* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download UNIT 2
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Living things in culture wikipedia , lookup
Animal nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
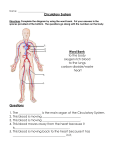
o Nutrition is a combination of processes. Through nutrition, living beings take in food and convert it into their own matter and into energy. o Living beings can be classified by type of nutrition as: o Autotrophs: Living beings which make their own organic matter from inorganic matter using a source of energy • Depending on the type of energy they use to obtain nutrient, autotrophs can be: • Photoautotrophs. They use energy from light to synthesize food. For example green plant use sunlight. • Chemoautotrophs. They use energy from chemical reactions to synthesize food. For example sulphur bacteria and iron bacteria. o Heterotrophs: Living beings which feed on organic matter produced by other living being. They transform this matter to obtain nutrients and energy. • Heterotrophs can be classified as: • Herbivores • Carnivores • Omnivores feed on plants feed on other animals feed on plants and other animals o In multicellular living being like animal, not all cells have a direct access to nutrient. Nutrients are found in food. They are complex mixture of many different substances which have to be transformed by their bodies to use them. o Multicellular organism have a number of organs, grouped together in the systems in our bodies. These organs prepare nutrients, distribute them to all the cells and expel the waste product from cellular activity. These systems are as follows: o Digestive system: Processes foods so that the cells can use it and eliminate the undigested product. o Respiratory system: Supplies oxygen needed for cells and eliminates carbon dioxide released during cell metabolism. o Circulatory system: Takes oxygen and nutrient to the cell and takes away waste products. o Excretory system: Expels waste product released during cell metabolism o Digestion includes all the processes which break down food into simple substances which are used for produce energy, growth and cell repair. o The digestive process in animals has four stages: 1. 2. 3. 4. Ingestion: is the intake of food into the body through the mouth. Digestion: is the transformation of nutrient which the body can absorb. There are two types of digestion: • Intracellular digestion: takes place inside the cells of single and primitive multicellular organisms. • Extracellular digestion: takes places outside the cells. Can be: • External digestion: takes place outside the body. Many insects • Internal digestion: takes place inside the digestive system. The transformation of food is both mechanical (food is broken down into smaller pieces) and chemical (food is transformed chemically through the action of enzymes). Absorption: is the passage of nutrients from the digestive system into blood. The blood carries the nutrient to the cells. Egestion: is the elimination of undigested and waste product from the digestive system. These product are transformed into faeces and expelled from the organism. o There are two main types of digestive systems: o Gastry cavity. A type of sac which is lined with cells. This structure is characteristic of animals with intracellular digestion, such as sponges and polyps. o There are two main types of digestive systems: o Digestive tube. A tube which begins in the mouth where food enters. It ends in the anus where food wastes are expelled. This systems is characteristic of animals with extracellular digestion. The digestive system varies according to the type of food ingested. Accessory gland are found along the digestive tube (salivary gland, liver and pancreas) and produce enzymes and other substances which aid digestion. In general, the digestive tube consist of the following parts: o EXAMPLES OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS: o Animals breathe by inhaling oxygen from the outside and exhaling carbon dioxide. o This gas exchange is carried out by the respiratory system. Respiratory system require surfaces where gas exchange can take place effectively. This surfaces are very thin, moist and covered in blood vessels. o There are four types of respiration in animals: o o o CUTANEOUS RESPIRATION Gas exchange is carried out through the skin, which is very thin and moist. Is characteristic of earthworm and adult amphibians. o o o TRACHEAL RESPIRATION Gas exchange takes place through internal tubes or tracheae. The tracheae end in orifices called spiracles where the air enters. The tracheae then branch our into tracheoles which carry air directly to the cells. Is characteristic of terrestrial arthropods. o o o BRANCHIAL RESPIRATION Gas exchange takes place through the gills. Gills are thin extensions on the surface of the body, surrounded by blood vessels Is characteristic of aquatic animals such as fish and some crustaceans. o o o o PULMONARY RESPIRATION Gas exchange takes place in the lungs. Lungs are internal cavities which have very thin, damp walls full of blood vessels. Pulmonary respiration takes place in two different movements: inhalation, when the air is taken into the lungs, and exhalation when the air is expelled from the lungs. Is characteristic of some vertebrates and a few invertebrates like terrestrial snails. o o The circulatory system has two basic functions: o It carries nutrient and oxygen to the cells o It remove carbon dioxide and waste product from the metabolism The circulatory system is made up of: o Circulatory fluid. Internal circulating fluid. Can be: blood ( in vertebrates) or hydrolymph and haemolymph ( in invertebrates) o Vessels: Ducts which carry circulatory fluid. Arteries carry blood from the heart to the body and veins carry blood from the body back to the heart. Capillaries connect arteries with veins. o Heart: An organ like a pump which makes circulatory fluid circulate through the vessels. o There are two types of circulatory systems: o Open circulatory system: the circulating fluid is pumped by the heart. From there, it flows through the body cavity, directly to the internal organs. o There are two types of circulatory systems: o Closed circulatory system: the blood always circulates inside blood vessels, pumped by a heart. The vessels deliver blood to body cells and return it to the heart. There are two types of closed systems: o o Excretion is the process of colleting waste product and expelling them outside the body. Waste product include: carbon dioxide, ammoniac and urea. Carbon dioxide is expelled by the respiratory systems. Other substances are eliminated by the excretory system. o EXCRETORY SYSTEM o Some animals, such as sponges, do not posses an excretory system. They expel waste product directly through the pores in their body. Insect use Malpighian tubules to expel waste products. These tubules are thin tubes in the abdominal cavity which collect wastes from the digestive tube. In vertebrates, the excretory system consist of various organs. The main organs are the kidneys. These produce urine which contains the urea. Urine leaves the kidneys through thin tubes called ureters. It then flows into the bladder where it is stored. Eventually, urine is expelled from the body through the urethra. o o o EXCRETORY SYSTEM o o Plants are autotrophs. They produce organic matter from inorganic matter, such carbon dioxide, water and mineral salts. Plant nutrition involves these processes: o Absorption: is the movement of water and mineral salt from the ground to the inside of the roots. There, water and mineral salts are absorbed by the roots. These inorganic nutrient are called raw sap. Raw sap consists of water and mineral salt. o Transport of raw sap: transport begins inside the root, when the raw sap enters long tubes called xylem vessels. Then the sap travels up the stem to the leaves and other green parts of the plant o Gas exchange: gas exchange takes place in the leaf stomata. Carbon dioxide enter the plant and oxygen leaves the plant through the stomata. Also water evaporates. Water evaporation is called transpiration. o Photosynthesis: takes place in the chloroplast where chlorophyll is found. Chlorophyll absorbs sunlight to produce energy. This energy transform raw sap and carbon dioxide into elaborated sap. o Transport of elaborated sap: elaborated sap is transported from the green plant cells to all parts of the plant. This sap, or food, travels through tubes called phloem vessels. o Respiration. Plants breathe. During respiration, plant leaves take in oxygen from the air and release carbon dioxide. o Excretion. Remove the waste product produce in the metabolism of the plant. Metabolism produce some harmful substances that the organisms must then eliminate.