transition
... The universe is a cooling expanding sea of photons and small pieces of slightly clumped matter. The Universe remains ionized as the electrons can not yet recombine with the protons to make neutral hydrogen. When the temperature cools to 3000K, recombination happens, the surface of last scattering is ...
... The universe is a cooling expanding sea of photons and small pieces of slightly clumped matter. The Universe remains ionized as the electrons can not yet recombine with the protons to make neutral hydrogen. When the temperature cools to 3000K, recombination happens, the surface of last scattering is ...
How do stars shine?
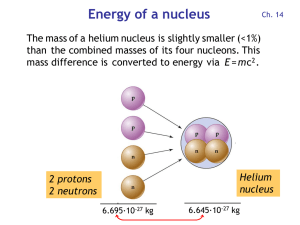
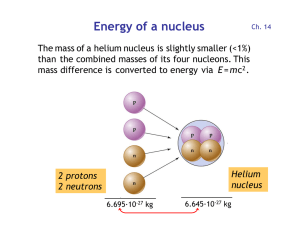
... the famous equation E=mc2, and suddenly new possibilities opened up for sources of power. Einstein’s famous equation means we can convert mass into energy, and c, being the speed of light, and a very big number, then squared, means a small amount of mass can make a lot of energy. It was known throug ...
... the famous equation E=mc2, and suddenly new possibilities opened up for sources of power. Einstein’s famous equation means we can convert mass into energy, and c, being the speed of light, and a very big number, then squared, means a small amount of mass can make a lot of energy. It was known throug ...
The “Big Bang” Theory
... • These life forms were the simplest form of life – _______ _________. • There is evidence of multi-cellular life as far back as ___________ years. • As organisms with _________ and eventually __________ arrive the fossil record becomes more detailed because these are more easily ___________. ...
... • These life forms were the simplest form of life – _______ _________. • There is evidence of multi-cellular life as far back as ___________ years. • As organisms with _________ and eventually __________ arrive the fossil record becomes more detailed because these are more easily ___________. ...
Facts - GreenSpirit
... In the middle of these condensation points, pressure of the gases build producing heat ...
... In the middle of these condensation points, pressure of the gases build producing heat ...
Energy of a nucleus
... When Fe and Ni are reached, fusion stops. The star has burnt its nuclear fuel and collapses under its own gravity. • In massive stars, this collapse releases a huge amount of gravitational energy that leads to a supernova.The outer 90% of the star is ejected, and the center becomes either a black ho ...
... When Fe and Ni are reached, fusion stops. The star has burnt its nuclear fuel and collapses under its own gravity. • In massive stars, this collapse releases a huge amount of gravitational energy that leads to a supernova.The outer 90% of the star is ejected, and the center becomes either a black ho ...
Chem 1721 Brief Notes: Chapter 20 Chapter 20: Nuclear Chemistry
... atomic number = # protons in the nucleus; this does not change for atoms of a specific element i.e. every atom of calcium has 20 protons in the nucleus if the number of protons changes the identity of the element changes mass number = # protons + # neutrons; mass number can change because the number ...
... atomic number = # protons in the nucleus; this does not change for atoms of a specific element i.e. every atom of calcium has 20 protons in the nucleus if the number of protons changes the identity of the element changes mass number = # protons + # neutrons; mass number can change because the number ...
Document
... • Gravity pulls the core of the star to a size smaller than the Earth’s diameter. • The core compresses so much that protons and electrons merge into neutrons, taking energy away from the core. • The core collapses, and the layers above fall rapidly toward the center, where they collide with the cor ...
... • Gravity pulls the core of the star to a size smaller than the Earth’s diameter. • The core compresses so much that protons and electrons merge into neutrons, taking energy away from the core. • The core collapses, and the layers above fall rapidly toward the center, where they collide with the cor ...
Stellar Evolution Notes
... formed iron, no more reactions can occur, and the core violently collapses in on itself Supernova ...
... formed iron, no more reactions can occur, and the core violently collapses in on itself Supernova ...
Homework problems for Quiz 2: AY5 Spring 2015
... The reason main-sequence stars do not collapse due to gravity is the thermal pressure of the gases they are composed of The fuel that provides the energy source for main-sequence stars is mass A star that is not in hydrostatic equilibrium with react by changing its radius 7. How much energy is produ ...
