ExamView - Untitled.tst
... ____ 13. Thomson made his discovery about the atom during an experiment using a. thermal energy. c. cathode rays b. kinetic energy. d. X rays. ____ 14. In _____ atomic model, negative electrons orbit the positively charged nucleus. a. Dalton’s c. Rutherford’s b. Thomson’s d. Democritus’s ____ 15. Wh ...
... ____ 13. Thomson made his discovery about the atom during an experiment using a. thermal energy. c. cathode rays b. kinetic energy. d. X rays. ____ 14. In _____ atomic model, negative electrons orbit the positively charged nucleus. a. Dalton’s c. Rutherford’s b. Thomson’s d. Democritus’s ____ 15. Wh ...
Chemical Equations and Reactions notes File
... Solid sodium oxide is added to water at room temperature and forms sodium hydroxide. Word Equation: sodium oxide + water sodium hydroxide Formula ...
... Solid sodium oxide is added to water at room temperature and forms sodium hydroxide. Word Equation: sodium oxide + water sodium hydroxide Formula ...
Organic Chemistry (HL) Revision Questions
... Two compounds, A and D, each have the formula C4H9Cl. Compound A is reacted with dilute aqueous sodium hydroxide to produce compound B with a formula of C4H10O. Compound B is then oxidized with acidified potassium manganate(VII) to produce compound C with a formula of C4H8O. Compound C resists furth ...
... Two compounds, A and D, each have the formula C4H9Cl. Compound A is reacted with dilute aqueous sodium hydroxide to produce compound B with a formula of C4H10O. Compound B is then oxidized with acidified potassium manganate(VII) to produce compound C with a formula of C4H8O. Compound C resists furth ...
Name
... hydro- = water (hydrocarbon: an organic molecule consisting only of carbon and hydrogen) iso- = equal (isomer: one of several organic compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures and, therefore, different properties) enanti- = opposite (enantiomer: molecules that are mirror ima ...
... hydro- = water (hydrocarbon: an organic molecule consisting only of carbon and hydrogen) iso- = equal (isomer: one of several organic compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures and, therefore, different properties) enanti- = opposite (enantiomer: molecules that are mirror ima ...
Chemistry Lesson 40 Organic Chemistry
... functional groups. The student will classify compounds, given as names or structures, as containing one of the six common organic functional groups. PA Science and Technology Standards: 3.4.10.A; 3.4.12.A; 3.1.10.C ...
... functional groups. The student will classify compounds, given as names or structures, as containing one of the six common organic functional groups. PA Science and Technology Standards: 3.4.10.A; 3.4.12.A; 3.1.10.C ...
Atomic structure and bonding I can name group 1, 7 and 0 of the
... I can state the definition of an isotope. I can state the meaning of atomic number and mass number. I can use the atomic number and mass number to determine the number of protons, neutrons and electrons within an atom. I can use the data book to write the electronic arrangement of the first 20 eleme ...
... I can state the definition of an isotope. I can state the meaning of atomic number and mass number. I can use the atomic number and mass number to determine the number of protons, neutrons and electrons within an atom. I can use the data book to write the electronic arrangement of the first 20 eleme ...
Review Sheet: Unit 6 Name__________________ CHEMISTRY: A
... reaction. The symbol for a liquid is ____________; for a solid, ____________; for a gas, ____________ or ____________; and for a precipitate (an ____________ solid), a ____________ or ____________. A substance that is dissolved in water is designated ____________. We recognize five general types of ...
... reaction. The symbol for a liquid is ____________; for a solid, ____________; for a gas, ____________ or ____________; and for a precipitate (an ____________ solid), a ____________ or ____________. A substance that is dissolved in water is designated ____________. We recognize five general types of ...
HS-PS1-6
... happens at the molecular level. Examples of designs could include different ways to increase product formation including adding reactants or removing products.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment is limited to specifying the change in only one variable at a time. Assessment does not include calculatin ...
... happens at the molecular level. Examples of designs could include different ways to increase product formation including adding reactants or removing products.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment is limited to specifying the change in only one variable at a time. Assessment does not include calculatin ...
CHEMISTRY 3
... After making an ester by heating a carboxylic acid with an alcohol in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid, water is added to the mixture and the ester separates out as an oily layer that floats to the top and produces a strong fruity odour. Comment on the physical properties of esters that th ...
... After making an ester by heating a carboxylic acid with an alcohol in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid, water is added to the mixture and the ester separates out as an oily layer that floats to the top and produces a strong fruity odour. Comment on the physical properties of esters that th ...
