
Physical and Chemical Changes in Digestion Key
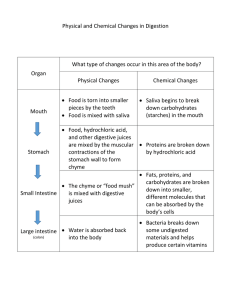
... are mixed by the muscular Proteins are broken down Stomach contractions of the by hydrochloric acid stomach wall to form chyme Fats, proteins, and carbohydrates are broken The chyme or “food mush” down into smaller, Small Intestine is mixed with digestive different molecules that juices can be ...
... are mixed by the muscular Proteins are broken down Stomach contractions of the by hydrochloric acid stomach wall to form chyme Fats, proteins, and carbohydrates are broken The chyme or “food mush” down into smaller, Small Intestine is mixed with digestive different molecules that juices can be ...
Digestion - Mocks.ie
... Pushes food to stomach by peristalsis Mixes food with HCl to kill bacteria Pepsin to break down protein Produces bile to neutralise acid from stomach Produces Amylase to digest carbohydrates Lipase to digest fats Protease to digest proteins Insulin to control blood sugar levels Abs ...
... Pushes food to stomach by peristalsis Mixes food with HCl to kill bacteria Pepsin to break down protein Produces bile to neutralise acid from stomach Produces Amylase to digest carbohydrates Lipase to digest fats Protease to digest proteins Insulin to control blood sugar levels Abs ...
Nutrition and balanced diet
... Healthy diets are balanced in the context of Proteins – build muscle and cells Carbohydrates- starch and sugars - energy Fats and oils – cell membranes and energy Minerals and vitamins - health Fibre – helps food move through the intestine Water – hydration of the body ...
... Healthy diets are balanced in the context of Proteins – build muscle and cells Carbohydrates- starch and sugars - energy Fats and oils – cell membranes and energy Minerals and vitamins - health Fibre – helps food move through the intestine Water – hydration of the body ...
The Digestive system
... In the stomach, the food is crushed and broken down using strong muscles, as well as a strong acid. ...
... In the stomach, the food is crushed and broken down using strong muscles, as well as a strong acid. ...
Gastrointestinal System
... severe physical complications-tube or parenteral feedings may be utilized, but only as temporary intervention (not a cure for anorexia nervosa). ...
... severe physical complications-tube or parenteral feedings may be utilized, but only as temporary intervention (not a cure for anorexia nervosa). ...
19.2 Notes The Digestive System -What is it? The system that breaks
... Mechanical Digestion- The actual physical break down of food into smaller pieces Chemical Digestion- The act or process of converting food into chemical substances that can be absorbed Saliva- The clear liquid secreted into the mouth by the salivary glands, consisting of water, mucin, protein, and e ...
... Mechanical Digestion- The actual physical break down of food into smaller pieces Chemical Digestion- The act or process of converting food into chemical substances that can be absorbed Saliva- The clear liquid secreted into the mouth by the salivary glands, consisting of water, mucin, protein, and e ...
Getting a Handle on Obesity
... match the drop in food consumed, but models representing food intake and energy expenditure as a dynamical system show that such a weight plateau doesn’t take effect until much later. The likely culprit is a combination of slower metabolism and a lack of adherence to the diet. Most people are in app ...
... match the drop in food consumed, but models representing food intake and energy expenditure as a dynamical system show that such a weight plateau doesn’t take effect until much later. The likely culprit is a combination of slower metabolism and a lack of adherence to the diet. Most people are in app ...
Digestion Test - Net Start Class
... wall of your digestive system into your blood. 21. _________________is a thick, slippery substance that lines the esophagus. 22. The process of breaking down food into small nutrient molecules is called _____________. ...
... wall of your digestive system into your blood. 21. _________________is a thick, slippery substance that lines the esophagus. 22. The process of breaking down food into small nutrient molecules is called _____________. ...
practice vocab quiz
... 1. the largest gland in the body, on the RUQ; & has lobes. It produces bile 2. involuntary action that involves alternating waves of contraction/relaxation of the muscles in the organ wall. Moves food along alimentary canal. 3. food that has been processed in the stomach that looks like heavy crea ...