... The reason main-sequence stars do not collapse due to gravity is the thermal pressure of the gases they are composed of The fuel that provides the energy source for main-sequence stars is mass A star that is not in hydrostatic equilibrium with react by changing its radius 7. How much energy is produ ...
Where Do Chemical Elements Come From?
... force of gravity resulting from all of the matter above the core, and the core collapses under its own weight. ...
... force of gravity resulting from all of the matter above the core, and the core collapses under its own weight. ...
Review: How does a star`s mass determine its life story?
... white dwarf limit and collapses into a neutron star, causing explosion White dwarf supernova: Carbon fusion suddenly begins as white dwarf in close binary system reaches white dwarf limit, causing total explosion ...
... white dwarf limit and collapses into a neutron star, causing explosion White dwarf supernova: Carbon fusion suddenly begins as white dwarf in close binary system reaches white dwarf limit, causing total explosion ...
Stellar Evolution: 33.2
... • If more massive stars, more elements can be fused (C-Ne-O-Si–Fe) , red giant becomes larger. • Fe core is formed and when the temperature gets hot enough, photodisintegration (nuclei break up) occurs, and the core collapses. • 1s = core the size of earth to 10km radius of neutrons. Inverse beta de ...
... • If more massive stars, more elements can be fused (C-Ne-O-Si–Fe) , red giant becomes larger. • Fe core is formed and when the temperature gets hot enough, photodisintegration (nuclei break up) occurs, and the core collapses. • 1s = core the size of earth to 10km radius of neutrons. Inverse beta de ...
Chapter 27.2
... brightness to increase by thousands of times for a few days. • Believed to be caused by gas (from a companion star) buildup on the white dwarf’s surface. ...
... brightness to increase by thousands of times for a few days. • Believed to be caused by gas (from a companion star) buildup on the white dwarf’s surface. ...
Isotope Half-Life Radiation Emitted
... B. Exposure A.Background radiation All around us from stars, rocks, etc. Earth’s atmosphere and magnetic field stops most of the cosmic radiation. ...
... B. Exposure A.Background radiation All around us from stars, rocks, etc. Earth’s atmosphere and magnetic field stops most of the cosmic radiation. ...
File
... A neutral atom consists of a positively charged nucleus (composed of protons and neutrons) associated with orbital electrons. The atomic number (Z) is the number of protons in the nucleus The neutron number (N) is the number of neutrons in the nucleus. The mass number (A) is the sum of the protons a ...
... A neutral atom consists of a positively charged nucleus (composed of protons and neutrons) associated with orbital electrons. The atomic number (Z) is the number of protons in the nucleus The neutron number (N) is the number of neutrons in the nucleus. The mass number (A) is the sum of the protons a ...
nuclear force
... that of an electron, but has a positive charge. • A positron is emitted from the nucleus as a proton is converted into a neutron. • The atomic number decreases by one but the mass number stays the same. ...
... that of an electron, but has a positive charge. • A positron is emitted from the nucleus as a proton is converted into a neutron. • The atomic number decreases by one but the mass number stays the same. ...
Initial Evolution-The Main Sequence
... Two scenarios: stars with as mass less than 8 times the mass of the sun and stars with a mass greater than 8 times the mass of the sun. ...
... Two scenarios: stars with as mass less than 8 times the mass of the sun and stars with a mass greater than 8 times the mass of the sun. ...
The Sun`s Size, Heat, and Structure
... largest star known, Epsilon Aurigae, would be the size of a football field. ...
... largest star known, Epsilon Aurigae, would be the size of a football field. ...
Elements and Isotopes - University of California, Berkeley
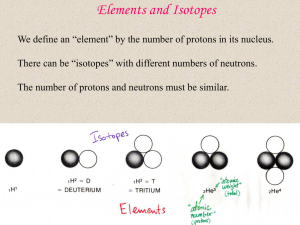
... We define an “element” by the number of protons in its nucleus. There can be “isotopes” with different numbers of neutrons. The number of protons and neutrons must be similar. ...
... We define an “element” by the number of protons in its nucleus. There can be “isotopes” with different numbers of neutrons. The number of protons and neutrons must be similar. ...
P-nuclei
p-Nuclei (p stands for proton-rich) are certain proton-rich, naturally occurring isotopes of some elements between selenium and mercury which cannot be produced in either s- or r-process.