angle of inclination
... the latitude on the Earth’s surface where an Fe-rich rock formed, we can use this information to determine the “paleolatitude” for an iron-rich rock. British geophysicists measured the angles of inclination of Ferich rocks of a wide range of ages. What did they find? Each rock recorded a different a ...
... the latitude on the Earth’s surface where an Fe-rich rock formed, we can use this information to determine the “paleolatitude” for an iron-rich rock. British geophysicists measured the angles of inclination of Ferich rocks of a wide range of ages. What did they find? Each rock recorded a different a ...
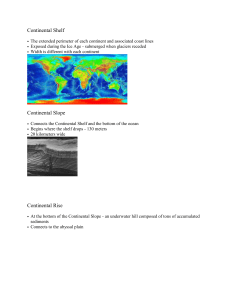
Continental Shelf • The extended perimeter of each continent and
... • The extended perimeter of each continent and associated coast lines • Exposed during the Ice Age - submerged when glaciers receded • Width is different with each continent ...
... • The extended perimeter of each continent and associated coast lines • Exposed during the Ice Age - submerged when glaciers receded • Width is different with each continent ...
Rev. 2013 Fast and Slow Changes to Earth`s Surface Volcano – Fast
... form mountains. This is similar to cars crashing head-on into each other in slow motion. Mountain Building is a slow change in the Earth’s surface. ...
... form mountains. This is similar to cars crashing head-on into each other in slow motion. Mountain Building is a slow change in the Earth’s surface. ...
Protecting the Biosphere
... • The variations in concentration from the Earth to Mars and Venus result from the different processes that influenced the development of each atmosphere. • While Venus is too warm and Mars is too cold for liquid water the Earth is at just such a distance from the Sun that water was able to form in ...
... • The variations in concentration from the Earth to Mars and Venus result from the different processes that influenced the development of each atmosphere. • While Venus is too warm and Mars is too cold for liquid water the Earth is at just such a distance from the Sun that water was able to form in ...
Plate Tectonics
... Continental drift is Wegener’s theory that all continents had once been joined together in a single landmass and have drifted apart since. Wegener named this supercontinent Pangaea. Wegener’s theory was rejected by scientists because he could not explain what force pushes or pulls continents. ...
... Continental drift is Wegener’s theory that all continents had once been joined together in a single landmass and have drifted apart since. Wegener named this supercontinent Pangaea. Wegener’s theory was rejected by scientists because he could not explain what force pushes or pulls continents. ...
Question Set #2 - elyceum-beta
... 5) Is a hard-boiled egg a good model of the Earth’s different interior zones? Explain your answer ...
... 5) Is a hard-boiled egg a good model of the Earth’s different interior zones? Explain your answer ...
Earth`s Structure Worksheet
... made of hot semi rock is located directly below the ________ and is about 1800 miles thick. Lithosphere – made up of the crust and tiny bit of the mantle, this layer is divided into several constantly (very slowly) moving plates of ___________ ________ that hold the continents and oceans Asthenosphe ...
... made of hot semi rock is located directly below the ________ and is about 1800 miles thick. Lithosphere – made up of the crust and tiny bit of the mantle, this layer is divided into several constantly (very slowly) moving plates of ___________ ________ that hold the continents and oceans Asthenosphe ...
Interior Crust Hydrosphere Atmosphere Magnetosphere Tides
... Earth’s Atmosphere The ionosphere is ionized by high energy solar radiation. It is a good conductor. It is heated by absorbed X rays The ionosphere reflects radio waves in the AM range, but it is transparent to FM and TV The ozone layer is between the ionosphere and the mesosphere; it absorbs ultra ...
... Earth’s Atmosphere The ionosphere is ionized by high energy solar radiation. It is a good conductor. It is heated by absorbed X rays The ionosphere reflects radio waves in the AM range, but it is transparent to FM and TV The ozone layer is between the ionosphere and the mesosphere; it absorbs ultra ...
Magma Supply Vs Magma Plumbing
... Earth Plate tectonics replace 2/3 of the surface every ~100 Myr and modifies the remaining 1/3 on geologically short timescales. Evidence at a scale we might see on other planets 1. Linear rifts and arcuate compression zones 2. Transform faults and fracture zones (adjacent transform faults are para ...
... Earth Plate tectonics replace 2/3 of the surface every ~100 Myr and modifies the remaining 1/3 on geologically short timescales. Evidence at a scale we might see on other planets 1. Linear rifts and arcuate compression zones 2. Transform faults and fracture zones (adjacent transform faults are para ...
Key terms are bolded. 1.
... b. convergent (ocean/ocean) can cause volcanoes to form on the ocean floor c. convergent (ocean/continental) leads to volcanic eruptions d. convergent (continental/ continental) can cause the formation of mountain systems e. transform? can cause earthquake activity 62. At which boundary is seafloor ...
... b. convergent (ocean/ocean) can cause volcanoes to form on the ocean floor c. convergent (ocean/continental) leads to volcanic eruptions d. convergent (continental/ continental) can cause the formation of mountain systems e. transform? can cause earthquake activity 62. At which boundary is seafloor ...
Week 27 CCA Review
... Earth is composed of layers. Starting with the center of the earth, they are: Inner Core, Outer Core, Mantle, and Crust. The Inner Core and Outer Core are made of Iron and Nickel. The Inner Core is solid, while the Outer Core is liquid. The Mantle is both a liquid and solid. Think of it as a solid t ...
... Earth is composed of layers. Starting with the center of the earth, they are: Inner Core, Outer Core, Mantle, and Crust. The Inner Core and Outer Core are made of Iron and Nickel. The Inner Core is solid, while the Outer Core is liquid. The Mantle is both a liquid and solid. Think of it as a solid t ...
