Chps 2 and 3
... The Earth is made up of the core (iron & nickel) surrounded by the mantle (which is the majority of the earth’s mass). Alfred Wegener (1912) believed that all the continents were once united as PANGEA ...
... The Earth is made up of the core (iron & nickel) surrounded by the mantle (which is the majority of the earth’s mass). Alfred Wegener (1912) believed that all the continents were once united as PANGEA ...
The Earth - Indiana University Astronomy
... Unique Features of Earth Plate Tectonics – the only planet with a surface shaped by this type of tectonics Atmospheric Oxygen – the only planet with significant Oxygen in its atmosphere Surface Liquid Water – the only planet where temperature & pressure allow surface water to be stable as a l ...
... Unique Features of Earth Plate Tectonics – the only planet with a surface shaped by this type of tectonics Atmospheric Oxygen – the only planet with significant Oxygen in its atmosphere Surface Liquid Water – the only planet where temperature & pressure allow surface water to be stable as a l ...
EARTH`S INTERIOR
... lower mantle) based on the physical characteristics of those layers. Overall, the mantle is nearly 3000 km thick. ...
... lower mantle) based on the physical characteristics of those layers. Overall, the mantle is nearly 3000 km thick. ...
Study Guide: Plate tectonics TEST 2/soil Rocks/Weathering and
... 6. What is weathering? The breaking down of rocks and plants into smaller pieces 7. What is erosion? The movement of broken down rocks and plants by wind, water, gravity or ice 8. The lithosphere is broken into what? Tectonic plates 9. What are the theories of Continental Drift & Plate Tectonics? Th ...
... 6. What is weathering? The breaking down of rocks and plants into smaller pieces 7. What is erosion? The movement of broken down rocks and plants by wind, water, gravity or ice 8. The lithosphere is broken into what? Tectonic plates 9. What are the theories of Continental Drift & Plate Tectonics? Th ...
Science 7--Chapter 14-Lesson 2 Notes1ans
... Earthquakes and Volcanoes liquefaction—solid material acts more like a liquid than a solid due to extreme shaking tsunamis—huge ocean waves Earthquakes can cause huge waves in the ocean from the upward movement of rock. volcanoes—landforms that form when magma erupts onto Earth’s surface as lava lav ...
... Earthquakes and Volcanoes liquefaction—solid material acts more like a liquid than a solid due to extreme shaking tsunamis—huge ocean waves Earthquakes can cause huge waves in the ocean from the upward movement of rock. volcanoes—landforms that form when magma erupts onto Earth’s surface as lava lav ...
PLATE MOVEMENT AND CONTINENTAL GROWTH
... APPALACHAIN AND URAL MTNS. – AGE OF ROCKS IN OCEAN BASINS – FOSSILS – LAND AREAS – TROPICAL AND POLAR REVERSES ...
... APPALACHAIN AND URAL MTNS. – AGE OF ROCKS IN OCEAN BASINS – FOSSILS – LAND AREAS – TROPICAL AND POLAR REVERSES ...
86:12 And by the Earth full of cracks/faults
... and hardens into new oceanic crust. • At present there are about twenty plates of different sizes and shapes moving about the surface of the planet. • Some underlie ocean, while others underlie ocean and continent. • Driven by convection currents in the mantle, plates can move at the dizzying speed ...
... and hardens into new oceanic crust. • At present there are about twenty plates of different sizes and shapes moving about the surface of the planet. • Some underlie ocean, while others underlie ocean and continent. • Driven by convection currents in the mantle, plates can move at the dizzying speed ...
Investigating Earth`s Interior
... 10. Name the 3 chemical layers of the Earth, and name the 5 mechanical layers of the Earth. We will work with names from both categories through this unit. ...
... 10. Name the 3 chemical layers of the Earth, and name the 5 mechanical layers of the Earth. We will work with names from both categories through this unit. ...
EARTH SCIENCE - Regional School District 17
... the weather, most of the water vapor and clouds. ...
... the weather, most of the water vapor and clouds. ...
Canadians prove humans are causing climate change
... The scientists gathered global rainfall data from 1925 to 1999, and then compared it to 14 complex computer climate models. The rainfall data confirmed what the scientists had speculated could occur thanks to human activity, and in some cases the weather changes went beyond what scientists had predi ...
... The scientists gathered global rainfall data from 1925 to 1999, and then compared it to 14 complex computer climate models. The rainfall data confirmed what the scientists had speculated could occur thanks to human activity, and in some cases the weather changes went beyond what scientists had predi ...
Curriculum Mapping: Integrating Magnet Theme with Ongoing Units
... Class set of rocks and minerals Mineral testing kits Field Guide to minerals Framed Rock Displays Class seminar: San Diego County tectonic faults from, “Earthquakes and Faults in San Diego County” by Philip Kern. Text: Page 5 and 6 copied and read pre-seminar. Doc-Cam and Projector Framed Rock Displ ...
... Class set of rocks and minerals Mineral testing kits Field Guide to minerals Framed Rock Displays Class seminar: San Diego County tectonic faults from, “Earthquakes and Faults in San Diego County” by Philip Kern. Text: Page 5 and 6 copied and read pre-seminar. Doc-Cam and Projector Framed Rock Displ ...
