* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nutrition and balanced diet
Waist–hip ratio wikipedia , lookup
Overeaters Anonymous wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cigarette smoking for weight loss wikipedia , lookup
Thrifty gene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbohydrate diet wikipedia , lookup
Malnutrition wikipedia , lookup
Malnutrition in South Africa wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology of metabolic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Gastric bypass surgery wikipedia , lookup
Food choice wikipedia , lookup
Abdominal obesity wikipedia , lookup
Body mass index wikipedia , lookup
Human nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Diet-induced obesity model wikipedia , lookup
Obesity and the environment wikipedia , lookup
Childhood obesity wikipedia , lookup
Obesity in the Middle East and North Africa wikipedia , lookup
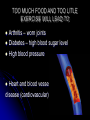
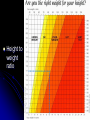
Nutrition and Health AQA 11.2 b1a gcse Diet - the basics Healthy diets are balanced in the context of Proteins – build muscle and cells Carbohydrates- starch and sugars - energy Fats and oils – cell membranes and energy Minerals and vitamins - health Fibre – helps food move through the intestine Water – hydration of the body Eat more of some and less of others What is malnutrition? Health and Body image What factors influence how we see ourselves? Advertising? Models, film stars or famous people? Popular music culture Who are most vulnerable to images of so called ‘desirable’ body shape and size? What do you think? Anorexia – physiological disease Lack of food and health problems Deficiencies – there are so many you don’t need to know any – (Scurvy – lack of vitamin C is one) BUT you must know that ‘starvation’ causes: Reduced resistance to disease. Irregular periods in women - Obesity How would you describe an obese person? Where does being overweight stop and obesity start? Obesity – is also malnutrition However it can be linked to a persons genes, some families are more likely to become overweight without careful dietary control, particularly when linked with poor exercise routine TOO MUCH FOOD AND TOO LITLE EXERCISE WILL LEAD TO Arthritis – worn joints Diabetes – high blood sugar level High blood pressure Heart and blood vessel disease (cardiovascular) A question of balance To maintain your weight Energy intake = energy output Does a bricklayer need to eat more than a teacher? Do Eskimos need to eat more high energy foods than us? Height to weight ratio Body mass index Doctors can assess whether people are obese using BMI – however it is not totally reliable. What is your BMI? BMI = weight Kg ÷ height2 m2 BMI Categories: Underweight = <18.5 Normal weight = 18.5-24.9 Overweight = 25-29.9 Obesity = BMI of 30 or greater Fast foods High in fats and salt – not good if eaten to excess. Diets – which do you choose? G.I diet F-plan Weight watchers Atkins and the rest