... 1. the largest gland in the body, on the RUQ; & has lobes. It produces bile 2. involuntary action that involves alternating waves of contraction/relaxation of the muscles in the organ wall. Moves food along alimentary canal. 3. food that has been processed in the stomach that looks like heavy crea ...
Patient Education Presentation
... Multivitamin, Calcium, B12, other B vitamins, Iron Needs somewhat vary depending on gender, age, AND surgical procedure ...
... Multivitamin, Calcium, B12, other B vitamins, Iron Needs somewhat vary depending on gender, age, AND surgical procedure ...
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The organs that break down food so that it can
... The organs that break down food so that it can be used by the body. 1) Digestion, 2) Absorption, 3) Elimination ...
... The organs that break down food so that it can be used by the body. 1) Digestion, 2) Absorption, 3) Elimination ...
digestion reviewppt - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]
... smooth muscles in the digestive tract to move the food is called _________________ ...
... smooth muscles in the digestive tract to move the food is called _________________ ...
The Digestive System
... » Intestinal absorption of minerals increases when the body is lacking the particular nutrient. ...
... » Intestinal absorption of minerals increases when the body is lacking the particular nutrient. ...
Digestive System Foldable
... Chemical Digestion- amylase- a special chemical called an enzyme that breaks starches into sugars ...
... Chemical Digestion- amylase- a special chemical called an enzyme that breaks starches into sugars ...
Digestive System Crossword
... considered the first region of the large intestine 4. A narrow pouch of tissue which resemblance to the worm had inspired its name 5. A small storage organ located inferior and posterior to the liver 7. Brown, flat, and oval-shaped lymphatic organ that filters blood to prevent blood loss and infecti ...
... considered the first region of the large intestine 4. A narrow pouch of tissue which resemblance to the worm had inspired its name 5. A small storage organ located inferior and posterior to the liver 7. Brown, flat, and oval-shaped lymphatic organ that filters blood to prevent blood loss and infecti ...
11. The organ w/4 lobes is called?
... 6. The small finger-like projections in the small intestine are called _____? ...
... 6. The small finger-like projections in the small intestine are called _____? ...
Pharmacotherapy of Obesity
... • Patients with history of psychiatric disorders should have appropriate care before and after bariatric surgery. • We are not able to fully predict which surgical patients will have suboptimal weight loss or suffer from clinically significant psychosocial complications. • Patients with active psyc ...
... • Patients with history of psychiatric disorders should have appropriate care before and after bariatric surgery. • We are not able to fully predict which surgical patients will have suboptimal weight loss or suffer from clinically significant psychosocial complications. • Patients with active psyc ...
Digestion - questions
... 8 Are the contents of the stomach (a) acid, (b) alkaline,{c) neutral? 9 What class of food is partially digested in the stomach? 10 What is the name of the enzyme in gastric juice? 11 What types of enzymes are produced by the pancreas? 12 Into which part of the alimentary canal does the pancreas sec ...
... 8 Are the contents of the stomach (a) acid, (b) alkaline,{c) neutral? 9 What class of food is partially digested in the stomach? 10 What is the name of the enzyme in gastric juice? 11 What types of enzymes are produced by the pancreas? 12 Into which part of the alimentary canal does the pancreas sec ...
How is Food Digested
... breaking down of food is called digestion. You may have heard your stomach gurgling after you have eaten. The stomach, teeth, tongue and intestines all help to digest food. When you chew your food, digestion begins. The food is pushed by the tongue to the trapdoor at the back of the mouth called the ...
... breaking down of food is called digestion. You may have heard your stomach gurgling after you have eaten. The stomach, teeth, tongue and intestines all help to digest food. When you chew your food, digestion begins. The food is pushed by the tongue to the trapdoor at the back of the mouth called the ...
From lunch to loo! - Baradine Central School
... The waste products and water pass into the large intestine , here all the water needed is taken into the body. ...
... The waste products and water pass into the large intestine , here all the water needed is taken into the body. ...













![digestion reviewppt - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/020964404_1-fd7e7b1a796f79cf09a3c59b903b07b2-300x300.png)








