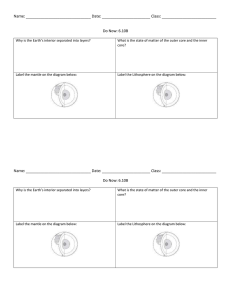
Assignment - 1
... 2.6. Summarize the various lines of evidence that we incorporated into the theory of plate tectonics? A: Wegener's lines of evidence ...
... 2.6. Summarize the various lines of evidence that we incorporated into the theory of plate tectonics? A: Wegener's lines of evidence ...
REVISED EXAM 3 STUDY GUIDE – PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY
... b. Around the Pacific Ring of Fire c. In California d. In the Appalachians ...
... b. Around the Pacific Ring of Fire c. In California d. In the Appalachians ...
Photosynthesis Jeopardy - River Vale Public Schools
... 100 – What is the theory call where pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant motion? Plate Tectonics 200 – What type of stress is cause when two plates are moving in opposite directions? Tension 300 – What type of heat transfer occurs when the sun heats the Earth Radiation 400 – Who came up wit ...
... 100 – What is the theory call where pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant motion? Plate Tectonics 200 – What type of stress is cause when two plates are moving in opposite directions? Tension 300 – What type of heat transfer occurs when the sun heats the Earth Radiation 400 – Who came up wit ...
Chapter 13 Earth`s Interior and Tectonics
... Atoms>>>Elements>>>Minerals>>>Rocks>>>Continents Bedrock: solid rock that underlies the surface material of the Earth. Regolith: the layer above the bedrock, usually composed of weathered down bedrock. Outcrop: exposure of rock at the Earth’s surface. Mineral Classification What does it take to be a ...
... Atoms>>>Elements>>>Minerals>>>Rocks>>>Continents Bedrock: solid rock that underlies the surface material of the Earth. Regolith: the layer above the bedrock, usually composed of weathered down bedrock. Outcrop: exposure of rock at the Earth’s surface. Mineral Classification What does it take to be a ...
Chapter 5 Test - Bloomsburg Area School District
... 9. What is a large body of weathered rock deposited at the edge of a glacier? ...
... 9. What is a large body of weathered rock deposited at the edge of a glacier? ...
IMPORTANT CONCEPTS
... • Erosion--due to water, ice, wind, gravity • Rock formed at high temperature becomes unstable at surface ...
... • Erosion--due to water, ice, wind, gravity • Rock formed at high temperature becomes unstable at surface ...
Teacher Pre-assessment
... a. the cementation of rock fragments b. the carrying away of sediment c. the development of mineral crystals d. the decomposition of organisms 24. Fossils are generally found in what type of rocks? a. rocks from volcanoes b. sedimentary rocks c. metamorphic rocks d. rocks containing quartz 25. Which ...
... a. the cementation of rock fragments b. the carrying away of sediment c. the development of mineral crystals d. the decomposition of organisms 24. Fossils are generally found in what type of rocks? a. rocks from volcanoes b. sedimentary rocks c. metamorphic rocks d. rocks containing quartz 25. Which ...
Earth Science Introduction
... • 3 hours to retreat of glaciers from Wisconsin • 12 days = 1 million years • 2 years to extinction of dinosaurs • 14 years to age of Niagara Escarpment • 31 years = 1 billion years ...
... • 3 hours to retreat of glaciers from Wisconsin • 12 days = 1 million years • 2 years to extinction of dinosaurs • 14 years to age of Niagara Escarpment • 31 years = 1 billion years ...
Slide 1
... • Focus- center of earthquake beneath Earth • Epicenter- center of earthquake on Earth’s surface • P waves- longitudinal waves like sound waves (accordion), first detected • S waves- transverse waves, can’t travel through liquid • Surface waves- when seismic waves reach Earth’s surface, slower than ...
... • Focus- center of earthquake beneath Earth • Epicenter- center of earthquake on Earth’s surface • P waves- longitudinal waves like sound waves (accordion), first detected • S waves- transverse waves, can’t travel through liquid • Surface waves- when seismic waves reach Earth’s surface, slower than ...
AGE080 Week 8 Worksheet - KEY Powerpoint: “Geologic Processes
... energy release associated with that number is about 32 times as great as the previous number. 6. Earthquake damage depends more on ground acceleration than on earthquake magnitude. 7. Volcanoes occur where melted (molten) rock reaches the earth’s surface. They can occur in a number of plate tectonic ...
... energy release associated with that number is about 32 times as great as the previous number. 6. Earthquake damage depends more on ground acceleration than on earthquake magnitude. 7. Volcanoes occur where melted (molten) rock reaches the earth’s surface. They can occur in a number of plate tectonic ...
