Stellar energy - schoolphysics
... Part of the energy in the first reaction is high-speed neutrinos and these can be detected on the Earth. Note: the apparent imbalance between particles in these equations can be understood if we look at the first of these. On the left we have two protons and no neutrons. On the right we have one pro ...
... Part of the energy in the first reaction is high-speed neutrinos and these can be detected on the Earth. Note: the apparent imbalance between particles in these equations can be understood if we look at the first of these. On the left we have two protons and no neutrons. On the right we have one pro ...
大爆炸---宇宙的起源 - 中正大學化學系
... silicon burning starts at this point. Silicon burning entails the alpha process which creates new elements by adding the equivalent of one helium nucleus (two protons plus two neutrons) per step in the following sequence: (to Fe and Ni) ...
... silicon burning starts at this point. Silicon burning entails the alpha process which creates new elements by adding the equivalent of one helium nucleus (two protons plus two neutrons) per step in the following sequence: (to Fe and Ni) ...
Document
... • Per unit volume, an atom bomb may be millions or billions of times more powerful than TNT. • Nuclear reactions (rxn) occur: neutrons r fired @ closely packed atoms w/ heavy nuclei (uranium or plutonium isotopes). ...
... • Per unit volume, an atom bomb may be millions or billions of times more powerful than TNT. • Nuclear reactions (rxn) occur: neutrons r fired @ closely packed atoms w/ heavy nuclei (uranium or plutonium isotopes). ...
Name: Notes – #54 White Dwarf Supernovae
... 9. Radioactive nickel is created that then decays into _______________ and then into ________________. In the process _________________________ (very high energy light) is produced. 10. How much nickel is formed during a Type 1a supernova explosion? 11. What would we see if the radioactive nickel a ...
... 9. Radioactive nickel is created that then decays into _______________ and then into ________________. In the process _________________________ (very high energy light) is produced. 10. How much nickel is formed during a Type 1a supernova explosion? 11. What would we see if the radioactive nickel a ...
Chapter 19 Nuclear Chemistry
... • Nuclides with 84 or more protons are unstable. • Light nuclides are stable when Z equals A – Z (neutron/proton ratio is 1). • For heavier elements the neutron/proton ratio required for stability is greater than 1 and increases with Z. ...
... • Nuclides with 84 or more protons are unstable. • Light nuclides are stable when Z equals A – Z (neutron/proton ratio is 1). • For heavier elements the neutron/proton ratio required for stability is greater than 1 and increases with Z. ...
radioactive decay - Aurora City Schools
... • Atomic number (Z) tells you number of protons – Always the same for an element; change the atomic number and you change the element ...
... • Atomic number (Z) tells you number of protons – Always the same for an element; change the atomic number and you change the element ...
The Emerging Theory of Supernova Explosions
... Talk Title: "The Emerging Theory of Supernova Explosions" Abstract: Core-collapse supernovae have challenged theorists and computational science for half a century. Such explosions are the source of many of the heavy elements in the Universe and the birthplace of neutron stars and stellar-mass black ...
... Talk Title: "The Emerging Theory of Supernova Explosions" Abstract: Core-collapse supernovae have challenged theorists and computational science for half a century. Such explosions are the source of many of the heavy elements in the Universe and the birthplace of neutron stars and stellar-mass black ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... electrons of atoms are forced into the nucleus. The protons join with the electrons to form neutrons. Each atom is 100,000 times smaller for the same mass and so incredibly dense. This creates a large ‘gravity well’. ...
... electrons of atoms are forced into the nucleus. The protons join with the electrons to form neutrons. Each atom is 100,000 times smaller for the same mass and so incredibly dense. This creates a large ‘gravity well’. ...
NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
... 6. Label the following decay sequence as α or β emission: 238 U 234 Th 234 Pa 230 Th 226 Ra 222 Rn ...
... 6. Label the following decay sequence as α or β emission: 238 U 234 Th 234 Pa 230 Th 226 Ra 222 Rn ...
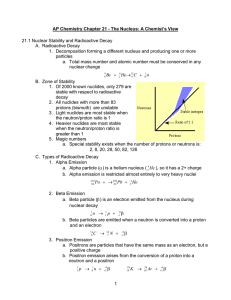
1 AP Chemistry Chapter 21 - The Nucleus: A Chemist`s View 21.1
... 2. The mass of the products is less than the mass of the reactants. Missing mass is converted to energy B. Chain Reaction 1. A reaction in which the material that starts the reaction is also one of the products and can start another reaction ...
... 2. The mass of the products is less than the mass of the reactants. Missing mass is converted to energy B. Chain Reaction 1. A reaction in which the material that starts the reaction is also one of the products and can start another reaction ...