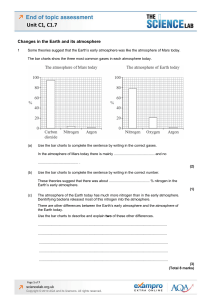
Changes in the Earth and its Atmosphere
... Evidence for tectonic plate movement. Copy and complete • We call movement of the tectonic plates __________ drift. • A scientist called __________ proposed this theory. • Convection currents within the Earth’s ______ driven by heat released by natural radioactive processes cause the plates to ...
... Evidence for tectonic plate movement. Copy and complete • We call movement of the tectonic plates __________ drift. • A scientist called __________ proposed this theory. • Convection currents within the Earth’s ______ driven by heat released by natural radioactive processes cause the plates to ...
Plate Tectonics
... The scientist at he time believed that mountains formed from the cooling of the Earth. Wegener said that if that was true then there would be mountains all over the Earth. Wegener proposed that mountains formed from the collision of continents. We now know that the continents move by means of convec ...
... The scientist at he time believed that mountains formed from the cooling of the Earth. Wegener said that if that was true then there would be mountains all over the Earth. Wegener proposed that mountains formed from the collision of continents. We now know that the continents move by means of convec ...
Earth Science - Atlanta Public Schools
... full moon Jan 15, a third (last) quarter moon Jan 22, and the next new moon Jan 29 16. Explain the Theory of Continental Drift. ...
... full moon Jan 15, a third (last) quarter moon Jan 22, and the next new moon Jan 29 16. Explain the Theory of Continental Drift. ...
Grade 8 Science - St. Paul's Intermediate School
... area of land that drains into a body of water such as a river, pond, lake or ocean. There may be many small within a larger basin. ...
... area of land that drains into a body of water such as a river, pond, lake or ocean. There may be many small within a larger basin. ...
Standard 3.1 Earth`s Structure
... Grade 6 – Science Standard 3.1 Earth Systems.3.1 - Complex interrelationships exist between Earth's structure and natural processes that over time are both constructive and destructive. Related Colorado Department of Education Sample Units: ...
... Grade 6 – Science Standard 3.1 Earth Systems.3.1 - Complex interrelationships exist between Earth's structure and natural processes that over time are both constructive and destructive. Related Colorado Department of Education Sample Units: ...
Vocabulary #1 7th Grade Science
... Solid layer of the mantle beneath lithosphere; made of mantle rock that flows very slowly allowing tectonic plates to move on top of it. ...
... Solid layer of the mantle beneath lithosphere; made of mantle rock that flows very slowly allowing tectonic plates to move on top of it. ...
Study Guide Chapter 5 – Volcanoes GPS: S6E5. Students will
... S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth’s surface is formed. d. Describe processes that change rocks and the surface of the Earth. e. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. f. Explain the effects of ph ...
... S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth’s surface is formed. d. Describe processes that change rocks and the surface of the Earth. e. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. f. Explain the effects of ph ...
The Earth`s Interior
... And if you are at the beach and can't see any crust, because you are looking out at the ocean, it is still there under the water. The whole earth is coated with a thin (about 3 kilometers under the oceans, and about 19 kilometers under the land) layer of rocky crust. ...
... And if you are at the beach and can't see any crust, because you are looking out at the ocean, it is still there under the water. The whole earth is coated with a thin (about 3 kilometers under the oceans, and about 19 kilometers under the land) layer of rocky crust. ...
7th Grade Earth Science State and District Outcomes Summary
... 3.1a Gather, analyze, and communicate data that explains Earth’s plates, plate motions, and the results of plate motions 3.1b Identify, interpret, and explain models of plates motions on Earth 3.1c Use maps to locate likely geologic “hot spots”, using evidence of earthquakes and volcanic activity 3. ...
... 3.1a Gather, analyze, and communicate data that explains Earth’s plates, plate motions, and the results of plate motions 3.1b Identify, interpret, and explain models of plates motions on Earth 3.1c Use maps to locate likely geologic “hot spots”, using evidence of earthquakes and volcanic activity 3. ...
Earth Space EOC Review Test #1 NAME
... Keisha should slowly lift the globe above her head and then lower it. Keisha should slowly spin the globe one complete time about its axis. ...
... Keisha should slowly lift the globe above her head and then lower it. Keisha should slowly spin the globe one complete time about its axis. ...
StudyGuide-for-Oceans-2015-key
... 30. A large stream of moving water that flows through an ocean is known as a _Current_.In the 31. Surface currents are caused by _____Wind____. 32. Northern Hemisphere currents curve to the right because of the Coriolis Effect_ 33. A large powerful warm surface current in the Atlantic Ocean that aff ...
... 30. A large stream of moving water that flows through an ocean is known as a _Current_.In the 31. Surface currents are caused by _____Wind____. 32. Northern Hemisphere currents curve to the right because of the Coriolis Effect_ 33. A large powerful warm surface current in the Atlantic Ocean that aff ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.