BUGS Rocks Station 1 Plate Tectonics and the Rock Cycle
... • an apple cut in half Activity and Discussion: After reading the materials about rocks, use the apple (described on the pg. The Rocky Earth) to explain the earth’s layers-core, mantle and crust. Direct the students’ attention to the plate tectonic map. Discuss how we have come to understand that th ...
... • an apple cut in half Activity and Discussion: After reading the materials about rocks, use the apple (described on the pg. The Rocky Earth) to explain the earth’s layers-core, mantle and crust. Direct the students’ attention to the plate tectonic map. Discuss how we have come to understand that th ...
8th Grade Science FOCUS on Achievement
... Overall Summary: There are, after combining the physical and mechanical properties, four layers of the Earth. At the surface is the crust which contains the tectonic plates. Below the crust is the mantle. It contains the plastic-like material that moves around in currents (convection.) Below the man ...
... Overall Summary: There are, after combining the physical and mechanical properties, four layers of the Earth. At the surface is the crust which contains the tectonic plates. Below the crust is the mantle. It contains the plastic-like material that moves around in currents (convection.) Below the man ...
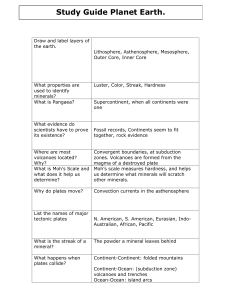
Earth History – Study Guide Investigations: Sedimentary Rocks +
... 10. Where do river sediments often accumulate? 11. Where do windblown sediments often accumulate? 12. Name two other places where sediments can accumulate. 13. What type of rock is most easily broken down by carbonic acid? 14. What are the four natural forces that cause erosion? 15. Of the four from ...
... 10. Where do river sediments often accumulate? 11. Where do windblown sediments often accumulate? 12. Name two other places where sediments can accumulate. 13. What type of rock is most easily broken down by carbonic acid? 14. What are the four natural forces that cause erosion? 15. Of the four from ...
ACROSS 3 ______ is the way a mineral reflects light off it`s surface 6
... 6 Chalk is an ______ sedimentary rock formed form the remains of shells of ancient organisms 7 ______ reaction series details how igneous rock minerals start to form when cooling. 8 The process that changes rock from 1 type to another over a long period of time is known as the ______ ______. 9 _____ ...
... 6 Chalk is an ______ sedimentary rock formed form the remains of shells of ancient organisms 7 ______ reaction series details how igneous rock minerals start to form when cooling. 8 The process that changes rock from 1 type to another over a long period of time is known as the ______ ______. 9 _____ ...
Rock Cycle Unit Vocabulary
... Rock Cycle Unit Vocabulary 1. lithosphere – rigid, top layer of Earth made of the crust and upper mantle - broken into plates that move around on the lower mantle 2. mantle – largest layer of Earth’s interior that lies below the crust - although solid, it flows slowly like putty 3. igneous rock – ro ...
... Rock Cycle Unit Vocabulary 1. lithosphere – rigid, top layer of Earth made of the crust and upper mantle - broken into plates that move around on the lower mantle 2. mantle – largest layer of Earth’s interior that lies below the crust - although solid, it flows slowly like putty 3. igneous rock – ro ...
Name: Earth Space Spiraling Questions Earth`s Structure 1. The
... metamorphic, and sedimentary. These rock types are formed in different ways, however because of the rock cycle they are able to transform into one another. A rock that has been transformed from a striated (layered) rock to one that is under intense heat and pressure. What was the rock type before an ...
... metamorphic, and sedimentary. These rock types are formed in different ways, however because of the rock cycle they are able to transform into one another. A rock that has been transformed from a striated (layered) rock to one that is under intense heat and pressure. What was the rock type before an ...
Mid Term Review Sample Questions
... 18. Compared to the Rocky Mountains, are the Appalachian Mountains younger or older? 19. What region of Virginia contains the most coal? _______________________________ 20. What principle of relative dating states that the oldest rocks layers are on the bottom? _______________ 21. What created the f ...
... 18. Compared to the Rocky Mountains, are the Appalachian Mountains younger or older? 19. What region of Virginia contains the most coal? _______________________________ 20. What principle of relative dating states that the oldest rocks layers are on the bottom? _______________ 21. What created the f ...
Review Unit 1 - Effingham County Schools
... • Section III and II are magma (liquid) – convection currents • Section I is solid ...
... • Section III and II are magma (liquid) – convection currents • Section I is solid ...
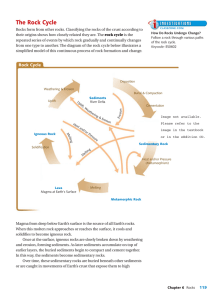
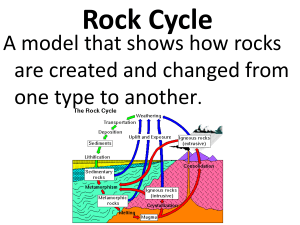
Rock Cycle
... Metamorphic Rock Rocks that form when existing rocks are heated and squeezed deep inside the Earth. ...
... Metamorphic Rock Rocks that form when existing rocks are heated and squeezed deep inside the Earth. ...
Chapter 1
... • How does the lithosphere relate to Earth’s inner regions, and how does it move and deform? ...
... • How does the lithosphere relate to Earth’s inner regions, and how does it move and deform? ...
