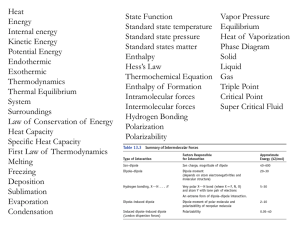
Atomic Structure, Molecular Structure & Bonding
... – H is never central; C is often central 3. Draw in electrons to fulfill octet and duet rules – C “likes” 8 electrons; H “likes” 2 electrons 4. Count ve-’s and compare to #2 5. If too many e-’s, make a double bond 6. Calculate formal charge (FC) to double check structure – No or low FCs (e.g. +1) mo ...
... – H is never central; C is often central 3. Draw in electrons to fulfill octet and duet rules – C “likes” 8 electrons; H “likes” 2 electrons 4. Count ve-’s and compare to #2 5. If too many e-’s, make a double bond 6. Calculate formal charge (FC) to double check structure – No or low FCs (e.g. +1) mo ...
Chemistry
... Kinetic theory of gases and derivation of gas law. Non-ideal Behaviour of gases; Van Der Waal equation, the critical temperature and liquefaction of gases. Heat capacities of gases, law of equiparition of energy. Mean free path, collision diameter and collision number. Liquids: Vapor pressure, visco ...
... Kinetic theory of gases and derivation of gas law. Non-ideal Behaviour of gases; Van Der Waal equation, the critical temperature and liquefaction of gases. Heat capacities of gases, law of equiparition of energy. Mean free path, collision diameter and collision number. Liquids: Vapor pressure, visco ...
Chem 101 notes review
... The symbol for the magnetic quantum number is m which defines the orbital. m = - , (- + 1), (- +2), .....0, ......., ( -2), ( -1), The last quantum number is the spin quantum number which has the symbol m s which characterizes the single electron. The spin quantum number only has two pos ...
... The symbol for the magnetic quantum number is m which defines the orbital. m = - , (- + 1), (- +2), .....0, ......., ( -2), ( -1), The last quantum number is the spin quantum number which has the symbol m s which characterizes the single electron. The spin quantum number only has two pos ...
ANSWERS Concept Checks: Ch. 5 The Molecules of Life Concept
... 2. Relate amino acids, polypeptides, and proteins. Amino acids make up polypeptides; polypeptides make up proteins. 3. Explain how heat can destroy a protein. Heat breaks and weakens chemical bonds in a protein, thus unfolding and denaturing of the protein. 4. Which parts of an amino acid's structur ...
... 2. Relate amino acids, polypeptides, and proteins. Amino acids make up polypeptides; polypeptides make up proteins. 3. Explain how heat can destroy a protein. Heat breaks and weakens chemical bonds in a protein, thus unfolding and denaturing of the protein. 4. Which parts of an amino acid's structur ...
science background - CMA
... and energy is released as new bonds form in products. The net result of these steps depends on the relative sizes of the energies associated with breaking and forming bonds and determines if the reaction absorbs or releases energy The amount of heat involved in a reaction depends not only on what th ...
... and energy is released as new bonds form in products. The net result of these steps depends on the relative sizes of the energies associated with breaking and forming bonds and determines if the reaction absorbs or releases energy The amount of heat involved in a reaction depends not only on what th ...
Lectute 2
... those molecules. • The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction(s) regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of. • However, its relative reactivity can be modified by nearby functional groups ...
... those molecules. • The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction(s) regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of. • However, its relative reactivity can be modified by nearby functional groups ...
Biochemistry Carbon Compounds Supplement 1 Name: . Answer
... Answer the following questions on a separate sheet of paper and staple this handout and the answers together. This handout should be the top sheet. Vocabulary: Organic Compound functional group monomer hydrolysis adenosine triphosphate (ATP) ...
... Answer the following questions on a separate sheet of paper and staple this handout and the answers together. This handout should be the top sheet. Vocabulary: Organic Compound functional group monomer hydrolysis adenosine triphosphate (ATP) ...
Conjugate (1,4
... This synthesis is by G. H. Posner, T. P. Kogan, S. R. Haines, L. L. Frye, Tetrahedron ...
... This synthesis is by G. H. Posner, T. P. Kogan, S. R. Haines, L. L. Frye, Tetrahedron ...
Chapter 4 – Carbon
... •Organic compounds with hydroxyl groups are alcohols and their names typically end in -ol. •A carbonyl group (>CO) consists of an O atom joined to the C skeleton by a double bond. • If the carbonyl group is on the end of the skeleton, the compound is an aldelhyde. •If not, then the compound is a ket ...
