PowerPoint - Chandra X
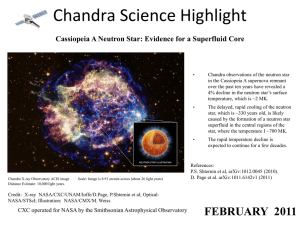
... The delayed, rapid cooling of the neutron star, which is ~330 years old, is likely caused by the formation of a neutron star superfluid in the central regions of the star, where the temperature I ~700 MK. ...
... The delayed, rapid cooling of the neutron star, which is ~330 years old, is likely caused by the formation of a neutron star superfluid in the central regions of the star, where the temperature I ~700 MK. ...
Nineteenth lecture
... Soooooo, ultimately we wind up with the solar system we call HOME. (Ever wonder why all the planets except for Pluto rotate in the same direction around the sun, in a flat plane?) ...
... Soooooo, ultimately we wind up with the solar system we call HOME. (Ever wonder why all the planets except for Pluto rotate in the same direction around the sun, in a flat plane?) ...
The Band of Stability
... Radioactive decay changes the nature of an atom’s nucleus, and it happens for a reason. Each element from hydrogen (atomic number 1) to lead (atomic number 82) has stable isotopes in which the tendency of protons to repel one another is overcome by attractive nuclear forces. These attractive nuclear ...
... Radioactive decay changes the nature of an atom’s nucleus, and it happens for a reason. Each element from hydrogen (atomic number 1) to lead (atomic number 82) has stable isotopes in which the tendency of protons to repel one another is overcome by attractive nuclear forces. These attractive nuclear ...
Chapter 7 Vocabulary212
... 1. Spectroscope- used to study star’s characteristics by spreading light into different wavelengths 2. Nuclear fusion- nuclei of several atoms combine to form on large nucleus 3. astronomical unit- average distance between Earth and Sun (150 million km) 4. light year- distance light travels in 1 yea ...
... 1. Spectroscope- used to study star’s characteristics by spreading light into different wavelengths 2. Nuclear fusion- nuclei of several atoms combine to form on large nucleus 3. astronomical unit- average distance between Earth and Sun (150 million km) 4. light year- distance light travels in 1 yea ...
Nuclear Stability
... • All nuclides with 84 or more protons are unstable with respect to radio active decay. • Light nuclides are stable when neutron/proton = 1. For heavier elements the neutron /proton ratio required for stability is greater than 1 and increases with Z. • Nuclides with even numbers of protons and neutr ...
... • All nuclides with 84 or more protons are unstable with respect to radio active decay. • Light nuclides are stable when neutron/proton = 1. For heavier elements the neutron /proton ratio required for stability is greater than 1 and increases with Z. • Nuclides with even numbers of protons and neutr ...
powerpoint - Physics @ IUPUI
... • The probability of this tunneling is very small, and it depends very highly on how close they get. • This means that how rapidly you fuse protons depends very highly on the temperature (and also on the density squared). • Fusion in the proton – proton chain (sometimes call p-p chain) relies on tem ...
... • The probability of this tunneling is very small, and it depends very highly on how close they get. • This means that how rapidly you fuse protons depends very highly on the temperature (and also on the density squared). • Fusion in the proton – proton chain (sometimes call p-p chain) relies on tem ...
4550-15Lecture33
... Subsequent reactions produced 3He, 4He and a wee bit of Li. Within 20 minutes or so, the universe cooled below 3 x 108 K and nuclear reactions were no longer possible. Some 400,000 years later, the universe had cooled to about 3000 K, cool enough for electrons to be bound to nuclei, forming ...
... Subsequent reactions produced 3He, 4He and a wee bit of Li. Within 20 minutes or so, the universe cooled below 3 x 108 K and nuclear reactions were no longer possible. Some 400,000 years later, the universe had cooled to about 3000 K, cool enough for electrons to be bound to nuclei, forming ...
112501. r-process beam neutron
... nucleosynthesis. Weak rates in this mass region are not well understood: GT strength distributions first-forbidden contribution Fröhlich et al., PRL 96 (2006) ...
... nucleosynthesis. Weak rates in this mass region are not well understood: GT strength distributions first-forbidden contribution Fröhlich et al., PRL 96 (2006) ...
Origin of Elements - Madison Public Schools
... • The Sun has been converting hydrogen to helium for the past 4.5 billion years, and continue to do so for the next 4.5 billion years. • As the Sun runs out of hydrogen, the process will slow down, and the Sun’s core will get hotter and denser, and a new series of reactions will take place: ...