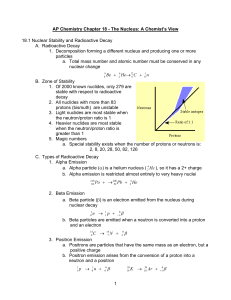
Chapter 18 Notes
... 2. The mass of the products is less than the mass of the reactants. Missing mass is converted to energy B. Chain Reaction 1. A reaction in which the material that starts the reaction is also one of the products and can start another reaction ...
... 2. The mass of the products is less than the mass of the reactants. Missing mass is converted to energy B. Chain Reaction 1. A reaction in which the material that starts the reaction is also one of the products and can start another reaction ...
Lund Observatory Department of Astronomy and Theoretical Physics
... Department of Astronomy and Theoretical Physics LUND ...
... Department of Astronomy and Theoretical Physics LUND ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... • N/P ratio of stable nuclei • Stable small atoms (atomic # less than 20) are near 1/1 ratio • Stable large atoms are near 1.5/1 ratio. • Predict the stability of the following: carbon-12 mercury-200 hydrogen-3 uranium-238 ...
... • N/P ratio of stable nuclei • Stable small atoms (atomic # less than 20) are near 1/1 ratio • Stable large atoms are near 1.5/1 ratio. • Predict the stability of the following: carbon-12 mercury-200 hydrogen-3 uranium-238 ...
MAJOR NUCLEAR BURNING STAGES The Coulomb barrier is
... Three general principles influence the roles that these nuclear burning stages may play: 1.Successive nuclear burning stages, involving more massive nuclei with higher charges, will require increasingly high temperatures to overcome the increased electrical repulsion. 2.The amount of energy released ...
... Three general principles influence the roles that these nuclear burning stages may play: 1.Successive nuclear burning stages, involving more massive nuclei with higher charges, will require increasingly high temperatures to overcome the increased electrical repulsion. 2.The amount of energy released ...
Nuclear Notes
... A crucial factor in the stability of a nucleus is the ratio of neutron number to proton number. Nuclides with more the 20 protons require a larger number of neutrons than protons to moderate the effect of increasing proton repulsions. (Nuclides with less that 20 protons tend to have an equal number ...
... A crucial factor in the stability of a nucleus is the ratio of neutron number to proton number. Nuclides with more the 20 protons require a larger number of neutrons than protons to moderate the effect of increasing proton repulsions. (Nuclides with less that 20 protons tend to have an equal number ...
Supernova
... • Broken nuclei fuse with iron to create heavy elements. • This matter goes to form new stars and planets. ...
... • Broken nuclei fuse with iron to create heavy elements. • This matter goes to form new stars and planets. ...
A SUMMARY OF SELF
... 1. Write down the semi-empirical mass formula (you do not have to give numerical values of constants) and give a motivation for the different terms. 2. Derive an expression for the β-stability line. 3. Discuss different types of instability in atomic nuclei. In which part of the nuclear chart are th ...
... 1. Write down the semi-empirical mass formula (you do not have to give numerical values of constants) and give a motivation for the different terms. 2. Derive an expression for the β-stability line. 3. Discuss different types of instability in atomic nuclei. In which part of the nuclear chart are th ...
How the Universe Works Extreme Stars Name 1. When a star dies
... How the Universe Works Extreme Stars Name _______________ 1. When a star dies (gravity) (fusion) wins out. 2. The sun will run out of fuel in about (3) (7) (10) billion years. 3. When the sun runs out of hydrogen fuel, it will become a (red giant) (neutron star) (black hole). 4. Eventually, the heli ...
... How the Universe Works Extreme Stars Name _______________ 1. When a star dies (gravity) (fusion) wins out. 2. The sun will run out of fuel in about (3) (7) (10) billion years. 3. When the sun runs out of hydrogen fuel, it will become a (red giant) (neutron star) (black hole). 4. Eventually, the heli ...
SIMPLE NUCLEAR REACTIONS
... When a reaction causes a change to occur within the nucleus of an atom it is called a nuclear reaction. When balancing nuclear reactions, the sum of the mass numbers on both sides must be the same and the sum of the atomic numbers on both sides must be the same. NUCLEAR FUSION: This type of reaction ...
... When a reaction causes a change to occur within the nucleus of an atom it is called a nuclear reaction. When balancing nuclear reactions, the sum of the mass numbers on both sides must be the same and the sum of the atomic numbers on both sides must be the same. NUCLEAR FUSION: This type of reaction ...
P-nuclei
p-Nuclei (p stands for proton-rich) are certain proton-rich, naturally occurring isotopes of some elements between selenium and mercury which cannot be produced in either s- or r-process.