AST301.Ch21.StellarExpl - University of Texas Astronomy
... Death of a High-Mass Star In short: Envelope explodes as a core collapse supernova. The core implodes and ends up as a neutron star or (more massive) a black hole. Let’s see how this occurs. (Remember, this is all theoretical calculations, but later you’ll see that there is surprising observational ...
... Death of a High-Mass Star In short: Envelope explodes as a core collapse supernova. The core implodes and ends up as a neutron star or (more massive) a black hole. Let’s see how this occurs. (Remember, this is all theoretical calculations, but later you’ll see that there is surprising observational ...
Chapter 32 Nuclear Physics
... The nucleus of an atom is incredibly small. The diameter of the nucleus is about 100,000 times smaller than the diameter of the atom. Although small, the nucleus contains more than 99.9% of the mass of an atom, because each of its constitutes (protons and neutrons) is about 1800 times more massive t ...
... The nucleus of an atom is incredibly small. The diameter of the nucleus is about 100,000 times smaller than the diameter of the atom. Although small, the nucleus contains more than 99.9% of the mass of an atom, because each of its constitutes (protons and neutrons) is about 1800 times more massive t ...
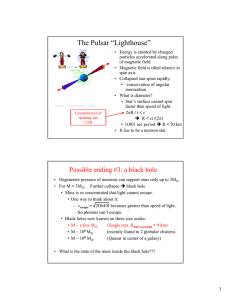
The Pulsar “Lighthouse”
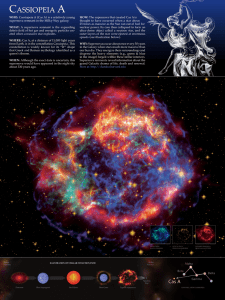
... This material ejected in 1843. • Major brightening recorded. • Ejected 3 M • 2nd brightest star in sky at that time. Brightness Î ...
... This material ejected in 1843. • Major brightening recorded. • Ejected 3 M • 2nd brightest star in sky at that time. Brightness Î ...
White dwarfs - University of Toronto
... A Type Ia supernova more than twice as bright as others of its type has been observed, suggesting it arose from a star that managed to grow more massive than the Chandrasekhar limit. This mass cut-off was thought to make all such supernovae explode with about the same intrinsic brightness, allowing ...
... A Type Ia supernova more than twice as bright as others of its type has been observed, suggesting it arose from a star that managed to grow more massive than the Chandrasekhar limit. This mass cut-off was thought to make all such supernovae explode with about the same intrinsic brightness, allowing ...
Lecture 33
... • A few seconds after the Big Bang, the main particle species present were protons, neutrons, neutrinos, and photons ...
... • A few seconds after the Big Bang, the main particle species present were protons, neutrons, neutrinos, and photons ...
Star Life Cycle Web Quiz
... Fill in the Chart: In order for a star to continue to exist as a ball of radiant energy it must have equilibrium between two strong forces. Fill in the chart below in each of the 3 columns. What is each force? ...
... Fill in the Chart: In order for a star to continue to exist as a ball of radiant energy it must have equilibrium between two strong forces. Fill in the chart below in each of the 3 columns. What is each force? ...
Chapter 28 Vocabulary
... Main sequence star - A star that is at the point in its life cycle in which it is actively fusing hydrogen nuclei into helium nuclei; also the band of the Hertzsprun-Russell diagram depicting such stars. ...
... Main sequence star - A star that is at the point in its life cycle in which it is actively fusing hydrogen nuclei into helium nuclei; also the band of the Hertzsprun-Russell diagram depicting such stars. ...
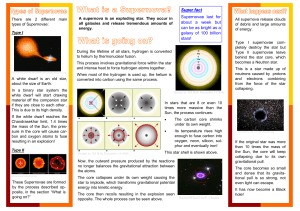
What is a supernova - University of Warwick
... When most of the hydrogen is used up, the helium is converted into carbon using the same process. ...
... When most of the hydrogen is used up, the helium is converted into carbon using the same process. ...
The Evolution of the Universe: from Cosmic Soup to Earth
... Element: a pure chemical substance which is determined by the number of protons in its nucleus. For example, hydrogen is the lightest element with 1 proton while something more interesting and shiny like gold has 79 protons. The only way elements can be created is via nucleosynthesis and not via ...