... • The Sun has been converting hydrogen to helium for the past 4.5 billion years, and continue to do so for the next 4.5 billion years. • As the Sun runs out of hydrogen, the process will slow down, and the Sun’s core will get hotter and denser, and a new series of reactions will take place: ...
Another exAmple: expository mode
... stars. Young stars convert hydrogen to helium through a process known as nuclear fusion to produce light. As stars use up this hydrogen, in a process that takes billions of years, they pass through certain phases or stages. In each stage, the star’s brightness, temperature, and size change. The redg ...
... stars. Young stars convert hydrogen to helium through a process known as nuclear fusion to produce light. As stars use up this hydrogen, in a process that takes billions of years, they pass through certain phases or stages. In each stage, the star’s brightness, temperature, and size change. The redg ...
No Slide Title
... Core burns all fuel, from hydrogen all the way to iron: then the star collapses! ...
... Core burns all fuel, from hydrogen all the way to iron: then the star collapses! ...
Nuclear Interactions in Supernovae .
... • The hydrogen is burned in a runaway reaction, and an enormous amount of energy is released from all the hydrogen being fused in a short amount of time. • This causes an explosion on the surface of the dwarf, which doesn’t affect the star, but increases its brightness by 50,000 to 100,000 times tha ...
... • The hydrogen is burned in a runaway reaction, and an enormous amount of energy is released from all the hydrogen being fused in a short amount of time. • This causes an explosion on the surface of the dwarf, which doesn’t affect the star, but increases its brightness by 50,000 to 100,000 times tha ...
Chemistry 1 CP Concept 4 Nuclear Chemistry Study Guide
... 6. Which process always decreases the number of protons by an even number? ________ ________________________________________________________________________ 7. Scientists are investigating the possibility of containing fusion reactions within _____ ___________________________________________________ ...
... 6. Which process always decreases the number of protons by an even number? ________ ________________________________________________________________________ 7. Scientists are investigating the possibility of containing fusion reactions within _____ ___________________________________________________ ...
Vocabulary Terms - Dayton Independent Schools
... together by gravity; most commonly can be elliptical, spiral, and irregular ...
... together by gravity; most commonly can be elliptical, spiral, and irregular ...
Opportunities for low energy nuclear physics with rare isotope
... RIB : nucleosynthesis of heavy elements by r-, gammaand rp-processes ...
... RIB : nucleosynthesis of heavy elements by r-, gammaand rp-processes ...
Astrobiology 101
... supergiant stars. As the core of the supergiant becomes saturated with iron, its pressure and temperature increase. Eventually, the blackbody radiation from the core produces gamma rays powerful enough to break apart the iron atoms in the core. This further increases the pressure to a point where el ...
... supergiant stars. As the core of the supergiant becomes saturated with iron, its pressure and temperature increase. Eventually, the blackbody radiation from the core produces gamma rays powerful enough to break apart the iron atoms in the core. This further increases the pressure to a point where el ...
Nuclear Notes Introduction
... nucleons (E = mc2 ). It can also be thought of as the amount of energy required to break apart the nucleus; therefore, the nuclear binding energy is also a measure of the stability of a nucleus. 5. band of stability- a stable nuclei cluster shown as a neutron to proton ratio a. most stable nuclei ar ...
... nucleons (E = mc2 ). It can also be thought of as the amount of energy required to break apart the nucleus; therefore, the nuclear binding energy is also a measure of the stability of a nucleus. 5. band of stability- a stable nuclei cluster shown as a neutron to proton ratio a. most stable nuclei ar ...
Introduction to Astrophysics Tutorial 4: Supernovae
... (but before actually reaching it), its C is ignited. Because of the high degeneracy (i.e. pressure weakly depends on temperature), the fusion process is a runaway one, burning the entire white dwarf, and producing a spectacular explosion. This process implies that all explosions of this type are ver ...
... (but before actually reaching it), its C is ignited. Because of the high degeneracy (i.e. pressure weakly depends on temperature), the fusion process is a runaway one, burning the entire white dwarf, and producing a spectacular explosion. This process implies that all explosions of this type are ver ...
P-nuclei
p-Nuclei (p stands for proton-rich) are certain proton-rich, naturally occurring isotopes of some elements between selenium and mercury which cannot be produced in either s- or r-process.