Homework 5
... 1. What is a stellar association, how big are they, how many stars do they contain, how long do they last? Finally, what is their fate? ...
... 1. What is a stellar association, how big are they, how many stars do they contain, how long do they last? Finally, what is their fate? ...
Chapter #20 Nuclear Chemistry
... together by overcoming the repulsive force of the protons. Neutrons are present to help dissipate the repulsive forces between the protons As the atomic number (number of protons) increases, so does the number of neutrons to shield the repulsion of the protons All nuclides with 84 or more protons ar ...
... together by overcoming the repulsive force of the protons. Neutrons are present to help dissipate the repulsive forces between the protons As the atomic number (number of protons) increases, so does the number of neutrons to shield the repulsion of the protons All nuclides with 84 or more protons ar ...
E5 stellar processes and stellar evolution (HL only)
... • If the core is above 1.4 solar masses (the Chandrasekhar limit) Electrons are forced into protons producing neutrons. • The core is only made of neutrons and contracting rapidly. ...
... • If the core is above 1.4 solar masses (the Chandrasekhar limit) Electrons are forced into protons producing neutrons. • The core is only made of neutrons and contracting rapidly. ...
The Sun
... a rate of 2 milliseconds/century. If this rate remains constant at the present value, how long will it take for one day on Earth to become 2 seconds longer than it is now: A: 1000 years B: 100,000 years C: 1 million years ...
... a rate of 2 milliseconds/century. If this rate remains constant at the present value, how long will it take for one day on Earth to become 2 seconds longer than it is now: A: 1000 years B: 100,000 years C: 1 million years ...
Stellar Nucleosynthesis
... • Single Burst of Star-formation • Galaxy starts of very blue as the light is dominated by the massive hot blue stars • After the burst the massive stars live only a short time and soon the light of the galaxy as a whole is dominated by the red light of the less massive, longer lived stars • Galaxy ...
... • Single Burst of Star-formation • Galaxy starts of very blue as the light is dominated by the massive hot blue stars • After the burst the massive stars live only a short time and soon the light of the galaxy as a whole is dominated by the red light of the less massive, longer lived stars • Galaxy ...
ASTR 31: Descriptive Astronomy
... Helium capture The triple-alpha reaction and the major carbon and oxygen burning reactions are helium capture reactions. The capture of helium nuclei continues until silicon is created, at which point the supply of helium nuclei in the star’s core is depleted: 20Ne + 4He → 24Mg + 24Mg + 4He ...
... Helium capture The triple-alpha reaction and the major carbon and oxygen burning reactions are helium capture reactions. The capture of helium nuclei continues until silicon is created, at which point the supply of helium nuclei in the star’s core is depleted: 20Ne + 4He → 24Mg + 24Mg + 4He ...
Chapter 13 Notes – The Deaths of Stars
... Sun will expand to a red giant in ______________ billion years Expands to ______________ radius Earth will then be ___________________ Sun MAY form a ________________ nebula (but uncertain) Sun’s C, O core will become a ______________ dwarf VIII. The Deaths of Massive Stars: Supernovae F ...
... Sun will expand to a red giant in ______________ billion years Expands to ______________ radius Earth will then be ___________________ Sun MAY form a ________________ nebula (but uncertain) Sun’s C, O core will become a ______________ dwarf VIII. The Deaths of Massive Stars: Supernovae F ...
Bez tytułu slajdu
... Evolution of stars depend on their mass. Those above 8 Solar masses, at the end of the life, were all the termonuclear fuel is burn into iron, first collapse, and then explode into supernova. A part of the mass is expelled and the remnants form a core of about 20 km diameter made of neutrons. The ex ...
... Evolution of stars depend on their mass. Those above 8 Solar masses, at the end of the life, were all the termonuclear fuel is burn into iron, first collapse, and then explode into supernova. A part of the mass is expelled and the remnants form a core of about 20 km diameter made of neutrons. The ex ...
Nuclear chemistry – the study of nuclear reactions and their uses in
... Nuclear power plants and nuclear weapons depend on fission. When heavy nuclei split due to the capture of neutrons, radioactive isotopes of many different elements are formed. If one fission produces 2 neutrons, these 2 neutrons can produce four fissions, and so forth. i. Reactions that multiple in ...
... Nuclear power plants and nuclear weapons depend on fission. When heavy nuclei split due to the capture of neutrons, radioactive isotopes of many different elements are formed. If one fission produces 2 neutrons, these 2 neutrons can produce four fissions, and so forth. i. Reactions that multiple in ...
Supernovae — Oct 18 10/18/2010
... What is the only element at the start? How many neutrons does it have? At what time did some gold form? Gold has 79 protons. Is this gold stable? At the end of the calculation, how many protons does the nucleus with the most protons have? What is the time at the end of the calculation? Are the end p ...
... What is the only element at the start? How many neutrons does it have? At what time did some gold form? Gold has 79 protons. Is this gold stable? At the end of the calculation, how many protons does the nucleus with the most protons have? What is the time at the end of the calculation? Are the end p ...
