Solubility of Organic Compounds
... Most organic molecules are relatively non-polar and are usually soluble in organic solvents (e.g. diethyl ether, dichloromethane, chloroform, petroleum ether, hexanes etc.) but not in polar solvents like water. However, some organic molecules are more polar and therefore soluble in water. This denot ...
... Most organic molecules are relatively non-polar and are usually soluble in organic solvents (e.g. diethyl ether, dichloromethane, chloroform, petroleum ether, hexanes etc.) but not in polar solvents like water. However, some organic molecules are more polar and therefore soluble in water. This denot ...
CCN1111 General Chemistry II
... theory, Molecular shape by VSEPR method and its physical properties. Molecular Orbital Theory of Chemical Bonding Principles of MO theory for homonuclear and heteronuclear diatomic molecules; Bonding and anti-bonding molecular orbitals; MO energylevel diagrams; Construction of MO election configurat ...
... theory, Molecular shape by VSEPR method and its physical properties. Molecular Orbital Theory of Chemical Bonding Principles of MO theory for homonuclear and heteronuclear diatomic molecules; Bonding and anti-bonding molecular orbitals; MO energylevel diagrams; Construction of MO election configurat ...
Chemistry 302
... If you have a disability and require specific accommodations to complete this course, contact Services for Students with Disabilities, at 323-3290. Changes to Syllabus: Any changes to the syllabus will be announced in class or via email. ...
... If you have a disability and require specific accommodations to complete this course, contact Services for Students with Disabilities, at 323-3290. Changes to Syllabus: Any changes to the syllabus will be announced in class or via email. ...
Coal is Formed From Decaying Organisms.
... What Is An Organic Compound? Compound that contains carbon and hydrogen atoms covalently bound together. Because they have four valence electrons they bind with many other elements to form branched and complex molecules. Hydrocarbons are organic compounds that are primarily composed of hydrog ...
... What Is An Organic Compound? Compound that contains carbon and hydrogen atoms covalently bound together. Because they have four valence electrons they bind with many other elements to form branched and complex molecules. Hydrocarbons are organic compounds that are primarily composed of hydrog ...
Lecture I
... • The very low critical pressure and temperature of helium, reflecting the very small intermolecular attractions of this atom. • Tc of the noble gas elements increases with atomic number. • Hydrogen gas cannot be liquified above 33 K; this poses a major difficulty in the use of hydrogen as an automo ...
... • The very low critical pressure and temperature of helium, reflecting the very small intermolecular attractions of this atom. • Tc of the noble gas elements increases with atomic number. • Hydrogen gas cannot be liquified above 33 K; this poses a major difficulty in the use of hydrogen as an automo ...
Acid Basics
... living organisms? Recall that C has 4 valence electrons that can form strong covalent bonds with other atoms including even stronger double and triple bonds. That’s important because living things need to survive bumps and bruises in a tough environment. Carbon also makes a tetrahedron pattern, thin ...
... living organisms? Recall that C has 4 valence electrons that can form strong covalent bonds with other atoms including even stronger double and triple bonds. That’s important because living things need to survive bumps and bruises in a tough environment. Carbon also makes a tetrahedron pattern, thin ...
Matter Study Guide
... metals/nonmetals, solids, gasses, liquids, man-made, symbols, atomic number, atomic mass -Know what chemical symbols and formulas are and how to read the formulas -Recognize symbols for basic elements and compounds including Ca (calcium), C (carbon), H (hydrogen), O (oxygen), CO (carbon monoxide), C ...
... metals/nonmetals, solids, gasses, liquids, man-made, symbols, atomic number, atomic mass -Know what chemical symbols and formulas are and how to read the formulas -Recognize symbols for basic elements and compounds including Ca (calcium), C (carbon), H (hydrogen), O (oxygen), CO (carbon monoxide), C ...
All organic compounds contain the element carbon
... increases, the reaction rate decreases. B. There is a direct relationship; as the enzyme concentration increases, the rate of reaction increases. C. There is no relationship between the enzyme concentration and the reaction rate. D. The experiment is invalid because it was performed in the pre ...
... increases, the reaction rate decreases. B. There is a direct relationship; as the enzyme concentration increases, the rate of reaction increases. C. There is no relationship between the enzyme concentration and the reaction rate. D. The experiment is invalid because it was performed in the pre ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... b) the molecule has some polarity c) they ionize completely in water solution ...
... b) the molecule has some polarity c) they ionize completely in water solution ...
Acrobat - chemmybear.com
... b) the molecule has some polarity c) they ionize completely in water solution ...
... b) the molecule has some polarity c) they ionize completely in water solution ...
Enantiospecific skeleton expanding cross
... pathway for the modification and expansion of α-hydroxy carbonyls, which are themselves readily available from the chiral pool. Grignard reagents possessing a range of potential substituents are reacted under mild conditions with a triflate modified carbonyl at the α-carbon to bind a wide range of s ...
... pathway for the modification and expansion of α-hydroxy carbonyls, which are themselves readily available from the chiral pool. Grignard reagents possessing a range of potential substituents are reacted under mild conditions with a triflate modified carbonyl at the α-carbon to bind a wide range of s ...
ORDANOCHROMIUM CHEMISTRY SUPPORTED BY -DIIMINE LIGANDS
... α-Diimine ligands can accept up to two electrons; thus they can be used to stabilize organometallic compounds in unusually low formal oxidation states of the central metal. This redox ambiguity may be useful for facilitating catalytic reactions involving different oxidation states. We are exploring ...
... α-Diimine ligands can accept up to two electrons; thus they can be used to stabilize organometallic compounds in unusually low formal oxidation states of the central metal. This redox ambiguity may be useful for facilitating catalytic reactions involving different oxidation states. We are exploring ...
File - Ingolstadt Academy
... Density (definition and equation) Dimensional analysis Instruments that measure mass, volume, pressure, etc. (lab stuff!) The Scientific Method Atomic Structure: ...
... Density (definition and equation) Dimensional analysis Instruments that measure mass, volume, pressure, etc. (lab stuff!) The Scientific Method Atomic Structure: ...
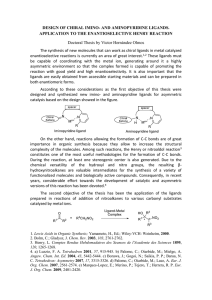
DESIGN OF CHIRAL IMINO- AND AMINOPYRIDINE LIGANDS
... On the other hand, reactions allowing the formation of C-C bonds are of great importance in organic synthesis because they allow to increase the structural complexity of the molecules. Among such reactions, the Henry or nitroaldol reaction 3 constitutes one of the most useful methodologies for the f ...
... On the other hand, reactions allowing the formation of C-C bonds are of great importance in organic synthesis because they allow to increase the structural complexity of the molecules. Among such reactions, the Henry or nitroaldol reaction 3 constitutes one of the most useful methodologies for the f ...