Basic Physical Chemistry 3
... applications of the first and second laws to chemical and physical changes. Applications are made to chemical equilibrium, electrochemical cells, and other spontaneous processes. Course Objectives: Upon successful completion of this course the student should be able to: 1. Apply physical chemistry p ...
... applications of the first and second laws to chemical and physical changes. Applications are made to chemical equilibrium, electrochemical cells, and other spontaneous processes. Course Objectives: Upon successful completion of this course the student should be able to: 1. Apply physical chemistry p ...
Chapter 8: Chemical Reactions and Physical Changes
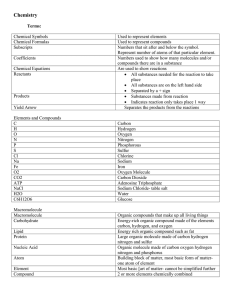
... • Mass number: total protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus • Atomic mass: the average mass of a sample of atoms of that element found in nature • Periodic table: chart that arranges elements by atomic number into rows and columns according to similarities in their properties ...
... • Mass number: total protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus • Atomic mass: the average mass of a sample of atoms of that element found in nature • Periodic table: chart that arranges elements by atomic number into rows and columns according to similarities in their properties ...
Biology Fall Semester Test 1 Study Guide
... Two products of cellular respiration are: In producers, chlorophyll and sunlight are necessary for the process of: The closing of its shell when a clam is removed from its watery environment is an example of how a clam maintains its: In a trophic pyramid, _______% of the energy from a source is pass ...
... Two products of cellular respiration are: In producers, chlorophyll and sunlight are necessary for the process of: The closing of its shell when a clam is removed from its watery environment is an example of how a clam maintains its: In a trophic pyramid, _______% of the energy from a source is pass ...
+ Y
... cis addition – both groups attach to the same side of the double bond trans addition –groups attach to the opposite side of the double bond ...
... cis addition – both groups attach to the same side of the double bond trans addition –groups attach to the opposite side of the double bond ...
F017006 - Fluorous Technologies
... TYPICAL TAGGING PROCEDURE:1 The alcohol 1 (8.86 g, 34.3 mmol) was suspended in 18 mL of THF and added to a 0°C suspension of NaH ( 2.67 g, 95% purity, 106.4 mmol) in THF (10 mL) and DMF (10 mL). After stirring for 10 min, the FPMB-Br (16.1 mL, 89.3 mmol) was added and the mixture stirred at 22°C for ...
... TYPICAL TAGGING PROCEDURE:1 The alcohol 1 (8.86 g, 34.3 mmol) was suspended in 18 mL of THF and added to a 0°C suspension of NaH ( 2.67 g, 95% purity, 106.4 mmol) in THF (10 mL) and DMF (10 mL). After stirring for 10 min, the FPMB-Br (16.1 mL, 89.3 mmol) was added and the mixture stirred at 22°C for ...
Unit 1 Tro Textbook Enlow`s Brief: Chapter 1: Matter, Measurement
... Temperature – a measure of the average KE of the atoms (it’s a measure of molecular motion) ; it determines the direction of thermal energy transfer (always from hotter to colder systems) ; Kelvin is the absolute temperature scale and does not utilize negative #s ...
... Temperature – a measure of the average KE of the atoms (it’s a measure of molecular motion) ; it determines the direction of thermal energy transfer (always from hotter to colder systems) ; Kelvin is the absolute temperature scale and does not utilize negative #s ...
CCN2275 Physical Chemistry
... thermodynamics. (b) demonstrate an understanding of the fundamental principles of reaction rate theories as well as their contemporary applications. (c) perform basic physical chemistry experiments as well as evaluate, analyse and interpret the effects of external conditions on the experimental equi ...
... thermodynamics. (b) demonstrate an understanding of the fundamental principles of reaction rate theories as well as their contemporary applications. (c) perform basic physical chemistry experiments as well as evaluate, analyse and interpret the effects of external conditions on the experimental equi ...
Notes - HCC Learning Web
... 1. The skeletons vary in a) length b) it may be straight, branched, or arranged in closed rings c) some carbon skeletons have double bonds, which vary in number & location. d) atoms of other elements can be bonded to the skeletons at available sites. C. Hydrocarbons 1. Hydrocarbons are organic molec ...
... 1. The skeletons vary in a) length b) it may be straight, branched, or arranged in closed rings c) some carbon skeletons have double bonds, which vary in number & location. d) atoms of other elements can be bonded to the skeletons at available sites. C. Hydrocarbons 1. Hydrocarbons are organic molec ...
1. What does forensic science provide?
... 7. How many hydrogen atoms are in a cyclic alkane with 4 carbons? a. b. c. d. ...
... 7. How many hydrogen atoms are in a cyclic alkane with 4 carbons? a. b. c. d. ...
$doc.title
... Chem 343 – Organic Reactions Chapter 10 Prepared by José Laboy, MS http://www.chem.wisc.edu/areas/clc (Resource page) Reactions of Alcohols #8: Reaction of a 1° Alcohol with Hydrogen Halides ...
... Chem 343 – Organic Reactions Chapter 10 Prepared by José Laboy, MS http://www.chem.wisc.edu/areas/clc (Resource page) Reactions of Alcohols #8: Reaction of a 1° Alcohol with Hydrogen Halides ...
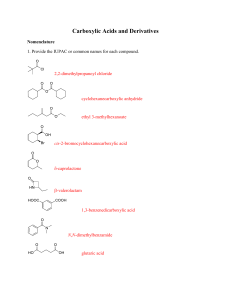
CHE 275 - SU Chemistry
... chemistry of carbon-based molecular systems, with an emphasis on the chemistry of the carbonoxygen and carbon-nitrogen bonds, reactions of organic compounds and structural analysis of organic systems. A primary focus of the course will be the manipulation of the carbonyl and related functional group ...
... chemistry of carbon-based molecular systems, with an emphasis on the chemistry of the carbonoxygen and carbon-nitrogen bonds, reactions of organic compounds and structural analysis of organic systems. A primary focus of the course will be the manipulation of the carbonyl and related functional group ...
CHM 2045C - State College of Florida
... (5 Credit Hours) (A.A.) Three hours lecture, three hours laboratory per week. Prerequisites: Completion of MAC 1105. Completion of CHM 1025C with a grade of “C” or better or one year of high school college preparatory honors or AP chemistry within last three ...
... (5 Credit Hours) (A.A.) Three hours lecture, three hours laboratory per week. Prerequisites: Completion of MAC 1105. Completion of CHM 1025C with a grade of “C” or better or one year of high school college preparatory honors or AP chemistry within last three ...
Functional Groups and Isomers
... 10. Adenosine triphosphate is used as the energy currency molecule of the cell. Why is ATP so likely to react with water? 11. Functional groups can modify the properties of organic molecules. In the following table, indicate whether each functional group is polar or nonpolar and hydrophobic or hydro ...
... 10. Adenosine triphosphate is used as the energy currency molecule of the cell. Why is ATP so likely to react with water? 11. Functional groups can modify the properties of organic molecules. In the following table, indicate whether each functional group is polar or nonpolar and hydrophobic or hydro ...
Organic Chemistry Basics
... Carbon to carbon bonds are strong but not unbreakable, making them good for structural components Carbon can also form double and triple bonds with itself Carbon can form straight or branched chains as well as rings ...
... Carbon to carbon bonds are strong but not unbreakable, making them good for structural components Carbon can also form double and triple bonds with itself Carbon can form straight or branched chains as well as rings ...