File
... 8-25 X larger than our Sun Consume their fuel very fast – die more quickly and more violently Star expands into a Supergiant which causes the core to collapse and the outer portion to explode creating a Supernova then a Neutron Star ...
... 8-25 X larger than our Sun Consume their fuel very fast – die more quickly and more violently Star expands into a Supergiant which causes the core to collapse and the outer portion to explode creating a Supernova then a Neutron Star ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... A supermassive black hole (SMBH) is the largest type of black hole, on the order of hundreds of thousands to billions of solar masses. Most—and possibly all—galaxies are inferred to contain a supermassive black hole at their centers. In the case of the Milky Way, the SMBH is believed to correspond w ...
... A supermassive black hole (SMBH) is the largest type of black hole, on the order of hundreds of thousands to billions of solar masses. Most—and possibly all—galaxies are inferred to contain a supermassive black hole at their centers. In the case of the Milky Way, the SMBH is believed to correspond w ...
Life Cycles of Stars
... • Build from C to Fe by fusing successively heavier atoms • Can’t Build Beyond Fe by Adding Protons – Repulsion of nuclei = Charge1 x Charge2 ...
... • Build from C to Fe by fusing successively heavier atoms • Can’t Build Beyond Fe by Adding Protons – Repulsion of nuclei = Charge1 x Charge2 ...
The Nuclear Reactions
... Following the Triple-alpha process there are a variety of reactions which may occur depending on the mass of the star. Three general principles influence the roles that these nuclear burning stages may play: * Successive nuclear burning stages, involving more massive nuclei with higher charges, will ...
... Following the Triple-alpha process there are a variety of reactions which may occur depending on the mass of the star. Three general principles influence the roles that these nuclear burning stages may play: * Successive nuclear burning stages, involving more massive nuclei with higher charges, will ...
2nd Japanese-German Workshop on Nuclear Structure and
... T. Nakatsukasa (12+3) Convergent configuration-mixing calculation for light nuclei with mean-field Hamiltonian H. Baba (12+3) Highly excited states of 14O with the (alpha,alpha') reaction M. Kimura (12+3) Alpha clustering, molecular-oribitals and breaking of N=20 magic number in F isotopes ...
... T. Nakatsukasa (12+3) Convergent configuration-mixing calculation for light nuclei with mean-field Hamiltonian H. Baba (12+3) Highly excited states of 14O with the (alpha,alpha') reaction M. Kimura (12+3) Alpha clustering, molecular-oribitals and breaking of N=20 magic number in F isotopes ...
Radioactivity
... magnetic field • Long range, very penetrating • Accompanies many other types of decay ...
... magnetic field • Long range, very penetrating • Accompanies many other types of decay ...
Radioactivity
... • If there are too many protons in a nucleus, it may capture an electron • A proton becomes a neutron ...
... • If there are too many protons in a nucleus, it may capture an electron • A proton becomes a neutron ...
Exploration of the Universe
... 6. Describe two features of the Sun. 7. Define asteroids, comets, meteors and meteorites. 8. Name three types of electromagnetic radiation. 9. What two factors affect the brightness of a star? 10. What do astronomers observe to determine the temperature of a star? 11. What do astronomers observe to ...
... 6. Describe two features of the Sun. 7. Define asteroids, comets, meteors and meteorites. 8. Name three types of electromagnetic radiation. 9. What two factors affect the brightness of a star? 10. What do astronomers observe to determine the temperature of a star? 11. What do astronomers observe to ...
View Transcript
... And one of the first things that you’ll notice is that the data, for the most part, fall above the line of one neutron per proton. Another way to say that is that, except for hydrogen 1, just a plain old proton, and helium-3, which is 1 proton and 2 neutrons, all are stable nuclei – have 1 or more n ...
... And one of the first things that you’ll notice is that the data, for the most part, fall above the line of one neutron per proton. Another way to say that is that, except for hydrogen 1, just a plain old proton, and helium-3, which is 1 proton and 2 neutrons, all are stable nuclei – have 1 or more n ...
123mt13-2a
... Two hydrogen atoms combine to form a molecule (red herring) Two hydrogen atoms collide – 3 points for this because this can happen but it does not “occur whenever” A hydrogen atom captures and electron (unphysical process) A hydrogen atom absorbs a red photon (red photons have insufficient energy to ...
... Two hydrogen atoms combine to form a molecule (red herring) Two hydrogen atoms collide – 3 points for this because this can happen but it does not “occur whenever” A hydrogen atom captures and electron (unphysical process) A hydrogen atom absorbs a red photon (red photons have insufficient energy to ...