... Element: a pure chemical substance which is determined by the number of protons in its nucleus. For example, hydrogen is the lightest element with 1 proton while something more interesting and shiny like gold has 79 protons. The only way elements can be created is via nucleosynthesis and not via ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... •When atomic nuclei form a nucleus •Hydrogen fuses into helium •All stars (low and high mass) go through this •How long a star lives depends on its mass •Small stars use their fuel slow = longer lives ...
... •When atomic nuclei form a nucleus •Hydrogen fuses into helium •All stars (low and high mass) go through this •How long a star lives depends on its mass •Small stars use their fuel slow = longer lives ...
A-105 Homework 1
... 19. (1 pt.) If a star the size of the sun collapses to form a white dwarf the size of Earth, by what factor will its density increase? (The volume of a sphere is 43 r 3 . See Appendix A for the radii of the sun and Earth.) ...
... 19. (1 pt.) If a star the size of the sun collapses to form a white dwarf the size of Earth, by what factor will its density increase? (The volume of a sphere is 43 r 3 . See Appendix A for the radii of the sun and Earth.) ...
Evolution and the Big Bang, ET Life Lec. 6, Jan 18, 2002
... capture electrons to form chemical elements). Nuclei are made of protons and neutrons. These particles have similar mass but only protons have an electric charge. Protons and neutrons are each made of three quarks. By about 3 min. after Big Bang all of the neutrons are bound into 4He nuclei which ha ...
... capture electrons to form chemical elements). Nuclei are made of protons and neutrons. These particles have similar mass but only protons have an electric charge. Protons and neutrons are each made of three quarks. By about 3 min. after Big Bang all of the neutrons are bound into 4He nuclei which ha ...
Physical Science: Nuclear Chemistry Study Guide
... 34. What is the name for the process in which light nuclei combine at extremely high temperatures, forming heavier nuclei and releasing energy? 35. What is one example of a place where naturally occurring extreme temperatures provide the energy needed to bring hydrogen nuclei together in a fusion re ...
... 34. What is the name for the process in which light nuclei combine at extremely high temperatures, forming heavier nuclei and releasing energy? 35. What is one example of a place where naturally occurring extreme temperatures provide the energy needed to bring hydrogen nuclei together in a fusion re ...
Where Did the Elements Come From?
... Formation of Stars • Huge hydrogen clouds were pulled closer and closer by gravity. • As the clouds became more dense the temperature and pressure at the center of the clouds increased and stars were born. • Nuclear reactions took place in the center of the stars these reactions are the same as tho ...
... Formation of Stars • Huge hydrogen clouds were pulled closer and closer by gravity. • As the clouds became more dense the temperature and pressure at the center of the clouds increased and stars were born. • Nuclear reactions took place in the center of the stars these reactions are the same as tho ...
Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
... electric force (the force that would cause the protons to repel each other). • The strong force is a short range force that quickly becomes extremely weak as protons and neutrons get farther apart. ...
... electric force (the force that would cause the protons to repel each other). • The strong force is a short range force that quickly becomes extremely weak as protons and neutrons get farther apart. ...
–1– Order of Magnitude Astrophysics
... When the stars are plotted in a log T s – log L plane we thus expect them to lie within a line with slope (1/12) ≈ 0.08. The observed slope is ∼ 0.13. We saw above that stars are gravitationally bound systems in which self-sustaining nuclear reactions are taking place in the center. The process of c ...
... When the stars are plotted in a log T s – log L plane we thus expect them to lie within a line with slope (1/12) ≈ 0.08. The observed slope is ∼ 0.13. We saw above that stars are gravitationally bound systems in which self-sustaining nuclear reactions are taking place in the center. The process of c ...
AP Chem
... even number of neutrons. The least stable situation is when both numbers are odd. There are only four (or five) stable odd/odd nuclei. Nuclides with a mass number over 200 usually undergo alpha decay. They emit a particle consisting of two protons and two neutrons. Nuclides with too many neutrons un ...
... even number of neutrons. The least stable situation is when both numbers are odd. There are only four (or five) stable odd/odd nuclei. Nuclides with a mass number over 200 usually undergo alpha decay. They emit a particle consisting of two protons and two neutrons. Nuclides with too many neutrons un ...
Stellar Notes
... Stellar Nursery What concepts, facts, details can you come up with for a Stellar Nursery, or better known as a Nebula? ...
... Stellar Nursery What concepts, facts, details can you come up with for a Stellar Nursery, or better known as a Nebula? ...
P-nuclei
p-Nuclei (p stands for proton-rich) are certain proton-rich, naturally occurring isotopes of some elements between selenium and mercury which cannot be produced in either s- or r-process.