Week - Mat-Su School District
... Chemistry or AP Chemistry. The course covers the equivalent of one full year of general Chemistry, comparable to a first year course at a college or university. The course is a rigorous math-based course, with a strong laboratory component. It is intended for students who have demonstrated a willing ...
... Chemistry or AP Chemistry. The course covers the equivalent of one full year of general Chemistry, comparable to a first year course at a college or university. The course is a rigorous math-based course, with a strong laboratory component. It is intended for students who have demonstrated a willing ...
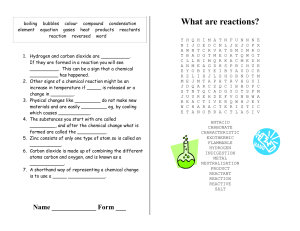
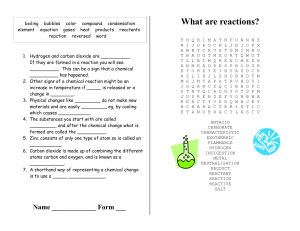
What are reactions? - UTLNET Secure Site
... If they are formed in a reaction you will see __________. This can be a sign that a chemical __________ has happened. 2. Other signs of a chemical reaction might be an increase in temperature if _____ is released or a change in ________. 3. Physical changes like _________ do not make new materials a ...
... If they are formed in a reaction you will see __________. This can be a sign that a chemical __________ has happened. 2. Other signs of a chemical reaction might be an increase in temperature if _____ is released or a change in ________. 3. Physical changes like _________ do not make new materials a ...
What are reactions?
... If they are formed in a reaction you will see __________. This can be a sign that a chemical __________ has happened. 2. Other signs of a chemical reaction might be an increase in temperature if _____ is released or a change in ________. 3. Physical changes like _________ do not make new materials a ...
... If they are formed in a reaction you will see __________. This can be a sign that a chemical __________ has happened. 2. Other signs of a chemical reaction might be an increase in temperature if _____ is released or a change in ________. 3. Physical changes like _________ do not make new materials a ...
Chapter 25 The Chemistry of Life: Organic Chemistry 25.1 Some
... Branched-chain hydrocarbons are possible for alkanes with four or more C atoms. Structures with different branches can be written for the same formula: ...
... Branched-chain hydrocarbons are possible for alkanes with four or more C atoms. Structures with different branches can be written for the same formula: ...
Course Syllabus - Honors Chemistry
... 1. The periodic table displays the elements in increasing atomic number and shows how periodicity of the physical and chemical properties of the elements relates to atomic structure. a. Atomic number and atomic mass. b. Identify metals, semimetals, nonmetals, halogens, alkali metals, alkaline earth ...
... 1. The periodic table displays the elements in increasing atomic number and shows how periodicity of the physical and chemical properties of the elements relates to atomic structure. a. Atomic number and atomic mass. b. Identify metals, semimetals, nonmetals, halogens, alkali metals, alkaline earth ...
Chapter 12: Basic Review Worksheet
... 1. In general, what do we mean by a chemical bond? Name the principal types of chemical bonds. 2. What do we mean by ionic bonding? Give an example of a substance whose particles are held together by ionic bonding. 3. What do we mean by covalent bonding and polar covalent bonding? How are these two ...
... 1. In general, what do we mean by a chemical bond? Name the principal types of chemical bonds. 2. What do we mean by ionic bonding? Give an example of a substance whose particles are held together by ionic bonding. 3. What do we mean by covalent bonding and polar covalent bonding? How are these two ...
NATIONAL 5 CHEMISTRY – UNIT 1 – CHEMICAL CHANGES AND
... concentration and volume and the mass of a substance through the number of moles present. Learners should have knowledge of pH and acids and bases including neutralisation reactions and salt formation. A very small proportion of water molecules will dissociate into an equal number of hydrogen and hy ...
... concentration and volume and the mass of a substance through the number of moles present. Learners should have knowledge of pH and acids and bases including neutralisation reactions and salt formation. A very small proportion of water molecules will dissociate into an equal number of hydrogen and hy ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... demonstrate that double bonds cannot rotate like a single bond. demonstrate cis- and trans- isomerism using dichloroethene, C2H2Cl2. recognize whether the molecule is an alkane, alkene, or alkyne given the formula. name a molecule, given the structural formula. write the correct structural ...
... demonstrate that double bonds cannot rotate like a single bond. demonstrate cis- and trans- isomerism using dichloroethene, C2H2Cl2. recognize whether the molecule is an alkane, alkene, or alkyne given the formula. name a molecule, given the structural formula. write the correct structural ...