Earth Science
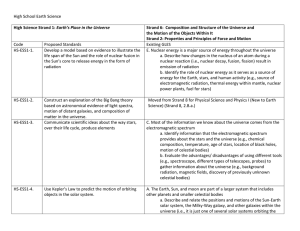
... c. students discover various resources which influence their lives by 1. developing an understanding of the earth's composition by studying the physical and chemical properties of matter. 2. relating how atoms combine to form valuable minerals and rocks. 3. exploring both mineral and energy resource ...
... c. students discover various resources which influence their lives by 1. developing an understanding of the earth's composition by studying the physical and chemical properties of matter. 2. relating how atoms combine to form valuable minerals and rocks. 3. exploring both mineral and energy resource ...
Earth`s Interior Notes
... 2. Secondary waves, also known as Swaves. - Travel in an up-anddown pattern much like the waves that move through water. - Can only travel through solid material, not liquids and gases. ...
... 2. Secondary waves, also known as Swaves. - Travel in an up-anddown pattern much like the waves that move through water. - Can only travel through solid material, not liquids and gases. ...
Interior Earth vocabulary.xlsx
... gas or liquid; in Earth's mantle, convection is thought to transfer energy by the motion of solid rock, which when under great heat and pressure can move like a liquid. A circulation pattern in which material is heated and rises in one area, then cools and sinks in another area, flowing in a continu ...
... gas or liquid; in Earth's mantle, convection is thought to transfer energy by the motion of solid rock, which when under great heat and pressure can move like a liquid. A circulation pattern in which material is heated and rises in one area, then cools and sinks in another area, flowing in a continu ...
HS Earth Science Crosswalk
... a. Describe the causes and consequences of observed and predicted changes in the ozone layer b. Describe the causes and consequences of observed and predicted changes in the ozone layer 2. Earth’s Systems (geosphere, atmosphere, and hydrosphere) interact with one another as they undergo change by co ...
... a. Describe the causes and consequences of observed and predicted changes in the ozone layer b. Describe the causes and consequences of observed and predicted changes in the ozone layer 2. Earth’s Systems (geosphere, atmosphere, and hydrosphere) interact with one another as they undergo change by co ...
File
... Atlantic Ocean floor. How many grams of Potassim-40 will be left from a 80g sample after 3,000 years? (If you forgot this, go watch the videos in Unit 1…) ...
... Atlantic Ocean floor. How many grams of Potassim-40 will be left from a 80g sample after 3,000 years? (If you forgot this, go watch the videos in Unit 1…) ...
The History of the Earth
... Steam Michael and Joshua said,”steam is hot water that comes from a geyser”. ...
... Steam Michael and Joshua said,”steam is hot water that comes from a geyser”. ...
GR. 6 EARTH SCIENCE CURRICULUM GUIDE Enduring
... Construct a styrofoam model of the layers of the ...
... Construct a styrofoam model of the layers of the ...
chapter_2_powerpoint_le
... amounts of U-238 and U-235: – U-235 makes up 0.7% of uranium ore – Uranium ore used in reactors is enriched to 2-4% U-235 – Because U-235 decays more rapidly than U-238, at some point in the past all uranium ore would have had about 2-4% U-235 – Sites in West Africa were natural nuclear reactors abo ...
... amounts of U-238 and U-235: – U-235 makes up 0.7% of uranium ore – Uranium ore used in reactors is enriched to 2-4% U-235 – Because U-235 decays more rapidly than U-238, at some point in the past all uranium ore would have had about 2-4% U-235 – Sites in West Africa were natural nuclear reactors abo ...
Earth System Science: The Big Ideas
... every American to understand? All too often, curricula are too ambitious and, as a result, may fail to cover topics in any substantial depth. An alternative approach is to build one’s curriculum upon a foundation of focused, interconnected big ideas. A well-designed set of big ideas can provide an a ...
... every American to understand? All too often, curricula are too ambitious and, as a result, may fail to cover topics in any substantial depth. An alternative approach is to build one’s curriculum upon a foundation of focused, interconnected big ideas. A well-designed set of big ideas can provide an a ...
GEOG - Unit 1
... • Wind transports sediment from one place to another • Loess—wind-blown silt and clay sediment; produces fertile soil Glacial Erosion • Glacier—large, long-lasting mass of ice; forms in mountainous areas • Glaciation — changing of landforms by slowly moving glaciers • Example: cutting u-shaped valle ...