Cycles in the Lithosphere pages 54-60
... 4. Shape-changing or ______________________ rocks are formed when great heat and pressure are applied to igneous or sedimentary rocks. 5. The earth’s rocks will cycle through the different stages _____________times . 6. In 1910, Alfred Wegener theorized that all the earth’s continents originally for ...
... 4. Shape-changing or ______________________ rocks are formed when great heat and pressure are applied to igneous or sedimentary rocks. 5. The earth’s rocks will cycle through the different stages _____________times . 6. In 1910, Alfred Wegener theorized that all the earth’s continents originally for ...
Sedimentary Rocks - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Igneous Rocks Sedimentary Rocks Metamorphic Rocks ...
... Igneous Rocks Sedimentary Rocks Metamorphic Rocks ...
Unit 3 Vocabulary
... motion; it involves the oceanic lithosphere sliding down the oceanic ridge under the 5. the location where plates meet; three types: Divergent, Convergent, Transform 6. the rigid outer layer of Earth, including the crust and upper mantle 7. the division of Earth’s history into block of times – eons, ...
... motion; it involves the oceanic lithosphere sliding down the oceanic ridge under the 5. the location where plates meet; three types: Divergent, Convergent, Transform 6. the rigid outer layer of Earth, including the crust and upper mantle 7. the division of Earth’s history into block of times – eons, ...
Chapter 1, Changes to Earth`s Surface
... Crust – other layer of Earth, made of rock Mantle – layer of rock beneath Earth’s crust Core – center layer of Earth Plates – rigid blocks of crust and upper mantle rock Magma – molten rock from Earth’s mantle Volcano – mountain formed by lava and ash Earthquake – shaking of the ground caused by the ...
... Crust – other layer of Earth, made of rock Mantle – layer of rock beneath Earth’s crust Core – center layer of Earth Plates – rigid blocks of crust and upper mantle rock Magma – molten rock from Earth’s mantle Volcano – mountain formed by lava and ash Earthquake – shaking of the ground caused by the ...
Name: Date: Class: Name: Date: Pod: Name: Date: Pod: Name: Date
... 2. In order for a rock to be classified as igneous, what must have happened during its formation? a. Solid rock changing under pressure b. Liquid rock changing its physical state. c. Small rocks becoming cemented together. d. Layered rocks breaking into smaller pieces. 3. Sedimentary rocks often con ...
... 2. In order for a rock to be classified as igneous, what must have happened during its formation? a. Solid rock changing under pressure b. Liquid rock changing its physical state. c. Small rocks becoming cemented together. d. Layered rocks breaking into smaller pieces. 3. Sedimentary rocks often con ...
Molten rock that comes to the surface of the earth is called:
... a. the cementation of rock fragments b. the carrying away of sediment c. the development of mineral crystals d. the decomposition of organisms 24. Fossils are generally found in what type of rocks? a. rocks from volcanoes b. sedimentary rocks c. metamorphic rocks d. rocks containing quartz 25. Which ...
... a. the cementation of rock fragments b. the carrying away of sediment c. the development of mineral crystals d. the decomposition of organisms 24. Fossils are generally found in what type of rocks? a. rocks from volcanoes b. sedimentary rocks c. metamorphic rocks d. rocks containing quartz 25. Which ...
Earth Processes Part 1: Lithosphere
... They can change from one type of rock to another. (For example, a sedimentary rock will not always be a sedimentary rock.) Weathering-the breaking down of rocks by weather. There are two types of weathering: Physical weathering (rocks broken) ...
... They can change from one type of rock to another. (For example, a sedimentary rock will not always be a sedimentary rock.) Weathering-the breaking down of rocks by weather. There are two types of weathering: Physical weathering (rocks broken) ...
hot liquid rock beneath the earth`s surface
... the earth's surface igneous rock rock formed by the cooling and hardening of magma or lava rocks formed from sediments that have been pressed and cemented into rock Created by A. Wong, Sugarland ES ...
... the earth's surface igneous rock rock formed by the cooling and hardening of magma or lava rocks formed from sediments that have been pressed and cemented into rock Created by A. Wong, Sugarland ES ...
Document
... steel, and glass all come made up of a mixture of shape, and pattern of the from substances found in _______ and other rock’s __________. Earth’s crust, they are not ___________. classified as minerals because they ___________ are organic are not naturally occuring ...
... steel, and glass all come made up of a mixture of shape, and pattern of the from substances found in _______ and other rock’s __________. Earth’s crust, they are not ___________. classified as minerals because they ___________ are organic are not naturally occuring ...
Study Guide Chapter 2 – Minerals and Rocks GPS: S6E5. Students
... c. Classify rocks by their process of formation. d. Describe processes that change rocks and the surface of the earth. e. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. f. Explain the effects of physical processes (plate tectonics, erosio ...
... c. Classify rocks by their process of formation. d. Describe processes that change rocks and the surface of the earth. e. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. f. Explain the effects of physical processes (plate tectonics, erosio ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.