Jeopardy Test Review CH 22
... a. A bend in layers of rock b. Many occur along plate boundaries c. Forms where rocks are squeezed, but not break d. A break in a mass of rock where movement happens A. fold ...
... a. A bend in layers of rock b. Many occur along plate boundaries c. Forms where rocks are squeezed, but not break d. A break in a mass of rock where movement happens A. fold ...
APES Review: “140 Ways to go APE(S) For the AP Environmental
... 64. Positive Feedback: when a change in some conditions triggers a response that intensifies the changing condition (warmer Earth—snow melts—less sunlight is reflected and more is absorbed, therefore a warmer Earth) 65. Negative Feedback: when a change in some condition triggers a response that coun ...
... 64. Positive Feedback: when a change in some conditions triggers a response that intensifies the changing condition (warmer Earth—snow melts—less sunlight is reflected and more is absorbed, therefore a warmer Earth) 65. Negative Feedback: when a change in some condition triggers a response that coun ...
APES Review - Magee Science
... 64. Positive Feedback: when a change in some conditions triggers a response that intensifies the changing condition (warmer Earth—snow melts—less sunlight is reflected and more is absorbed, therefore a warmer Earth) 65. Negative Feedback: when a change in some condition triggers a response that coun ...
... 64. Positive Feedback: when a change in some conditions triggers a response that intensifies the changing condition (warmer Earth—snow melts—less sunlight is reflected and more is absorbed, therefore a warmer Earth) 65. Negative Feedback: when a change in some condition triggers a response that coun ...
College Board APES Course Outline
... earthquakes, volcanism; seasons; solar intensity and latitude) The Atmosphere (Composition; structure; weather and climate; atmospheric circulation and the Coriolis Effect; atmosphere–ocean interactions; ENSO) Global Water Resources and Use (Freshwater/saltwater; ocean circulation; agricultural, ind ...
... earthquakes, volcanism; seasons; solar intensity and latitude) The Atmosphere (Composition; structure; weather and climate; atmospheric circulation and the Coriolis Effect; atmosphere–ocean interactions; ENSO) Global Water Resources and Use (Freshwater/saltwater; ocean circulation; agricultural, ind ...
Document
... • Wear down the Earth’s surface and move it around • Result from solar energy and gravity (wind, flowing water) • Weathering – Processes that break rocks down into smaller pieces • Plays key role in soil formation • Different kinds of rock will result in different soil properties ...
... • Wear down the Earth’s surface and move it around • Result from solar energy and gravity (wind, flowing water) • Weathering – Processes that break rocks down into smaller pieces • Plays key role in soil formation • Different kinds of rock will result in different soil properties ...
Name
... For the first two boundaries below the surface (Moho and LithosphereAsthenosphere), it is easier to measure downward (0.35 cm and 1.0 cm) from the surface to adjust the length of the string. Note that converting the depth and radius measurements, in kilometers on the Table, to the 1:10 million s ...
... For the first two boundaries below the surface (Moho and LithosphereAsthenosphere), it is easier to measure downward (0.35 cm and 1.0 cm) from the surface to adjust the length of the string. Note that converting the depth and radius measurements, in kilometers on the Table, to the 1:10 million s ...
Final_Exam_Review_Answer_Key
... 1. Global warming is due to enhanced greenhouse effect. The trapping of carbon dioxide that is “warming” the Earth. If global temperatures continue to increase, many things could happen: more storms, sea level rise, etc. but remember that a whole other group still claims global warming is a “natural ...
... 1. Global warming is due to enhanced greenhouse effect. The trapping of carbon dioxide that is “warming” the Earth. If global temperatures continue to increase, many things could happen: more storms, sea level rise, etc. but remember that a whole other group still claims global warming is a “natural ...
File
... 6. Materials that are M__________ D_______________ sink toward Earth’s center. 7. Earth’s core has two parts, the I__________ C__________ and the O__________ C___________. 8. The O__________ C___________ is L_______________ rock and the I__________ C__________ is S__________ because of the immense a ...
... 6. Materials that are M__________ D_______________ sink toward Earth’s center. 7. Earth’s core has two parts, the I__________ C__________ and the O__________ C___________. 8. The O__________ C___________ is L_______________ rock and the I__________ C__________ is S__________ because of the immense a ...
ExamView - Earth Science Study Guide Final.tst
... ____ 35. What plant will most likely grow first in secondary succession? a. pine tree c. crab grass b. lichen d. hardwood tree ____ 36. The dry prairie ecological community of Florida is found mostly in a. coastal areas. c. North Florida. b. Central Florida. d. South Florida. ____ 37. A byproduct of ...
... ____ 35. What plant will most likely grow first in secondary succession? a. pine tree c. crab grass b. lichen d. hardwood tree ____ 36. The dry prairie ecological community of Florida is found mostly in a. coastal areas. c. North Florida. b. Central Florida. d. South Florida. ____ 37. A byproduct of ...
KEY for Tectonics Study Guide #1
... In the asthenosphere, which is a layer of the mantle 17. Describe how convection currents work. (Begin at the core and tell what happens when the materials heat and then cool). ...
... In the asthenosphere, which is a layer of the mantle 17. Describe how convection currents work. (Begin at the core and tell what happens when the materials heat and then cool). ...
