A Star’s Life
... b. Search the internet for an appropriate real image. If a real life image is not available, please state this is an artist’s rendering. c. Please share the slide show with me when you create in Google slides. ...
... b. Search the internet for an appropriate real image. If a real life image is not available, please state this is an artist’s rendering. c. Please share the slide show with me when you create in Google slides. ...
Document
... Cosmic-ray (anti-)protons apt to arrive in polar regions Decayed protons trapped to form Van-Allen radiation belts (CRAND; cosmic-ray albedo neutron decay) Lower energy protons well trapped due to life time Higher energy Anti-protons may remain in radiation belts Protons and anti-protons are gathere ...
... Cosmic-ray (anti-)protons apt to arrive in polar regions Decayed protons trapped to form Van-Allen radiation belts (CRAND; cosmic-ray albedo neutron decay) Lower energy protons well trapped due to life time Higher energy Anti-protons may remain in radiation belts Protons and anti-protons are gathere ...
Essay - CLC Charter School
... are crushed together, temperatures reach billions of degrees Celsius, and then a series of nuclear reactions is unleashed. The supernova produces a giant shock wave that throws matter into space at 9,000 to 25,000 miles per second. Type Ia, Ib and Ic Supernovae There are several classes of supernova ...
... are crushed together, temperatures reach billions of degrees Celsius, and then a series of nuclear reactions is unleashed. The supernova produces a giant shock wave that throws matter into space at 9,000 to 25,000 miles per second. Type Ia, Ib and Ic Supernovae There are several classes of supernova ...
Binding Energy1
... # protons = # neutrons Pauli Principle - neutrons and protons have spin like electron, and thus ms= 1/2. ...
... # protons = # neutrons Pauli Principle - neutrons and protons have spin like electron, and thus ms= 1/2. ...
the free PDF resource
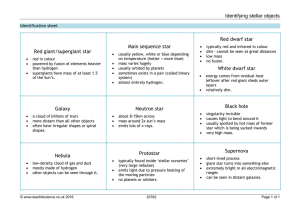
... usually yellow, white or blue depending on temperature (hotter = more blue) mass varies hugely usually orbited by planets sometimes exists in a pair (called binary system) almost entirely hydrogen. ...
... usually yellow, white or blue depending on temperature (hotter = more blue) mass varies hugely usually orbited by planets sometimes exists in a pair (called binary system) almost entirely hydrogen. ...
Abundances - Michigan State University
... (counting all protons including the ones contained in nuclei - not just free protons as described by the “proton abundance”) ...
... (counting all protons including the ones contained in nuclei - not just free protons as described by the “proton abundance”) ...
Neutron Spectroscopic Factors of 34Ar and 46Ar from transfer
... Spectroscopic factors (SF) are fundamental quantities in nuclear physics. They have been extensively used to understand single particle properties of nuclear structure to astrophysical network calculations. A recent analysis of ground state neutron spectroscopic factors from Z=3-24, using the conven ...
... Spectroscopic factors (SF) are fundamental quantities in nuclear physics. They have been extensively used to understand single particle properties of nuclear structure to astrophysical network calculations. A recent analysis of ground state neutron spectroscopic factors from Z=3-24, using the conven ...
ASTR2050 Spring 2005 •
... This is much hotter than the surface of the Sun, but the center of the Sun would be much higher pressure. This is the key to how the Sun and other stars shine! ...
... This is much hotter than the surface of the Sun, but the center of the Sun would be much higher pressure. This is the key to how the Sun and other stars shine! ...
Ch. 21
... 21.1 Life after Death for White Dwarfs A nova is a star that flares up very suddenly and then returns slowly to its former luminosity: ...
... 21.1 Life after Death for White Dwarfs A nova is a star that flares up very suddenly and then returns slowly to its former luminosity: ...
Nuclear Structure Studies of Neutron
... density profiles are however expected at the drip-line and in the region of super-heavy nuclei. Dripline nuclei are expected to display increased surface diffuseness (see Fig. 1) making the derivative of the nuclear density along the surface weaker and thus the SO splitting smaller. This increased d ...
... density profiles are however expected at the drip-line and in the region of super-heavy nuclei. Dripline nuclei are expected to display increased surface diffuseness (see Fig. 1) making the derivative of the nuclear density along the surface weaker and thus the SO splitting smaller. This increased d ...
first lecture - الدكتورة / زينب بنت زكي الفل
... Nuclei with the same Z, but different A are called isotopes. A particular element with a given Z may have isotopes of different mass numbers. Their nuclei contain the same number of protons and different number of neutrons. Isotopes were first discovered amongst naturally radioactive elements J.J. T ...
