Ch 5.1 The Nature of Chemical Reactions
... Objectives For this Chapter • Understand parts to a chemical equation (reactants, products, yeild sign, double arrow) • Conservation of matter is expressed through balancing chemical equations • Describe difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions ...
... Objectives For this Chapter • Understand parts to a chemical equation (reactants, products, yeild sign, double arrow) • Conservation of matter is expressed through balancing chemical equations • Describe difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions ...
Edexcel Chemistry for A2
... Candidates should be able to: a) give examples to illustrate the importance of organic synthesis in research for the production of useful products ...
... Candidates should be able to: a) give examples to illustrate the importance of organic synthesis in research for the production of useful products ...
topic-2.doc
... covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is attracted to another electronegative atom o weak attraction, 20X weaker than covalent o is a charge attraction between oppositely charged portions of polar molecules o generally between H that has slight positive charge and another highly electronegat ...
... covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is attracted to another electronegative atom o weak attraction, 20X weaker than covalent o is a charge attraction between oppositely charged portions of polar molecules o generally between H that has slight positive charge and another highly electronegat ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Slide 1 - University of Evansville Faculty
... on its carbon skeleton, but also on certain groups of atoms that are covalently linked to the skeleton. These groups of atoms are called functional groups, the name reflecting the fact that these parts of the organic molecules usually are involved in chemical reactions. See Table 4.1 in Campbell et ...
... on its carbon skeleton, but also on certain groups of atoms that are covalently linked to the skeleton. These groups of atoms are called functional groups, the name reflecting the fact that these parts of the organic molecules usually are involved in chemical reactions. See Table 4.1 in Campbell et ...
Dr. Audrey Lugo`s AP Chemistry Course Syllabus
... 2. Atomic masses; determination by chemical and physical means 3. Atomic number and mass number; isotopes ...
... 2. Atomic masses; determination by chemical and physical means 3. Atomic number and mass number; isotopes ...
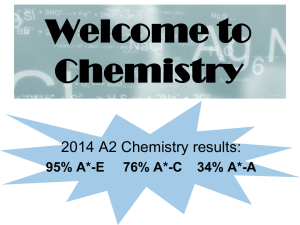
Welcome to Chemistry
... AS can be sat as a stand alone qualification over 1 year, exams are sat at the end of Y12. 2 written exams each 1 hour and 30 minutes. A level is the full 2 year qualification with all the exams at the end of Y13. 3 written papers each 2 hours. ...
... AS can be sat as a stand alone qualification over 1 year, exams are sat at the end of Y12. 2 written exams each 1 hour and 30 minutes. A level is the full 2 year qualification with all the exams at the end of Y13. 3 written papers each 2 hours. ...
Chemistry specialism additional subject knowledge audit Ratings S
... interpretation of the physical properties of materials in terms of structure and bonding Permanent and induced dipole– dipole interactions between molecules Shapes of simple molecules and ions with up to six outer pairs of electrons ...
... interpretation of the physical properties of materials in terms of structure and bonding Permanent and induced dipole– dipole interactions between molecules Shapes of simple molecules and ions with up to six outer pairs of electrons ...
Document
... Examples of nucleic acids DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is double stranded RNA (ribonucleic acid) is single stranded ...
... Examples of nucleic acids DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is double stranded RNA (ribonucleic acid) is single stranded ...
Chemical Reactions
... Catalysts and Inhibitors • A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a reaction. • An inhibitor is a substance used to slow down a reaction or prevent it completely. • The catalyst and the inhibitor do not participate in the reaction. They remain unchanged after the reaction is over. ...
... Catalysts and Inhibitors • A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a reaction. • An inhibitor is a substance used to slow down a reaction or prevent it completely. • The catalyst and the inhibitor do not participate in the reaction. They remain unchanged after the reaction is over. ...
1 of 20) Two part question
... a) How many electrons are in carbons 1st energy level? b) How many electrons are in carbons 2nd energy level? ...
... a) How many electrons are in carbons 1st energy level? b) How many electrons are in carbons 2nd energy level? ...
Carbon
... • Has 4 valence electrons • Tetravalence of carbon makes large, complex molecules possible by bonding COVALENTLY to FOUR other atoms • Living matter-mainly of carbon (C), oxygen (O), hydrogen (H), and nitrogen (N) with smaller amounts of sulfur (S) and phosphorus (P). SINGLE BOND shares pair of elec ...
... • Has 4 valence electrons • Tetravalence of carbon makes large, complex molecules possible by bonding COVALENTLY to FOUR other atoms • Living matter-mainly of carbon (C), oxygen (O), hydrogen (H), and nitrogen (N) with smaller amounts of sulfur (S) and phosphorus (P). SINGLE BOND shares pair of elec ...
CHAPTER 8
... reach equilibrium, reaction to stressors such as concentration, pressure or temperature changes, effect of catalysts. 6. Acids and bases: Definitions of Arrhenius, Bronsted-Lowry and Lewis acid/bases, conjugate acid/bases, strength of acid/base compared to water, equilibrium of water (Kw), pH, pOH, ...
... reach equilibrium, reaction to stressors such as concentration, pressure or temperature changes, effect of catalysts. 6. Acids and bases: Definitions of Arrhenius, Bronsted-Lowry and Lewis acid/bases, conjugate acid/bases, strength of acid/base compared to water, equilibrium of water (Kw), pH, pOH, ...
Outline 3 - MSU Billings
... Identify the four macromolecules. Know their basic chemical compositions and how each is important to living organisms. Understand the consequences of dehydration and hydrolysis reactions and how they are dependent upon water. Know how and why monosaccharides combine to form the various common disac ...
... Identify the four macromolecules. Know their basic chemical compositions and how each is important to living organisms. Understand the consequences of dehydration and hydrolysis reactions and how they are dependent upon water. Know how and why monosaccharides combine to form the various common disac ...
Organic Chemistry 25.2 Introduction to Hydrocarbons
... Hydrocarbons are relatively unreactive; for an organic molecule to be reactive it needs something additional. ...
... Hydrocarbons are relatively unreactive; for an organic molecule to be reactive it needs something additional. ...
Chabot College
... 1. measure and calculate mass, volume, density, pressure, and temperature; 2. use the periodic table to predict physical and chemical properties of the elements, including bond formation, ionic charge, and reactivity; 3. name, write chemical formulas for, and summarize the chemical properties of com ...
... 1. measure and calculate mass, volume, density, pressure, and temperature; 2. use the periodic table to predict physical and chemical properties of the elements, including bond formation, ionic charge, and reactivity; 3. name, write chemical formulas for, and summarize the chemical properties of com ...
virtual library of biological active molecules
... “Octane” type graphical workstations are using for support of the working with amounts of graphical images. Current base is saving on the server. The network accessible to it realize by standart mean. Commercial title, chemical formula and values of main parameters which influence biological activit ...
... “Octane” type graphical workstations are using for support of the working with amounts of graphical images. Current base is saving on the server. The network accessible to it realize by standart mean. Commercial title, chemical formula and values of main parameters which influence biological activit ...