Vocabulary
... b. Igneous: ______________________________________________________________________ ...
... b. Igneous: ______________________________________________________________________ ...
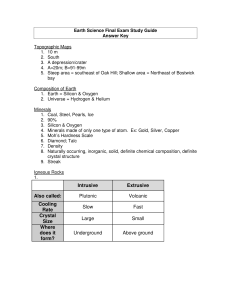
Final Exam Study Guide Answer Key
... 3. Areas with limestone bedrock 4. Calcite 5. Subsidence, saltwater contamination, over pumping, chemicals, sewage, etc. Plate Tectonics 1. Earth was once joined as a single landmass called Pangaea (Alfred Wegner), plates move because of convection currents in the mantle 2. Periods of time when the ...
... 3. Areas with limestone bedrock 4. Calcite 5. Subsidence, saltwater contamination, over pumping, chemicals, sewage, etc. Plate Tectonics 1. Earth was once joined as a single landmass called Pangaea (Alfred Wegner), plates move because of convection currents in the mantle 2. Periods of time when the ...
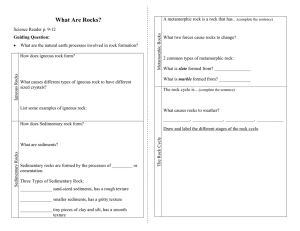
What Are Rocks - Lewiston School District
... What causes rocks to weather? ______________, ________________, _______________, ______________ ...
... What causes rocks to weather? ______________, ________________, _______________, ______________ ...
Exam Study Guide
... substance (in graph or tabular form) along with the ratio of daughter to parent substances present in the sample. E5.3f Explain why C-14 can be used to date a 40,000 year old tree but U-Pb cannot. E5.3g Identify a sequence of geologic events using relative-age dating principles. E3.3A Explain ...
... substance (in graph or tabular form) along with the ratio of daughter to parent substances present in the sample. E5.3f Explain why C-14 can be used to date a 40,000 year old tree but U-Pb cannot. E5.3g Identify a sequence of geologic events using relative-age dating principles. E3.3A Explain ...
Cycles of the Lithosphere
... riverbeds or lake bottoms and accumulate over long periods - Pressure is applied as more and more material is deposited - Upper layer presses down on lower layers, compacting and squeezing out water and air, and cementing the particles into layers [strata] in a horizontal pattern. - Geologic Time Sc ...
... riverbeds or lake bottoms and accumulate over long periods - Pressure is applied as more and more material is deposited - Upper layer presses down on lower layers, compacting and squeezing out water and air, and cementing the particles into layers [strata] in a horizontal pattern. - Geologic Time Sc ...
Review for Earth Science Test
... e. Found in nature 5. What is an Earthquake? It is the shaking that results from the movement of rock beneath Earth’s surface. 6. What is streak? It is the color of a mineral’s powder. 7. What is Mohs’ Hardness Scale? It is the scale used by scientists to classify minerals according to their hardnes ...
... e. Found in nature 5. What is an Earthquake? It is the shaking that results from the movement of rock beneath Earth’s surface. 6. What is streak? It is the color of a mineral’s powder. 7. What is Mohs’ Hardness Scale? It is the scale used by scientists to classify minerals according to their hardnes ...
geology exam is - Spring Branch ISD
... _________________ 3. Formed in the mantle, molten material called lava cools to form minerals below Earth’s surface. _________________ 4. The repeating pattern of atoms in a mineral form a solid known as a fracture. _________________ 5. The color of a mineral’s powder is known as luster. ___________ ...
... _________________ 3. Formed in the mantle, molten material called lava cools to form minerals below Earth’s surface. _________________ 4. The repeating pattern of atoms in a mineral form a solid known as a fracture. _________________ 5. The color of a mineral’s powder is known as luster. ___________ ...
Science Review: Land Formations (Rocks, Minerals, Soil, etc
... Erosion- moving sediment away (washing away) Deposition- putting new sediments in place Forms: beaches Dunes Deltas Example: A friend lives on Marblehead Neck and has a private beach at the water line. After a storm, the sand is not there! It is all rocks! It has been washed away- this is erosion. T ...
... Erosion- moving sediment away (washing away) Deposition- putting new sediments in place Forms: beaches Dunes Deltas Example: A friend lives on Marblehead Neck and has a private beach at the water line. After a storm, the sand is not there! It is all rocks! It has been washed away- this is erosion. T ...
Benchmark - Test 2 Study Guide
... 1. What is the temperature, density, and composition of the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core? Fill in the table AND explain the similarities and differences in a paragraph(s). Attach an additional sheet if needed. ...
... 1. What is the temperature, density, and composition of the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core? Fill in the table AND explain the similarities and differences in a paragraph(s). Attach an additional sheet if needed. ...
Dual Credit Major Topics for Studying
... Dual Credit Major Topics for Studying Plate Tectonics Earth’s structure: Layers and properties (i.e. crust, mantle core) Names of plates Continental Drift Types of volcanoes; magma types (felsic and maffic) Features of volcanoes Lava types Seismic waves, earthquakes liquefaction 20 ...
... Dual Credit Major Topics for Studying Plate Tectonics Earth’s structure: Layers and properties (i.e. crust, mantle core) Names of plates Continental Drift Types of volcanoes; magma types (felsic and maffic) Features of volcanoes Lava types Seismic waves, earthquakes liquefaction 20 ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.