How do you think his change in the structure of the red blood cells affects their function in patients that have this disease? Because red blood cells are disk shaped they can go through small blood vessels easily, if they are now sickle shaped they will not be able to flow through the body which will starve cells of oxygen. SPARTAN CHALLENGE QUESTIONS 1. The epidermal cells are usually covered with a waterproof layer 3. Leaves a part of the plants shoot system. that provides protection from injury and water loss. The stomata The xylem tissue in leaves transportsallow gas exchange. The epidermal cells and stomata have a. The bacteria needed for nitrogen functions similar to those of which two human body systems? fixation in root nodules a. Skeletal and respiratory b. The wax required to coat the surface b. Cardiovascular and skeletal of actively growing tissue c. Integumentary and respiratory c. The water and minerals that are d. Cardiovascular and integumentary absorbed by the roots 2. This process is an example of which of the following? d. The oxygen that regulated the rate of carbohydrate production 4. What two human systems work together to provide body cells with a constant supply of oxygen while removing carbon dioxide waste products? a. Nervous and endocrine b. Muscular and skeletal c. Respiratory and circulatory d. Excretory and integumentary 5. If a health care worker is exposed to a pathogen through a cut in her skin, which body systems are working together to help a. The role of the endocrine system in increasing the oxygen fight it off? content of red blood cells a. Muscular and vascular b. Control of urine production by the parasympathetic b. Digestive and excretory nervous system c. Circulatory and immune c. Maintenance of homeostasis by a feedback mechanism d. Endocrine and reproductive d. Disruption of homeostasis by exercise