Endpoints of Stellar Evolution
... the forst and only modern close-up look at the death of a massive star … … Including the first detection of extra-Solar neutrinos, thus confirming our basic model for core-collapse SNe: > 99% of the total SN energy emerges in neutrinos! ...
... the forst and only modern close-up look at the death of a massive star … … Including the first detection of extra-Solar neutrinos, thus confirming our basic model for core-collapse SNe: > 99% of the total SN energy emerges in neutrinos! ...
This chapter has a brief overview of astronomical topics that we will
... nothing before (as there was no time) and it was not an explosion in space (since space was created here). Why do we believe this? We see the galaxies flying apart from each other, the farthest moving faster. Since we see the more distant galaxies as they were long ago, this seems to imply an explos ...
... nothing before (as there was no time) and it was not an explosion in space (since space was created here). Why do we believe this? We see the galaxies flying apart from each other, the farthest moving faster. Since we see the more distant galaxies as they were long ago, this seems to imply an explos ...
U - Earth and Environmental Sciences
... Uranium-238 is abundant in the nuclear "fuel"; this leads to the production of plutonium. Nuclear fusion has the potential to yield enormous amounts of energy if it can be done in a controlled, sustained way. Consider the mass-to-energy numbers... 2 protons = 2 x 1.00728 u = 2.01456 u 2 neutrons = 2 ...
... Uranium-238 is abundant in the nuclear "fuel"; this leads to the production of plutonium. Nuclear fusion has the potential to yield enormous amounts of energy if it can be done in a controlled, sustained way. Consider the mass-to-energy numbers... 2 protons = 2 x 1.00728 u = 2.01456 u 2 neutrons = 2 ...
Earth Science
... of an object resulting from a change in the angle or in the position from which it is ...
... of an object resulting from a change in the angle or in the position from which it is ...
Physical Science 1 Quiz 10 1 ID # or name:
... 3. (1 pt.) Gas and dust distributed among the stars is known as the _______________. a. interstellar vacuum b. interstellar void c. ...
... 3. (1 pt.) Gas and dust distributed among the stars is known as the _______________. a. interstellar vacuum b. interstellar void c. ...
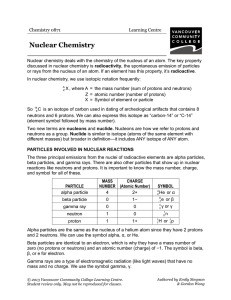
Nuclear Chemistry - VCC Library
... PARTICLES INVOLVED IN NUCLEAR REACTIONS The three principal emissions from the nuclei of radioactive elements are alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays. There are also other particles that show up in nuclear reactions like neutrons and protons. It is important to know the mass number, char ...
... PARTICLES INVOLVED IN NUCLEAR REACTIONS The three principal emissions from the nuclei of radioactive elements are alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays. There are also other particles that show up in nuclear reactions like neutrons and protons. It is important to know the mass number, char ...
Chapter 7 - Bakersfield College
... D. Binding energy makes stable heavier nuclei possible (beyond hydrogen) which in turn accounts for the various elements and forms of matter found in the physical universe. 7-9. Nuclear Fission A. In 1939, uranium-235 was discovered to undergo nuclear fission when struck by a neutron. 1. A nucleus o ...
... D. Binding energy makes stable heavier nuclei possible (beyond hydrogen) which in turn accounts for the various elements and forms of matter found in the physical universe. 7-9. Nuclear Fission A. In 1939, uranium-235 was discovered to undergo nuclear fission when struck by a neutron. 1. A nucleus o ...
Extension worksheet – Topic 6 - Cambridge Resources for the IB
... paths of these two stars with reference to a ...
... paths of these two stars with reference to a ...
Slide 1
... He continues to burn to C by triple alpha process. In larger mass stars, alpha particles are added one by one, creating elements with an even atomic number. Sometimes this is called the triple alpha process as well, even though more than three alpha particles are involved. ...
... He continues to burn to C by triple alpha process. In larger mass stars, alpha particles are added one by one, creating elements with an even atomic number. Sometimes this is called the triple alpha process as well, even though more than three alpha particles are involved. ...
The Death of Stars - Mounds Park Academy Blogs
... • A star 15 times the mass of the Sun burns up faster than the sun and ends its life in an abrupt way. • The core contracts as the outer layer expands. • This causes Helium to fuse to form carbon • By the time the Helium is exhausted the outer layers have expanded even further • This creates a huge ...
... • A star 15 times the mass of the Sun burns up faster than the sun and ends its life in an abrupt way. • The core contracts as the outer layer expands. • This causes Helium to fuse to form carbon • By the time the Helium is exhausted the outer layers have expanded even further • This creates a huge ...
P-nuclei
p-Nuclei (p stands for proton-rich) are certain proton-rich, naturally occurring isotopes of some elements between selenium and mercury which cannot be produced in either s- or r-process.