Changing Earth`s Surface
... Changing Earth’s Surface The most important agent of erosion is running water. Running water includes rivers, streams, creeks, melting ice and surface runoff after a rain. When water falls on a sloping landform, the water flows downhill, taking sediment with it. The particles carried by a stream ar ...
... Changing Earth’s Surface The most important agent of erosion is running water. Running water includes rivers, streams, creeks, melting ice and surface runoff after a rain. When water falls on a sloping landform, the water flows downhill, taking sediment with it. The particles carried by a stream ar ...
Chapter 2 – Planet Earth GRA Section Summary
... Energy from the sun, or solar energy, is necessary for life on Earth. It helps plants grow and provides light and heat. Several factors affect the amount of solar energy Earth receives. These are rotation, revolution, tilt, and latitude. Earth’s axis is an imaginary rod running from the North Pole t ...
... Energy from the sun, or solar energy, is necessary for life on Earth. It helps plants grow and provides light and heat. Several factors affect the amount of solar energy Earth receives. These are rotation, revolution, tilt, and latitude. Earth’s axis is an imaginary rod running from the North Pole t ...
APES Review: “155 Ways to go APE(S)” For the AP Environmental
... 64. Positive Feedback: when a change in some conditions triggers a response that intensifies the changing condition (warmer Earth—snow melts—less sunlight is reflected and more is absorbed, therefore a warmer Earth) 65. Negative Feedback: when a change in some condition triggers a response that c ...
... 64. Positive Feedback: when a change in some conditions triggers a response that intensifies the changing condition (warmer Earth—snow melts—less sunlight is reflected and more is absorbed, therefore a warmer Earth) 65. Negative Feedback: when a change in some condition triggers a response that c ...
Slide 1
... but not an exchange of sun light. e. “open or closed”, there is an occasional exchange of matter with energy. ...
... but not an exchange of sun light. e. “open or closed”, there is an occasional exchange of matter with energy. ...
Science Feb 15
... Which characteristic of this area indicates that the soil was formed as a result of the interaction between organisms and their environment? A. ...
... Which characteristic of this area indicates that the soil was formed as a result of the interaction between organisms and their environment? A. ...
Plate Tectonics
... Difficult to fathom as our life spans only 80 Simplified history of Earth – Waugh pg. 9 Oldest rocks are ~ 4 billion years old Found in the Northwest Territories ...
... Difficult to fathom as our life spans only 80 Simplified history of Earth – Waugh pg. 9 Oldest rocks are ~ 4 billion years old Found in the Northwest Territories ...
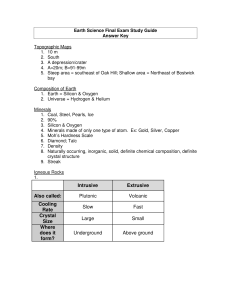
Final Exam Study Guide Answer Key
... 4. Carbonic acid (chemical weathering) draw a profile 5. Quartz 6. Type of cement holding together 7. Rich organic material in soil from decayed organic matter 8. Type of rock & climate Surface Water 1. High land that separates two watersheds 2. The material that a river carries; solution, suspensio ...
... 4. Carbonic acid (chemical weathering) draw a profile 5. Quartz 6. Type of cement holding together 7. Rich organic material in soil from decayed organic matter 8. Type of rock & climate Surface Water 1. High land that separates two watersheds 2. The material that a river carries; solution, suspensio ...
planetesimals - Mestre a casa
... As planetesimals were running out, the impacts ceased and the early Earth began to cool slowly. First fragments of mainland were formed, and the crust, which at first was very thin, was gradually becoming thicker as material into Earth were getting cooler. In the atmosphere, large clouds began to fo ...
... As planetesimals were running out, the impacts ceased and the early Earth began to cool slowly. First fragments of mainland were formed, and the crust, which at first was very thin, was gradually becoming thicker as material into Earth were getting cooler. In the atmosphere, large clouds began to fo ...
Questions from the committee:
... • Platforms for studying the environment and fundamental processes within it in real time (hours, seasons, years, decades) at large scales. ...
... • Platforms for studying the environment and fundamental processes within it in real time (hours, seasons, years, decades) at large scales. ...
3.1.1 - Biosphere
... 25 kilometers and then gradually increases up to the upper boundary of the layer. The amount of water vapor in the stratosphere is very low, so it is not an important factor in the temperature regulation of the layer. Instead, it is ozone (O3) that causes the observed temperature inversion. The thir ...
... 25 kilometers and then gradually increases up to the upper boundary of the layer. The amount of water vapor in the stratosphere is very low, so it is not an important factor in the temperature regulation of the layer. Instead, it is ozone (O3) that causes the observed temperature inversion. The thir ...
Ellen Wohl
... E-mail: [email protected] Area of Research/Teaching Fluvial geomorphology – physical process and form in rivers – with an emphasis on physical -biological and physical-human interactions in rivers. Current research projects focus on organic carbon storage associated with physical complexity i ...
... E-mail: [email protected] Area of Research/Teaching Fluvial geomorphology – physical process and form in rivers – with an emphasis on physical -biological and physical-human interactions in rivers. Current research projects focus on organic carbon storage associated with physical complexity i ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.