... Nuclei with the same Z, but different A are called isotopes. A particular element with a given Z may have isotopes of different mass numbers. Their nuclei contain the same number of protons and different number of neutrons. Isotopes were first discovered amongst naturally radioactive elements J.J. T ...
THE INCREDIBLE ORIGIN OF THE CHEMICAL ELEMENTS
... as our Sun, or heavier, shrink catastrophically, forming "neutron stars1" or even "black holes2". In many cases an enormous explosion (known as a "supernova") results, throwing much of the outer part of the star into space. During it's dying moments, just before it explodes, the temperature of the s ...
... as our Sun, or heavier, shrink catastrophically, forming "neutron stars1" or even "black holes2". In many cases an enormous explosion (known as a "supernova") results, throwing much of the outer part of the star into space. During it's dying moments, just before it explodes, the temperature of the s ...
Particle Physics at Soudan These questions will help you prepare
... (indivisible) particle called a lepton. It’s a lot smaller than a proton or neutron, with: me = 9.11X10-31 kg & mp and n = 1.67X10-27 kg How many electrons make up the same mass as a proton? Answer:________________ The electron neutrino (ve) is a neutral particle partnered with the electron in proce ...
... (indivisible) particle called a lepton. It’s a lot smaller than a proton or neutron, with: me = 9.11X10-31 kg & mp and n = 1.67X10-27 kg How many electrons make up the same mass as a proton? Answer:________________ The electron neutrino (ve) is a neutral particle partnered with the electron in proce ...
Introduction - Departamento de Astronomía
... the falling matter becames very hot and expands outwards. Finally, the star explodes and ejects the star’s outer layers into space. All that remains of is a very dense object: neutron star or black hole ...
... the falling matter becames very hot and expands outwards. Finally, the star explodes and ejects the star’s outer layers into space. All that remains of is a very dense object: neutron star or black hole ...
Nuclear Reactions and Their Applications
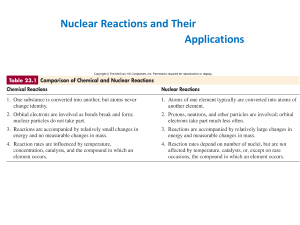
... Light nuclides are stable when Z equals A – Z (neutron/proton ratio is 1). For heavier elements the neutron/proton ratio required for stability is greater than 1 and increases with Z. Certain combinations of protons and neutrons seem to confer special stability. – Even numbers of protons and neutron ...
... Light nuclides are stable when Z equals A – Z (neutron/proton ratio is 1). For heavier elements the neutron/proton ratio required for stability is greater than 1 and increases with Z. Certain combinations of protons and neutrons seem to confer special stability. – Even numbers of protons and neutron ...
Stellar Explosions
... Life after Death for White Dwarfs A nova is a star that flares up very suddenly and then returns slowly to its former luminosity: ...
... Life after Death for White Dwarfs A nova is a star that flares up very suddenly and then returns slowly to its former luminosity: ...
document
... Usually involve atoms with large nucleii such as the Lathanides and Actinides They produce , and emissions. Involve a nucleus collapsing to form a smaller nucleus ...
... Usually involve atoms with large nucleii such as the Lathanides and Actinides They produce , and emissions. Involve a nucleus collapsing to form a smaller nucleus ...
Homework 1
... released in Joules from burning 1 mole of ethanol to the energy released from 1 mole of 235U above. ...
... released in Joules from burning 1 mole of ethanol to the energy released from 1 mole of 235U above. ...
Supernovae - Cloudfront.net
... binary system die the results can be explosive The more massive star will die first Its death will not be unlike the Sun’s though the other star will affect the form of the planetary nebula. Producing nebulae like the When the second becomes a red Rose Nebula giant it will trigger a type 1a super no ...
... binary system die the results can be explosive The more massive star will die first Its death will not be unlike the Sun’s though the other star will affect the form of the planetary nebula. Producing nebulae like the When the second becomes a red Rose Nebula giant it will trigger a type 1a super no ...
P-nuclei
p-Nuclei (p stands for proton-rich) are certain proton-rich, naturally occurring isotopes of some elements between selenium and mercury which cannot be produced in either s- or r-process.