g9u4c12part3
... consume their fuel faster than smaller stars Become red giants. (supergiants) last for only 7 billion years. they collapse in on themselves causing a massive explosion called a supernova. the remaining core of the supernova will eventually collapse to form a neutron star. A sphere only 10 km ...
... consume their fuel faster than smaller stars Become red giants. (supergiants) last for only 7 billion years. they collapse in on themselves causing a massive explosion called a supernova. the remaining core of the supernova will eventually collapse to form a neutron star. A sphere only 10 km ...
White Dwarfs and Neutron Stars
... discovery of pulsars (rapidly spinning neutron stars that emit beams of radiation) ...
... discovery of pulsars (rapidly spinning neutron stars that emit beams of radiation) ...
Due April 2 - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... Choose the best answer for each of the following and explain your reasoning with one or more complete sentences (required for full credit). Four points each question, 20 points total. Answers must be turned in on paper; do not email. Please write your name on each sheet that you hand in. 1. Which of ...
... Choose the best answer for each of the following and explain your reasoning with one or more complete sentences (required for full credit). Four points each question, 20 points total. Answers must be turned in on paper; do not email. Please write your name on each sheet that you hand in. 1. Which of ...
80.BrainPopLifeCycleStars
... ___________ of years. 2. They start out as clouds of gas and dust called __________ nurseries. The force of __________ within these clouds slowly pulls the particles together, causing dense clumps to form. 3. If the clump becomes large enough, the ____________ caused by gravity forms a __________, a ...
... ___________ of years. 2. They start out as clouds of gas and dust called __________ nurseries. The force of __________ within these clouds slowly pulls the particles together, causing dense clumps to form. 3. If the clump becomes large enough, the ____________ caused by gravity forms a __________, a ...
Probing nuclear correlations by two proton emission
... We describe emission of two particles by solving the Schrödinger equation with 1) pairing two-proton wave function on the nuclear surface as an initial condition and 2) outgoing boundary conditions at large distance. The main purpose is: to investigate the dependence of the half-life versus the para ...
... We describe emission of two particles by solving the Schrödinger equation with 1) pairing two-proton wave function on the nuclear surface as an initial condition and 2) outgoing boundary conditions at large distance. The main purpose is: to investigate the dependence of the half-life versus the para ...
August 29 - Astronomy
... How do the elements got out of the stars? Once enough iron builds up in the core of a massive star, it suddenly collapses. The outer layers of the star “bounce” off the core and are blasted into space in a supernova explosion. ...
... How do the elements got out of the stars? Once enough iron builds up in the core of a massive star, it suddenly collapses. The outer layers of the star “bounce” off the core and are blasted into space in a supernova explosion. ...
Big Bang Theory - Clark Planetarium
... . . . however, the mass of a proton is slightly less than the mass of a neutron, so . . . ...
... . . . however, the mass of a proton is slightly less than the mass of a neutron, so . . . ...
- Physics
... http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Positron_emission_tomography Isotopes that have too few neutrons are candidates for the inverse beta decay. page 8 Alpha Particles If you recall, Rutherford used alpha particles to probe the size of the nucleus. The alpha particles are helium nuclei, 2 protons and 2 neut ...
... http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Positron_emission_tomography Isotopes that have too few neutrons are candidates for the inverse beta decay. page 8 Alpha Particles If you recall, Rutherford used alpha particles to probe the size of the nucleus. The alpha particles are helium nuclei, 2 protons and 2 neut ...
Supernovae - Michigan State University
... depending on other spectral features there are sub types Ia, Ib, Ic, ... ...
... depending on other spectral features there are sub types Ia, Ib, Ic, ... ...
Neutron Stars
... – When a massive star reaches the end of its life, the gravitational contraction can overcome the degenerate electron pressure that held the core during the last stages of the star. – Then the electrons and protons can combine under this pressure and transform into neutrons. – Pulsars – rotating neu ...
... – When a massive star reaches the end of its life, the gravitational contraction can overcome the degenerate electron pressure that held the core during the last stages of the star. – Then the electrons and protons can combine under this pressure and transform into neutrons. – Pulsars – rotating neu ...
Starending jeopardy
... Once hydrogen is depleted it can no longer fuse hydrogen into helium. With no energy source to cause outware pressure the gravity is able to collapse the core and change the star’s structure. ...
... Once hydrogen is depleted it can no longer fuse hydrogen into helium. With no energy source to cause outware pressure the gravity is able to collapse the core and change the star’s structure. ...
Nuclear Physics Notes - Reading Community Schools
... It can also be indicated by its name followed by its isotopic mass (ex. Carbon-12 or Uranium-235). Since it is the number of protons that define the identity of the atom, given its atomic name or its atomic number you can identify the atom. The atomic mass number) is the sum of the protons and ne ...
... It can also be indicated by its name followed by its isotopic mass (ex. Carbon-12 or Uranium-235). Since it is the number of protons that define the identity of the atom, given its atomic name or its atomic number you can identify the atom. The atomic mass number) is the sum of the protons and ne ...
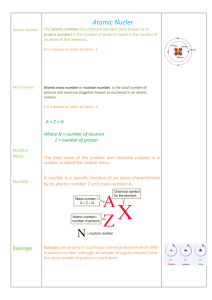
Deep Space Mystery Note Form 3
... The core could have temperatures of billions of degrees Celsius. Iron atoms are so squeezed so much. The forces of their nuclei create a recoil of the squeezed core. Then is the supernova. Type II Type II Binary stars are when there are two stars and they revolve around each other. In ...
... The core could have temperatures of billions of degrees Celsius. Iron atoms are so squeezed so much. The forces of their nuclei create a recoil of the squeezed core. Then is the supernova. Type II Type II Binary stars are when there are two stars and they revolve around each other. In ...
Powerpoint for today
... billion years ago. As Milky Way ages, the abundances of elements compared to H in gas and new stars are increasing due to fusion and supernovae. Elements up to iron (56Fe, 26 p + 30 n in nucleus) produced by steady fusion (less abundant elements we didn’t discuss, like Cl, Na, made in reactions that ...
... billion years ago. As Milky Way ages, the abundances of elements compared to H in gas and new stars are increasing due to fusion and supernovae. Elements up to iron (56Fe, 26 p + 30 n in nucleus) produced by steady fusion (less abundant elements we didn’t discuss, like Cl, Na, made in reactions that ...
The Earth in Space Scientific evidence indicates the universe is
... been continually expanding at an increasing rate since its formation about 13.7 billion years ago. E5.1A Describe the position and motion of our solar system in our galaxy and the overall scale, structure, and age of the universe. E5.2 The Sun Stars, including the Sun, transform matter into energy i ...
... been continually expanding at an increasing rate since its formation about 13.7 billion years ago. E5.1A Describe the position and motion of our solar system in our galaxy and the overall scale, structure, and age of the universe. E5.2 The Sun Stars, including the Sun, transform matter into energy i ...
Physics 202 Homework, Day 08: Chapter 15: #18,21,27, 39
... x 1012 m/s 2 . Find (a) the magnitude of the electrid force on the proton at that instant. [You will need to look up the charge and mass of a proton for this part.] (b) the magnitude and direction of the electric field at the surface of the generator. ...
... x 1012 m/s 2 . Find (a) the magnitude of the electrid force on the proton at that instant. [You will need to look up the charge and mass of a proton for this part.] (b) the magnitude and direction of the electric field at the surface of the generator. ...
P-nuclei
p-Nuclei (p stands for proton-rich) are certain proton-rich, naturally occurring isotopes of some elements between selenium and mercury which cannot be produced in either s- or r-process.