* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ANSWERS Concept Checks: Ch. 5 The Molecules of Life Concept
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
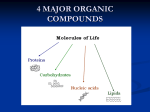
ANSWERS Concept Checks: Ch. 5 The Molecules of Life Concept Check 5.1 1. Draw a molecule that has a three-carbon skeleton and a hydroxyl group on the middle carbon. (Hint: The molecule's formula is C3H8O.) H OH H / / / H-C-C-C-H / / / HH H 2. Explain the connection between monomers and polymers. Polymers are large molecules made up of monomers 3. What molecule is released during construction of a polymer? What is this reaction called? Water molecules are released during construction of a polymer – called dehydration synthesis 4. Draw at least three ways in which five carbon atoms could be joined to make different carbon skeletons. C C-C-C-C / C-C-C-C-C / C-C-C C / C Concept Check 5.2 1. Explain the difference between a monosaccharide and a disaccharide. Give an example of each. Monosaccharide has one sugar unit or ring. Glucose, fructose or galactose. Disaccharide has two sugar units – like sucrose 2. Compare and contrast starch, glycogen, and cellulose. All three are polysaccharides. Starch is branched, looping chain of glucose monomers found in plants Glycogen is more highly branched and is found in animals Cellulose forms cable-like fibers and serves as building material in plants QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. 3. How do animals store excess glucose molecules? Polymer called glycogen Concept Check 5.3 1. What property do lipids share? Hydrophobic 2. What are the parts of a fat molecule? 3 hydrocarbon fatty acid chains attached to a 3-carbon glycerol backbone 3. Describe two ways that steroids differ from fats. Steroids form ring structures, some steroids serve as chemical signals in the body 4. What does the term unsaturated fat on a food label mean? Unsaturated means that at least one double bond is present in one of the fatty acid chains Concept Check 5.4 1. Give at least two examples of proteins you can "see" in the world around you. What are their functions? Hair insulates body, muscle moves bones 2. Relate amino acids, polypeptides, and proteins. Amino acids make up polypeptides; polypeptides make up proteins. 3. Explain how heat can destroy a protein. Heat breaks and weakens chemical bonds in a protein, thus unfolding and denaturing of the protein. 4. Which parts of an amino acid's structure are the same in all amino acids? Which part is unique? Central carbon is bonded to a hydrogen atom, an amino group, and a carboxyl group. The fourth bond is with a side or functional group that is unique to that amino acid. Concept Check 5.5 1. Explain the role of activation energy in a reaction. How does an enzyme affect activation energy? Activation energy is the energy needed to start a reaction. An enzyme affects the activation energy by lowering it. 2. Describe how a substrate interacts. Substrate binds to the enzyme’s active site where the substrate undergoes a chemical reaction. Once the reaction is complete the products are released