... •Organic compounds with hydroxyl groups are alcohols and their names typically end in -ol. •A carbonyl group (>CO) consists of an O atom joined to the C skeleton by a double bond. • If the carbonyl group is on the end of the skeleton, the compound is an aldelhyde. •If not, then the compound is a ket ...
Begin Chemical Equations Practice
... 4Al2(SO4)3 • How many of each atom are shown by 3(NH4)3PO4 ...
... 4Al2(SO4)3 • How many of each atom are shown by 3(NH4)3PO4 ...
MODULE 1: Chemistry for Life – The Elements of Life
... Contrast the benefits of chlorine use in water treatment (killing bacteria) with associated risks (hazards of toxic chlorine gas and possible risks from formation of chlorinated hydrocarbons). HOW SCIENCE WORKS (6a, 6b) Describe the precipitation reactions, including ionic equations, of the aqueous ...
... Contrast the benefits of chlorine use in water treatment (killing bacteria) with associated risks (hazards of toxic chlorine gas and possible risks from formation of chlorinated hydrocarbons). HOW SCIENCE WORKS (6a, 6b) Describe the precipitation reactions, including ionic equations, of the aqueous ...
Chemistry 488, (01:160:488), Spring 2013 Special Topics: Physical
... This is a one-semester physical chemistry course with an emphasis on applications to biochemical systems and to life sciences. It will cover three main areas: thermodynamics, biochemical kinetics and biochemical spectroscopy. This course is essentially the same course as I taught last year as Chem 3 ...
... This is a one-semester physical chemistry course with an emphasis on applications to biochemical systems and to life sciences. It will cover three main areas: thermodynamics, biochemical kinetics and biochemical spectroscopy. This course is essentially the same course as I taught last year as Chem 3 ...
國立屏東教育大學95學年度研究所碩士班入學考試
... 1. If matter is uniform throughout, cannot be separated into other substances by physical processes, but can be decomposed into other substances by chemical processes, it is called a (an) __________. (A) heterogeneous mixture (B) element (C) homogeneous mixture (D) compound (E) mixture of elements 2 ...
... 1. If matter is uniform throughout, cannot be separated into other substances by physical processes, but can be decomposed into other substances by chemical processes, it is called a (an) __________. (A) heterogeneous mixture (B) element (C) homogeneous mixture (D) compound (E) mixture of elements 2 ...
View PDF
... such as hygroscopicity, the activity of cloud condensation, the reactivity, the optical properties, etc. Aerosol particles consist of complex mixture of inorganic salts with hydrophilic and/or hygrophobic organic components which may evolved during their transportation into the atmosphere when they ...
... such as hygroscopicity, the activity of cloud condensation, the reactivity, the optical properties, etc. Aerosol particles consist of complex mixture of inorganic salts with hydrophilic and/or hygrophobic organic components which may evolved during their transportation into the atmosphere when they ...
chapter4_powerpoint - Northern Highlands Regional HS
... Cooled “rain” containing organic molecules ...
... Cooled “rain” containing organic molecules ...
CHM_207_201510 - Oakton Community College
... COURSE (CATALOG) DESCRIPTION Course is one-semester survey of organic chemistry. Content includes an introduction and overview of the structure, nomenclature, properties, preparation, and reactions of the main organic functional groups; introduces biochemistry, including categories of biomolecules a ...
... COURSE (CATALOG) DESCRIPTION Course is one-semester survey of organic chemistry. Content includes an introduction and overview of the structure, nomenclature, properties, preparation, and reactions of the main organic functional groups; introduces biochemistry, including categories of biomolecules a ...
Topic 16 IB Chemistry Definitions
... Chemistry: Definitions Topic 16 – Kinetics Activated complex: ...
... Chemistry: Definitions Topic 16 – Kinetics Activated complex: ...
Document
... 1. All organic molecules contain carbon. What is it about carbon that makes it such a fundamental building block? ...
... 1. All organic molecules contain carbon. What is it about carbon that makes it such a fundamental building block? ...
6 Biological Molecules-S - Elmwood Park Memorial Middle School
... Read This! When sugars are joined together the new bond that forms is a glycosidic bond. When amino acids are joined the new bond that forms is a peptide bond. When fatty acids are joined to a glycerol the bond that holds them is an ester bond. 18. On the diagrams in Model 2, circle and label the gl ...
... Read This! When sugars are joined together the new bond that forms is a glycosidic bond. When amino acids are joined the new bond that forms is a peptide bond. When fatty acids are joined to a glycerol the bond that holds them is an ester bond. 18. On the diagrams in Model 2, circle and label the gl ...