White Dwarf Stars
... • The heat generated by viscosity (friction) in this high speed gas produces X-rays. Some of the gas is ultimately swallowed by the black hole. ...
... • The heat generated by viscosity (friction) in this high speed gas produces X-rays. Some of the gas is ultimately swallowed by the black hole. ...
Microsoft Word Document
... Video – How the Universe Works: Supernovas (Discovery Channel 2010) 1. If a supernova occurred within a few dozen lightyears of earth, how would it affect life on our ...
... Video – How the Universe Works: Supernovas (Discovery Channel 2010) 1. If a supernova occurred within a few dozen lightyears of earth, how would it affect life on our ...
Unit #12: Nuclear Chemistry
... •The left side (reactants side) of equation and the right side (products side) of equation ...
... •The left side (reactants side) of equation and the right side (products side) of equation ...
Lecture 3: Matter
... Gases: Higher temperature means more average kinetic energy (faster speeds) per atom or molecule. ...
... Gases: Higher temperature means more average kinetic energy (faster speeds) per atom or molecule. ...
The Death of Stars
... bound atomic nuclei. No more reactions in the Fe. • The Fe core continues to grow. • When the Fe core reaches 1.4Msun the core collapses. p + e- --> n + ν ...
... bound atomic nuclei. No more reactions in the Fe. • The Fe core continues to grow. • When the Fe core reaches 1.4Msun the core collapses. p + e- --> n + ν ...
PHYSICS OF THE SUN The Sun is a main
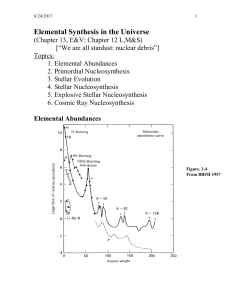
... Handout: Binding energies per nucleon (B/A) are shown as a function of atomic mass A. Unstable isotopes have lower binding energies than the stable ones, so they’re more apt to break apart. Being “higher up” on this diagram means it’s more stable. Thus, more input energy would be needed to break it ...
... Handout: Binding energies per nucleon (B/A) are shown as a function of atomic mass A. Unstable isotopes have lower binding energies than the stable ones, so they’re more apt to break apart. Being “higher up” on this diagram means it’s more stable. Thus, more input energy would be needed to break it ...
Chapter 29
... • The volume of the nucleus (assumed to be spherical) is directly proportional to the total number of nucleons • This suggests that all nuclei have nearly the same density • Nucleons combine to form a nucleus as though they were tightly packed spheres ...
... • The volume of the nucleus (assumed to be spherical) is directly proportional to the total number of nucleons • This suggests that all nuclei have nearly the same density • Nucleons combine to form a nucleus as though they were tightly packed spheres ...
P1_Physics_Summary_Topic_3
... Universe Nebulae Galaxy Star Solar System What type of waves can we use to explore space? Which type of waves are absorbed by the atmosphere? ...
... Universe Nebulae Galaxy Star Solar System What type of waves can we use to explore space? Which type of waves are absorbed by the atmosphere? ...
Lars Bildsten - nnpss
... started in), the core temperature rises! This is the same as what happens to a particle in orbit, as it loses energy (radiates!), it moves in (radius shrinks!), and moves faster (higher temperature!). Prior to ignition of any nuclear energy source, the loss of energy (at luminosity L) leads to a slo ...
... started in), the core temperature rises! This is the same as what happens to a particle in orbit, as it loses energy (radiates!), it moves in (radius shrinks!), and moves faster (higher temperature!). Prior to ignition of any nuclear energy source, the loss of energy (at luminosity L) leads to a slo ...
Homework problems for Quiz 2: AY5 Spring 2013
... The reason main-sequence stars do not collapse due to gravity is the thermal pressure of the gases they are composed of The fuel that provides the energy source for main-sequence stars is mass A star that is not in hydrostatic equilibrium with react by changing its radius 6. How much energy is produ ...
... The reason main-sequence stars do not collapse due to gravity is the thermal pressure of the gases they are composed of The fuel that provides the energy source for main-sequence stars is mass A star that is not in hydrostatic equilibrium with react by changing its radius 6. How much energy is produ ...
P-nuclei
p-Nuclei (p stands for proton-rich) are certain proton-rich, naturally occurring isotopes of some elements between selenium and mercury which cannot be produced in either s- or r-process.