... • Wind transports sediment from one place to another • Loess—wind-blown silt and clay sediment; produces fertile soil Glacial Erosion • Glacier—large, long-lasting mass of ice; forms in mountainous areas • Glaciation — changing of landforms by slowly moving glaciers • Example: cutting u-shaped valle ...
The Geologic Time Scale
... Earth’s biota – all living things – has evolved or changed through history. ...
... Earth’s biota – all living things – has evolved or changed through history. ...
Review Key - Walden Science
... At a river delta, the fresh water of the river flows into the salt water of the ocean. Since fresh water is less dense than salt water, the water from the river remains on top of the more dense salt water of the ocean. 26. List the 2 types of ocean currents and describe each one. Surface current – t ...
... At a river delta, the fresh water of the river flows into the salt water of the ocean. Since fresh water is less dense than salt water, the water from the river remains on top of the more dense salt water of the ocean. 26. List the 2 types of ocean currents and describe each one. Surface current – t ...
If you think about a volcano, you know Earth must be hot inside. The
... Earth was hot when it formed. A lot of Earth’s heat is leftover from when our planet formed, four-and-a-half billion years ago. ...
... Earth was hot when it formed. A lot of Earth’s heat is leftover from when our planet formed, four-and-a-half billion years ago. ...
Lecture 2 The Earth. I. The Interior Earth – vital statistics Planet size
... Presume planets with strong magnetic field have an internal dynamo converting the kinetic energy of a conducting, moving fluid into magnetic energy. ⇒ Strong evidence for molten material inside Earth ...
... Presume planets with strong magnetic field have an internal dynamo converting the kinetic energy of a conducting, moving fluid into magnetic energy. ⇒ Strong evidence for molten material inside Earth ...
Slide 1
... Intrusive rocks are coarse and large. Extrusive are smooth, small. They are usually dark in color. – Sedimentary- made from weathered or broken rocks, found in oceans, lakes, streams, deserts • Clastic- broken pieces held by cement • Chemical- chemical reactions, like evaporation or acid rain • Orga ...
... Intrusive rocks are coarse and large. Extrusive are smooth, small. They are usually dark in color. – Sedimentary- made from weathered or broken rocks, found in oceans, lakes, streams, deserts • Clastic- broken pieces held by cement • Chemical- chemical reactions, like evaporation or acid rain • Orga ...
The Earth`s Structure
... The three major types of rocks found in the earth’s crust—sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic—are recycled very slowly by the process of erosion, melting, and metamorphism. ...
... The three major types of rocks found in the earth’s crust—sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic—are recycled very slowly by the process of erosion, melting, and metamorphism. ...
Catastrophic Events – Parts 1-3
... b. The base will be warmer and there will be less oxygen than the top c. The base will be cooler and there will be less oxygen than the top d. The base will be cooler and there will be more oxygen than the top 4. If equal masses of soil and water are placed under a lamp for 30 minutes, which would y ...
... b. The base will be warmer and there will be less oxygen than the top c. The base will be cooler and there will be less oxygen than the top d. The base will be cooler and there will be more oxygen than the top 4. If equal masses of soil and water are placed under a lamp for 30 minutes, which would y ...
Geology - Rock Cycle Notes
... The three major types of rocks found in the earth’s crust—sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic—are recycled very slowly by the process of erosion, melting, and metamorphism. ...
... The three major types of rocks found in the earth’s crust—sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic—are recycled very slowly by the process of erosion, melting, and metamorphism. ...
Geology of the Inner Planets
... NASA's Mariner 10 spacecraft made its first flyby of Mercury in March 1974, and was also the only Mariner mission to visit two planets (the other was Venus). Images beamed back by the spacecraft from 437 miles above the planet revealed a surface very similar to that of the moon. However, Mariner 10 ...
... NASA's Mariner 10 spacecraft made its first flyby of Mercury in March 1974, and was also the only Mariner mission to visit two planets (the other was Venus). Images beamed back by the spacecraft from 437 miles above the planet revealed a surface very similar to that of the moon. However, Mariner 10 ...
chapter 5 ecosystems and the physical environment
... into rivers, lakes, and coastal areas, where it stimulates the growth of algae – as the algae decomposes, bacteria increase and rob the environment of oxygen – fish and other aquatic organisms suffocate • b. combustion of fossil fuels – photochemical smog – injures plant tissues, irritates eyes, and ...
... into rivers, lakes, and coastal areas, where it stimulates the growth of algae – as the algae decomposes, bacteria increase and rob the environment of oxygen – fish and other aquatic organisms suffocate • b. combustion of fossil fuels – photochemical smog – injures plant tissues, irritates eyes, and ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.