CHM 123-Chapter 2.7
... Protons: Atomic number (Z) is the number of protons in the nucleus of an element The atomic number defines the identity of an element. No two elements have the same atomic number Elements are ordered in the periodic table according to their atomic number. Neutrons: Atoms of a given element must all ...
... Protons: Atomic number (Z) is the number of protons in the nucleus of an element The atomic number defines the identity of an element. No two elements have the same atomic number Elements are ordered in the periodic table according to their atomic number. Neutrons: Atoms of a given element must all ...
Supernovae Type II
... nuclear density from the supernuclear density. We can think of the protons and neutrons as bags of quarks bound together by very strong springs (spring constant 10 GeV/fm2) which are compressed by the collapse, but then spring back to equilibrium, thus the bounce. 7. The bounce sends a shock wave ou ...
... nuclear density from the supernuclear density. We can think of the protons and neutrons as bags of quarks bound together by very strong springs (spring constant 10 GeV/fm2) which are compressed by the collapse, but then spring back to equilibrium, thus the bounce. 7. The bounce sends a shock wave ou ...
NOVAE and SUPERNOVAE
... WD. More violent (and luminous) novae occur less frequently. Novae can ONLY occur in close binary star systems, where the possibility for mass transfer exists. Single white dwarfs do not become novae; they slowly cool over billions of years, becoming a dead stellar “ember”. During a nova, some o ...
... WD. More violent (and luminous) novae occur less frequently. Novae can ONLY occur in close binary star systems, where the possibility for mass transfer exists. Single white dwarfs do not become novae; they slowly cool over billions of years, becoming a dead stellar “ember”. During a nova, some o ...
Supernovae, Neutron Stars, Black Holes
... Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology One of the most amazing discoveries in space science is the unambiguous evidence from meteorites that the solar nebula (the cloud of gas and dust in which the Sun and planets formed) contained radioactive isotopes with half-lives so short that they no ...
... Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology One of the most amazing discoveries in space science is the unambiguous evidence from meteorites that the solar nebula (the cloud of gas and dust in which the Sun and planets formed) contained radioactive isotopes with half-lives so short that they no ...
PHY320 Glossary of Terms - The University of Sheffield
... maintains stars while they are on the main sequence. Supernovae signal the explosive end of a massive star's life. They are thought to be responsible for most of the element production in the Universe. They are also the means whereby this synthesised material is dispersed in clouds out of which new ...
... maintains stars while they are on the main sequence. Supernovae signal the explosive end of a massive star's life. They are thought to be responsible for most of the element production in the Universe. They are also the means whereby this synthesised material is dispersed in clouds out of which new ...
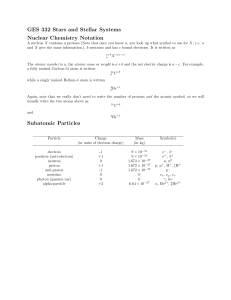
Nuclear Physics, Chemistry and Notation
... The atomic number is a, the atomic mass or weight is a + b and the net electric charge is a − c. For example, a fully ionized Carbon-14 atom is written ...
... The atomic number is a, the atomic mass or weight is a + b and the net electric charge is a − c. For example, a fully ionized Carbon-14 atom is written ...
gelletly-Charterhouse2-elements
... Neutron-Induced Reactions. In the years following its discovery Rutherford’s prediction that such a particle would readily interact with nuclei was amply fulfilled. The importance of the neutron capture reaction was highlighted by the work of E.Fermi and his collaborators. They produced many new ...
... Neutron-Induced Reactions. In the years following its discovery Rutherford’s prediction that such a particle would readily interact with nuclei was amply fulfilled. The importance of the neutron capture reaction was highlighted by the work of E.Fermi and his collaborators. They produced many new ...
regan-gas-10jul2010
... Medieval alchemist…trying to turn base metals into gold… Mistake…to try and use ‘chemistry’…needed nuclear physics ...
... Medieval alchemist…trying to turn base metals into gold… Mistake…to try and use ‘chemistry’…needed nuclear physics ...
Topic 12- Nuclear Chem Reg Rev
... 8. Energy released from nuclear reactions is much greater than energy released from chemical reactions ...
... 8. Energy released from nuclear reactions is much greater than energy released from chemical reactions ...
Unit_Phys_2_nuclear_fusion__fission
... Nuclear fusion a) Nuclear fusion is the joining of two atomic nuclei to form a larger one. b) Nuclear fusion is the process by which energy is released in stars. c) Stars form when enough dust and gas from space is pulled together by gravitational attraction. Smaller masses may also form and be attr ...
... Nuclear fusion a) Nuclear fusion is the joining of two atomic nuclei to form a larger one. b) Nuclear fusion is the process by which energy is released in stars. c) Stars form when enough dust and gas from space is pulled together by gravitational attraction. Smaller masses may also form and be attr ...
Prep Homework Solutions for HW due 10/04/10
... the white dwarf apart since it is not composed of “normal” matter that could expand and cool to achieve hydrostatic equilibrium. Thermonuclear supernovae differ from core-collapse supernovae in that they have a completely different source of energy (nuclear fusion rather than gravitational collapse ...
... the white dwarf apart since it is not composed of “normal” matter that could expand and cool to achieve hydrostatic equilibrium. Thermonuclear supernovae differ from core-collapse supernovae in that they have a completely different source of energy (nuclear fusion rather than gravitational collapse ...
The Interior Structure of Neutron Stars
... Beyond Neutron Drip & Complications Neutron drip proceeds from ρdrip=(4.3)(1014)kg/m3 until all nuclei have dripped free of nuclei by ρnuclear=(2.7)(1017)kg/m3 At very slightly higher densities we reach the muon Fermi energy and these will be created & we have neutron fluid + proton fluid + electro ...
... Beyond Neutron Drip & Complications Neutron drip proceeds from ρdrip=(4.3)(1014)kg/m3 until all nuclei have dripped free of nuclei by ρnuclear=(2.7)(1017)kg/m3 At very slightly higher densities we reach the muon Fermi energy and these will be created & we have neutron fluid + proton fluid + electro ...
atoms, three states of matter.
... The Kelvin scale is based upon the absolute zero point where the velocity of gas atoms or molecules would be zero. That is, 0 K corresponds to -273o C. The relationship between the Celsius and Kelvin scales is then ...
... The Kelvin scale is based upon the absolute zero point where the velocity of gas atoms or molecules would be zero. That is, 0 K corresponds to -273o C. The relationship between the Celsius and Kelvin scales is then ...
Nuclear Astrophysics (a Cosmic Cookbook)
... • In binary systems, one star can evolve to a compact white dwarf while the other can become a red giant • hydrogen-rich material is transferred (or accreted ) onto the white dwarf surface • the temperature and density get so high that hydrogen starts to fuse with carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and heavie ...
... • In binary systems, one star can evolve to a compact white dwarf while the other can become a red giant • hydrogen-rich material is transferred (or accreted ) onto the white dwarf surface • the temperature and density get so high that hydrogen starts to fuse with carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and heavie ...
atoms - Groupfusion.net
... Isotopes = atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons. = same atomic number ; different mass number Almost all elements have isotopes. Some have many and some have only a few. The isotopes of an element always occur in the same percentage. Isotopes of ...
... Isotopes = atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons. = same atomic number ; different mass number Almost all elements have isotopes. Some have many and some have only a few. The isotopes of an element always occur in the same percentage. Isotopes of ...
P-nuclei
p-Nuclei (p stands for proton-rich) are certain proton-rich, naturally occurring isotopes of some elements between selenium and mercury which cannot be produced in either s- or r-process.