Chapter 25 The History of Life on Earth 25.3 Key Events in Life`s
... landmasses, & the seas were largely iced over. o The snowball earth hypothesis suggests that most life would have been confined to the first major diversification of multicellular eukaryotes corresponds to when Earth thawed, which happened 40 million years ago The Cambrian Explosion Many present d ...
... landmasses, & the seas were largely iced over. o The snowball earth hypothesis suggests that most life would have been confined to the first major diversification of multicellular eukaryotes corresponds to when Earth thawed, which happened 40 million years ago The Cambrian Explosion Many present d ...
Venus
... • From the perspecVve of the Earth, Venus has phases like our moon. This is because Venus is located inside the orbit of the Earth. And unlike Mars, Jupiter and other planets outside Earth’s orbit, we don’t always see the sunlit side • Clouds are composed of sulfuric acid (H2SO4, really nasty ...
... • From the perspecVve of the Earth, Venus has phases like our moon. This is because Venus is located inside the orbit of the Earth. And unlike Mars, Jupiter and other planets outside Earth’s orbit, we don’t always see the sunlit side • Clouds are composed of sulfuric acid (H2SO4, really nasty ...
Chapter 7, Section 1 Directed Reading A
... while the densest compounds make up the core? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 4. List the three layers of the Earth, based on their chemical composition. A. B. C. 5. Complete Sentence - What three element ...
... while the densest compounds make up the core? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 4. List the three layers of the Earth, based on their chemical composition. A. B. C. 5. Complete Sentence - What three element ...
GEOL1033-SQS07R
... 18. What Earth subdivision is the primary source of magmas & lavas? ____________ 19. What is believed by most geologists to be the driving mechanism for plate tectonics? ______________________________________________________________ 20-22. The 3 agents of erosion are _____________, ______________, & ...
... 18. What Earth subdivision is the primary source of magmas & lavas? ____________ 19. What is believed by most geologists to be the driving mechanism for plate tectonics? ______________________________________________________________ 20-22. The 3 agents of erosion are _____________, ______________, & ...
Layers of the Earth - University of Dayton
... At this point in time an ice age ended The glaciers melted and oceans rose causing water to cover what was previously land ...
... At this point in time an ice age ended The glaciers melted and oceans rose causing water to cover what was previously land ...
Dynamic Notes
... this describes the grounds motion as the waves pass. Travel through solids, liquids or gas. S Waves- Secondary WavesTravel slower than P waves. Also called Side to Side waves because this describes their motion. Only travel through solids. Surface Waves- includes both push-pull motion and side to si ...
... this describes the grounds motion as the waves pass. Travel through solids, liquids or gas. S Waves- Secondary WavesTravel slower than P waves. Also called Side to Side waves because this describes their motion. Only travel through solids. Surface Waves- includes both push-pull motion and side to si ...
460:102 Notes Historical Geology Notes
... 1. Bacteria ➔ the origin of plants and animals C. Physical and biological components are intertwined 1. Must study system as a whole - not individual components 2. Physical environments influence life➔ creates niches for evolutions, hostile environments 3. Biology can influence physical environment ...
... 1. Bacteria ➔ the origin of plants and animals C. Physical and biological components are intertwined 1. Must study system as a whole - not individual components 2. Physical environments influence life➔ creates niches for evolutions, hostile environments 3. Biology can influence physical environment ...
earth interior - Red Hook Central Schools
... 80% of Earth is mantle • Core (outer core = liquid, inner core = solid) made of nickel and iron (magnetic) very dense! Earths interior animation ...
... 80% of Earth is mantle • Core (outer core = liquid, inner core = solid) made of nickel and iron (magnetic) very dense! Earths interior animation ...
Quick Review
... (sandstone, shale, limestone) 3) ___________________: a type of rock formed by the squeezing and heating of rocks deep below the surface of the earth (limestone marble; shale slate) ...
... (sandstone, shale, limestone) 3) ___________________: a type of rock formed by the squeezing and heating of rocks deep below the surface of the earth (limestone marble; shale slate) ...
Part I. The Layers of Earth - www .alexandria .k12 .mn .us
... A. Go to https://www.wisc-online.com/learn/natural-science/earthscience/sce304/heat-transfer--conduction--convection--radiation , then Convection, Conduction and Radiation , and also this Heat Transfer website. 1. How is heat transferred by conduction? _________________________________ _____________ ...
... A. Go to https://www.wisc-online.com/learn/natural-science/earthscience/sce304/heat-transfer--conduction--convection--radiation , then Convection, Conduction and Radiation , and also this Heat Transfer website. 1. How is heat transferred by conduction? _________________________________ _____________ ...
Chapter 34: The Changing Face of the Earth
... deposits of rough, unsorted debris called moraines when they melt. Moraines deposited by ancient glaciers are common landforms in some areas of the northeastern and midwestern parts of the United States. More glaciers seem to be receding than advancing today, but there have been times in the past wh ...
... deposits of rough, unsorted debris called moraines when they melt. Moraines deposited by ancient glaciers are common landforms in some areas of the northeastern and midwestern parts of the United States. More glaciers seem to be receding than advancing today, but there have been times in the past wh ...
Life and Biogeochemical Cycles
... dioxide (SO2) or the particles of sulfate (SO4=) compounds in the air. These compounds either fall out or are rained out of the atmosphere. Plants take up some forms of these compounds and incorporate them into their tissues. Then, as with nitrogen, these organic sulfur compounds are returned to the ...
... dioxide (SO2) or the particles of sulfate (SO4=) compounds in the air. These compounds either fall out or are rained out of the atmosphere. Plants take up some forms of these compounds and incorporate them into their tissues. Then, as with nitrogen, these organic sulfur compounds are returned to the ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.